Prepositions are words that show the relationship between a noun (or pronoun) and other words in a sentence. The object of a preposition is the noun or pronoun that follows the preposition and is affected by its relationship with other words in the sentence. It helps to complete the prepositional phrase and provides more context to the sentence. In this article, we’ll define the object of a preposition, explain its role in a sentence, and provide examples to help you understand how to use it correctly in writing and speaking. So let’s get started!
What is a Preposition?
Before proceeding further, let’s first understand what the preposition is.
A preposition is a small word that comes before a noun or a pronoun to show the relationship between that word and other words in a sentence. It often indicates location, direction, time, or relationships between different elements. For example, in the sentence “The book is on the table,” “on” is a preposition that shows the location of the book. In “She walked to the store,” “to” is a preposition that shows the direction of her movement. Prepositions can also indicate time, as in “in two hours” or “at midnight.” Common prepositions include “in,” “on,” “under,” “between,” “before,” and “after.”
Examples:
- The cat is in the box.
- The book is on the table.
- The keys are under the mat.
- They swam across the river.
- We’ll go for ice cream after dinner.
What Is the Object of a Preposition?
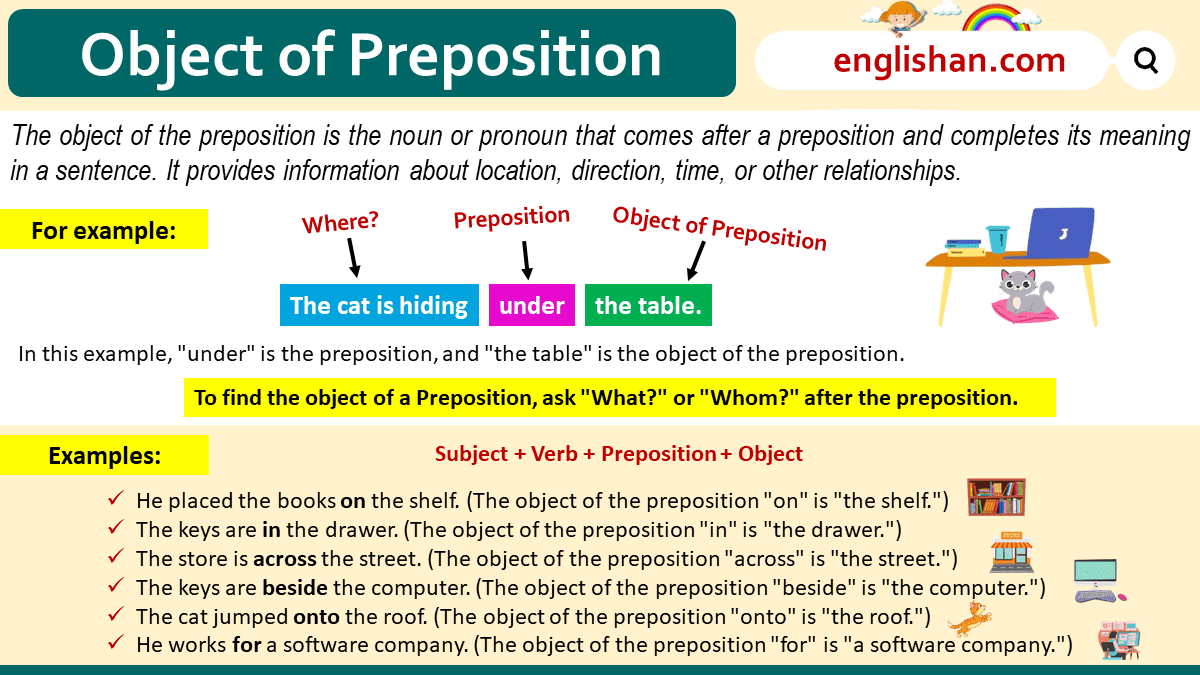
The object of the preposition is a noun or pronoun that follows the preposition in a sentence, providing more information about the relationship between the elements of the sentence. This noun or pronoun is essential for completing the meaning of the prepositional phrase. For example, in the sentence “The cat is on the mat,” “on” is the preposition, and “the mat” is the object of the preposition. It’s like saying, “Where is the cat? It’s on the mat.” The object completes the preposition’s message, helping us understand the cat’s location.
To identify the object of the preposition, you can ask yourself questions like “What?” or “Whom?” after the preposition. In the sentence “She is sitting on the chair,” asking “On what?” helps you find that “the chair” is the object of the preposition “on.”
Examples:
- She is sitting on the chair.
- The cat is under the table.
- We will meet at the park.
- The book is on the shelf.
- They live in the city.
In these examples, “the chair,” “the table,” “the park,” “the shelf,” and “the city,” are the objects of the prepositions “on,” “under,” “at,” “on,” and “in.”
How to Identify the Object of the Preposition?
Locate the Preposition: To find the object of the preposition, first, identify the preposition in the sentence. Common prepositions include “in,” “on,” “at,” “under,” “over,” “between,” “among,” and many others.
Ask “What?” or “Whom?”: Once the preposition is located, ask the question “What?” or “Whom?” to unveil the object. The answer to this question will be the object of the preposition.
Let’s take an example:
- She is sitting on the chair.
- Ask: On what?
- Answer: On the chair.
In this case, “the chair” is the object of the preposition “on.”
Types of Objects: Nouns and Pronouns
1. Noun as the Object: The most common type of object of the preposition is a noun. It could be a common noun, a proper noun, or a gerund (a verb form ending in -ing used as a noun).
Examples:
- He is interested in science. (common noun)
- She is friends with John. (proper noun)
- I enjoy hiking in the mountains. (gerund)
2. Pronoun as the Object: Pronouns can also serve as objects of prepositions. It is important to match the pronoun with the preposition in terms of case (subject or object).
Examples:
- She is sitting next to him.
- The gift is for her.
- They went with us.
Functions of the Object of Preposition
This object serves several important functions in a sentence for instance:
- Completes the Relationship: The object of the preposition finishes the meaning by telling us more about the connection between things or actions.
- Answers “What?” or “Whom?”: It responds to questions like “What?” or “Whom?” and gives us the specific person, place, or thing involved.
- Specifies Location or Direction: It helps pinpoint where something is happening or the direction in which it is moving.
- Essential for Clarity: Without the object of the preposition, the meaning of the sentence might be unclear or incomplete.
- Connects to Prepositions: The object is the word that directly follows a preposition and creates a connection between different parts of a sentence.
- Works with Time and Space: It plays a crucial role in expressing when something happens (time) or where it happens (space).
Example Sentences:
- She is sitting on the chair.
- We walked through the park.
- The book is on the shelf.
- She arrived at the airport.
- We will meet in the morning.
- The butterfly landed on the flower.
- They sat between the two trees.
- The train arrives at 3 PM.
- We will go with our friends.
- The bird is inside the cage.
- The movie starts at 7 o’clock.
- He stood against the wall.
- She sat beside her sister.
- We’ll meet at the coffee shop.
- The keys are in my pocket.
- The flowers are in the vase.
- I’ll see you at the party.
- The store is across the street.
- They met outside the restaurant.
- She is looking through the telescope.
FAQs:
The object of the preposition is the noun or pronoun that follows a preposition and completes the meaning of the prepositional phrase. It provides information about location, direction, time, or other relationships.
To identify the object of the preposition, locate the preposition in the sentence and ask the questions “What?” or “Whom?” The answer to these questions will be the object of the preposition.
It completes the relationship established by the preposition, providing essential information about location, direction, time, or other aspects. It contributes to the overall clarity and meaning of a sentence.
Common mistakes include using incorrect pronoun cases (e.g., “between you and I”), misplacing prepositions (e.g., “interested science in”), and creating dangling prepositions (e.g., “gift for you to open up”).
Common prepositions include “in,” “on,” “at,” “under,” “over,” “between,” and many others. Examples of their objects are: “in the box,” “on the table,” “at the park,” “under the bed,” and “between the two trees.”
You May Also Like
- Types of Chairs with Names
- Adverbs of Place with Examples
- 1000+ List of Objects in English
- Types of Prepositions with Examples
- Prepositions with Rules and Examples: