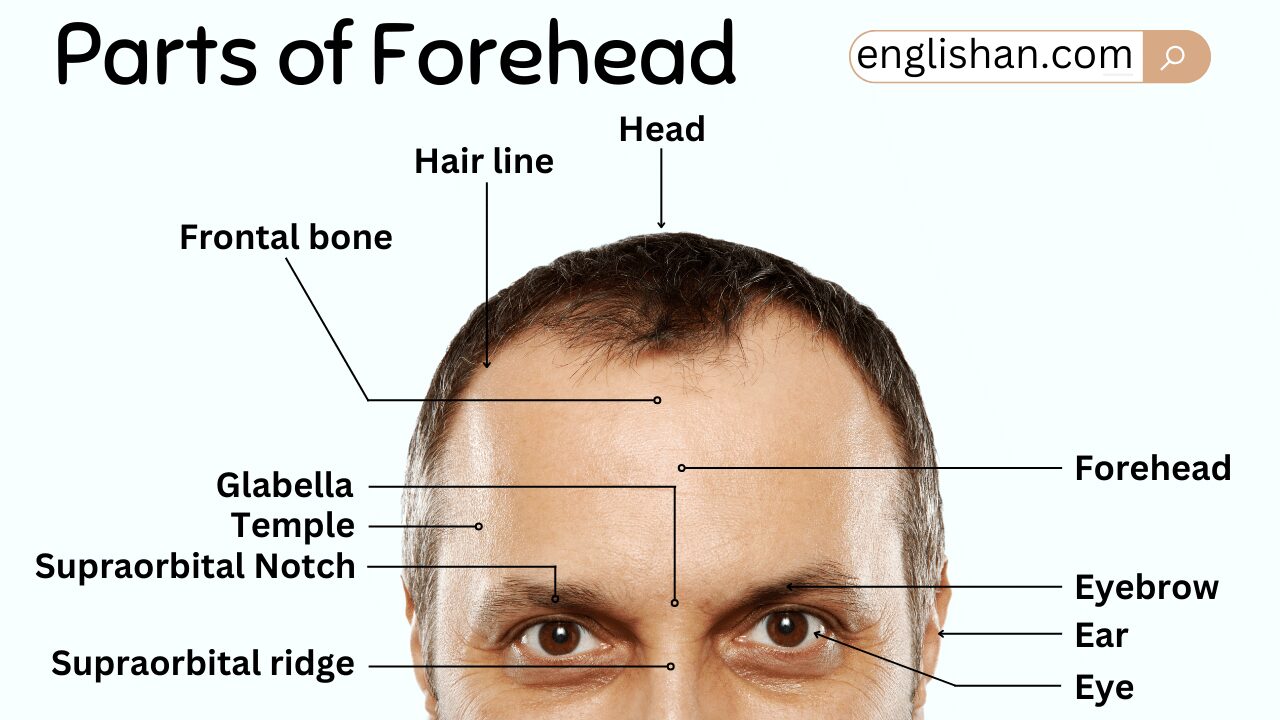
Struggling to describe a headache or shade a portrait is frustrating when you lack the right vocabulary. Learning the parts of the forehead allows you to communicate precisely, whether for a school assignment or a doctor’s visit.
We explain the main features in this post to help you learn fast. While the frontal bone provides structure, the hairline, temples, and glabella frame the face uniquely. The labeled diagram below matches the skin, brow ridge, and wrinkles to their locations instantly.
What Is the Forehead?
The forehead is the region of the face located above the eyes and below the hairline. It extends laterally to the temples and is a significant part of facial anatomy. The forehead plays a key role in protecting the brain, allowing facial expressions, and even contributing to the overall aesthetics of the face.
Parts Of The Forehead
Frontal Bone
Think of this as the sturdy front shield of the skull, built for shape and protection. It gives the upper face its hard framework while guarding deeper tissue from impact. Curvature and bone thickness also influence how the forehead contour reads.
Frontal Eminences
Two gentle bulges can add a rounded character to the upper forehead. Their prominence shifts with growth patterns and genetics, so faces can look softer or more angular without any change in skin. Light and shadowing often make them stand out.
Brow Ridge
A stronger ridge here can lend a more pronounced, sculpted look to the upper face. Bone projection influences how expression moves, especially during frowning or intense focus. Variation is normal and often tied to skull structure.
Glabella
Between the brows sits a small zone that is often used as a reference point in anatomy. Proportion and symmetry assessments frequently start here because it anchors the central upper face. Expression lines also tend to develop in this area with repeated movement.
Supraorbital Rim
A firm bony edge frames and protects the upper orbit. Its shape affects facial depth because it sets the boundary that casts shadow above the eyes. Structural strength here also supports the upper orbit under load.
Frontal Sinuses
Inside the frontal bone, air spaces connect with the nasal system and vary greatly from person to person. They can influence voice resonance and the way pressure feels during congestion. Size and internal shape differ even among close relatives.
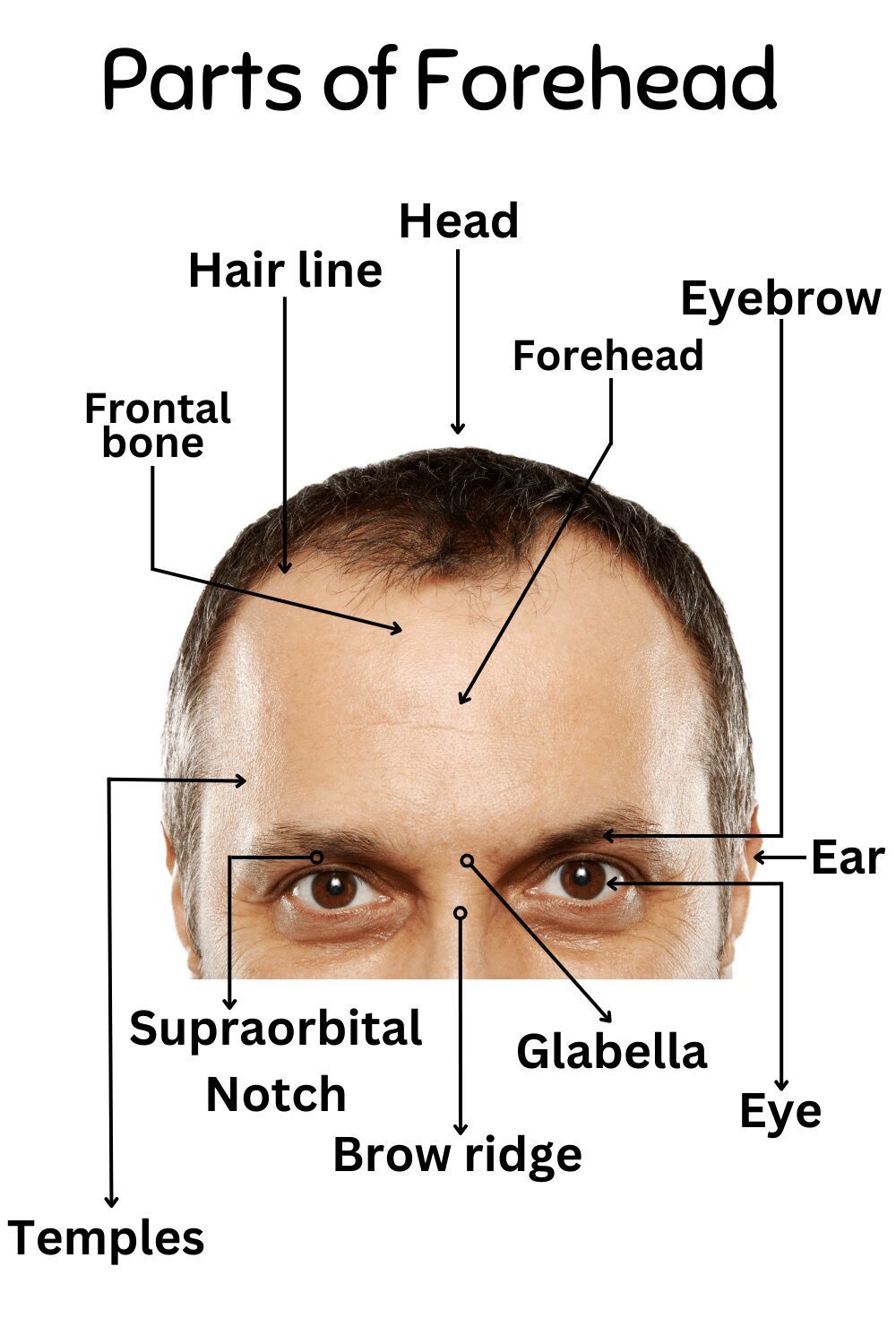
Muscles Of The Forehead
Frontalis Muscle
Across the upper face, this muscle drives forehead movement and eyebrow elevation. It plays a central role in expressions linked to surprise and attention. Repeated use often contributes to horizontal lines over time.
Corrugator Supercilii
Deep beneath the brow, this narrow muscle pulls the eyebrows inward. Its action creates vertical frown lines during concentration or concern. Persistent tension here is strongly tied to glabellar creases.
Procerus Muscle
Running over the bridge area, this muscle draws the skin downward between the brows. It shapes expressions of disapproval or strain. Activation commonly leads to transverse lines across the upper nose.
Depressor Supercilii
This small muscle works to lower the eyebrow toward the eye. It balances opposing muscle actions to fine-tune brow position. Subtle movement here affects expression control, especially during focused facial gestures.
Occipitofrontalis
Functioning as a paired muscle group, it links the forehead and scalp into one unit. This connection allows coordinated scalp movement and eyebrow lift. Tension patterns here influence overall facial expression rather than isolated motion.
Forehead Structure
Squamous Part Of The Frontal Bone
This broad plate forms the main forehead surface and gives the upper face its smooth contour. It protects underlying tissues while shaping facial profile. Thickness and bone curvature influence strength and visible form.
Orbital Part Of The Frontal Bone
Extending inward, this section creates the roof of the eye sockets and adds structural support to the upper facial skeleton. Its shape affects how force is distributed around the eyes. Smoothness and edge strength matter for protection and stability.
Nasal Part Of The Frontal Bone
At the center, this smaller section contributes to nasal structure and joins with surrounding bones. It supports the bridge area while maintaining airflow passage integrity. Size and bone alignment vary across individuals.
Functions of the Forehead
The forehead plays several important roles in the human body, ranging from protection to communication.
- Protection: The thick frontal bone of the forehead provides a sturdy shield for the frontal lobe of the brain. This protection is crucial, as the frontal lobe is responsible for higher cognitive functions, such as decision-making, problem-solving, and controlling behavior.
- Facial Expressions: The muscles of the forehead allow for a wide range of facial expressions, which are essential for non-verbal communication. Whether we are raising our eyebrows in surprise or furrowing them in concentration, the forehead muscles help convey our emotions to others.
- Aesthetic Balance: The forehead contributes to the overall balance and symmetry of the face. Its shape, size, and contour play a significant role in defining the face’s aesthetics. A well-proportioned forehead is often considered a sign of beauty and harmony in facial features.
- Sinus Function: The frontal sinuses within the forehead help in reducing the weight of the skull, filtering and humidifying the air we breathe, and enhancing our voice resonance. They also provide some protection to the brain by absorbing impact during head trauma.
Key Takeaways
The frontal bone works as one system, with its squamous, orbital, and nasal parts shaping and protecting the upper face together rather than acting alone. For parts of frontal bone, the core purpose is protection, especially for delicate structures linked to vision and airflow. Bone thickness affects strength because denser areas resist impact more effectively. Standard human anatomy follows consistent bone boundaries, even though surface form varies by genetics and age. We treat accurate naming as precision, so each term stays exact in writing and speech.
FAQs:
The forehead itself is a part of the face, and while it doesn’t have many “body parts” specifically, here are the areas and structures related to it:
1. Frontal Bone: The bone that forms the forehead.
2. Hairline: The edge where the forehead meets the hair.
3. Eyebrows: Located above the eyes, they sit on the brow ridge.
4. Glabella: The smooth area between the eyebrows.
5. Brow Ridge: The bony area above the eyes, just under the eyebrows.
6. Temples: The area on the sides of the forehead, near the ears.
These are the key body parts and areas connected to the forehead!
There are four types of foreheads:
1. High Forehead: A tall forehead, with a higher hairline.
2. Low Forehead: A shorter forehead, with the hairline close to the eyebrows.
3. Flat Forehead: A forehead that looks straight and even.
4. Rounded Forehead: A forehead with a smooth, curved shape.
These are just different shapes of the forehead!
The name of the forehead is the frontal region. It is also referred to as the frontal area of the face, named after the frontal bone that forms it.
You May Also Like