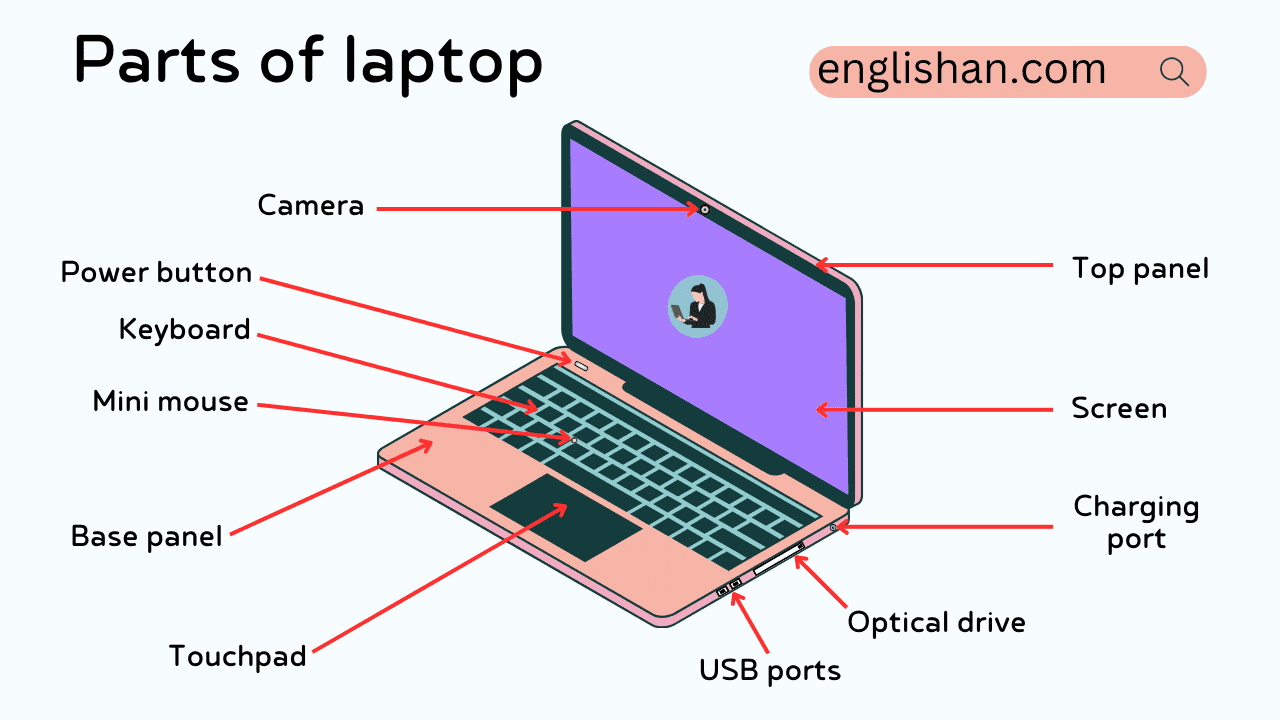
Every laptop works through a set of connected components, and learning the parts of a laptop becomes much easier when you can match each name to its place on the machine. From the screen, keyboard, and ports on the outside to the battery, processor, RAM, and storage inside, each part has a clear role in how the system runs.
This guide covers both external and internal laptop parts with clear names and labeled visuals, so you can quickly recognize each component and understand what it does. Whether you are studying computer hardware or checking the layout of your own device, this breakdown makes the parts easier to identify and remember.
What is a Laptop?
A laptop is a small, portable computer made for easy use anywhere. It has all the main parts—screen, keyboard, CPU, RAM, and storage—built into one device. You can carry it and use it without needing to plug in lots of extra equipment. Most laptops also have ports, wireless internet, and Bluetooth, so you can connect to Wi-Fi or other devices easily. People use laptops for many things like work, watching videos, or chatting online.
Key Functional Parts of a Laptop
Learning the key parts of a laptop gives a clear understanding of how laptops are structured. It helps learners recognize different components by their function and location.
External Laptop Parts
These parts are used most often and directly affect how the laptop is used every day. Learning them helps students understand user interaction areas and supports vocabulary for describing external laptop features.
- Display Screen: The part that shows text, pictures, and videos; it’s often LED or LCD based.
- Keyboard: A flat set of buttons for entering letters, numbers, and special symbols into the laptop.
- Touchpad: A surface used like a mouse to move the cursor and click items without a separate device.
- Power Button: Used to turn the laptop on or off; often found above the keyboard or on the side.
- Indicator Lights: Small lights that show information like charging, power, or caps lock status.
- Laptop Lid: The outer shell that holds the screen and protects it when closed.
Inside a Laptop: Main Components
This section introduces the important components inside a laptop that control speed, performance, and storage. Learning these helps students describe what powers a laptop and stores their data.
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): It’s the brain of the laptop that runs apps, programs, and background tasks.
- RAM (Random Access Memory): Temporary storage that helps the system perform many tasks at once.
- Storage Drive (HDD or SSD): Saves files, programs, and system data; SSDs are faster while HDDs offer more space.
- Motherboard: A large circuit board that connects and supports all internal parts inside the laptop.
- GPU (Graphics Processing Unit): Handles picture and video quality, especially useful for games and editing.
- Cooling Fan: Blows out heat from inside the laptop to stop it from overheating during use.
- Heat Sink: Draws heat away from hot components and works with the fan to keep the system cool.
Power and Peripheral Connectors
These ports and slots connect the laptop to power, other devices, or the internet. Learning these helps students describe how a laptop interacts with external tools.
- Charging Port: Used to plug in the laptop charger and recharge the battery.
- USB Ports: Allow the laptop to connect with flash drives, mice, phones, and many other tools.
- HDMI Port: Sends video and sound to projectors, monitors, or TVs with one cable.
- Audio Jack: A small round hole where you plug in headphones or microphones.
- Ethernet Port: Provides a wired internet connection that’s faster and more stable than Wi-Fi.
- SD Card Slot: Reads SD memory cards often used in phones, cameras, or storage expansion.
- Kensington Lock Slot: A small hole where a lock can be attached to physically secure the laptop.
Supporting Laptop Components and Built-in Tools
Understanding the built-in tools and key supporting components helps describe the full working structure of a laptop. These are not optional accessories but essential elements that complete the laptop’s usability and design.
- Internal Battery: Powers the laptop when unplugged; usually built into the bottom section of the device.
- Built-in Webcam: Placed above the screen, it lets users make video calls or take photos.
- Built-in Microphone: Often near the webcam, captures voice for recordings or meetings.
- Built-in Speakers: Located around the keyboard or sides; they play sound from videos, music, or apps.
- Wi-Fi Card: A small internal chip that connects the laptop to wireless internet networks.
- Bluetooth Module: Enables the laptop to connect wirelessly with nearby devices like phones or headphones.
- Internal Clock Battery (CMOS Battery): Keeps the date, time, and system settings stored even when the main battery is empty.
- Laptop Hinges: Allow the screen to open and close while holding the lid firmly in place.
- Bottom Case and Base Panel: The frame that holds internal parts and provides structure and support.
FAQs:
A laptop is a portable computer designed for on-the-go use, featuring a built-in display, keyboard, and internal components necessary for various computing tasks.
Laptops are portable and integrate all components into a single unit, while desktops are stationary and often have separate components like a monitor, keyboard, and system unit.
Consider factors such as performance (CPU, RAM, GPU), storage type and capacity, battery life, portability, display size, and the intended use (e.g., work, gaming, multimedia).
Adjust power settings, close unnecessary background applications, keep software updated, and consider upgrading to a solid-state drive (SSD).
Check for malware, close unused applications, upgrade RAM, and consider upgrading to an SSD for improved performance.
Clean it regularly, focusing on the keyboard, vents, and screen. However, the frequency depends on the environment; more often if exposed to dust or pet hair.
You May Also Like
- Parts of a PC
- Parts of a computer mouse
- Parts of Computer Monitor
- Parts of Speaker
- Parts of a Keyboard
- Types of Batteries