In this blog post, you will learn the different parts of a watch and their types in English. A watch has many parts, each with a specific function that helps it work properly. Understanding these terms will improve your vocabulary and help you describe different types of watches clearly. Whether you are studying for school or interested in watches, knowing these names will be useful.
To learn more vocabulary on different topics, visit our Vocabulary Category.
Types of Watch
It comes in various types, each designed to meet specific preferences, lifestyles, and purposes. Here are some common types of watches:
Analog:
- Display time using traditional hour and minute hands on a numbered dial.
Digital:
- Feature an electronic display that shows the time in numerical digits.
Dress:
- Elegant and minimalistic designs, suitable for formal occasions.
- Often characterized by thin cases, simple dials, and leather straps.
Sports:
- Designed for athletic and outdoor activities.
- Often water-resistant and may include features like a chronograph, tachymeter, or durable materials.
Diving:
- Specifically built for underwater use.
- Water-resistant to significant depths, with features like a unidirectional rotating bezel for tracking elapsed time.
Aviator/Pilot Watches:
- Originally designed for pilots.
- Typically large, with clear, easy-to-read dials and features like a slide rule for calculations.
Chronograph:
- Include stopwatch functionality, often displayed through subdials on the watch face.
Smartwatches:
- Combine traditional timekeeping with modern technology.
- Connect to smartphones, offer fitness tracking, receive notifications, and run apps.
Mechanical:
- Powered by a mechanical movement, either manual or automatic.
- Appreciated for craftsmanship and often found in luxury watches.
Automatic:
- A type of mechanical watch that winds itself through the motion of the wearer’s wrist.
Quartz:
- Powered by a quartz crystal and a battery.
- Known for accuracy and low maintenance.
- Built for durability and functionality.
- May include features like a 24-hour dial, luminescent markers, and rugged materials.
Fashion:
- Emphasize style and design trends.
- May prioritize aesthetics over advanced features.
Skeleton:
- Showcase the inner workings of the watch, with a transparent case or dial.
Moonphase:
- Display the phases of the moon.
- Often found in more intricate and luxury timepieces.
GMT:
- Feature an additional hand that tracks a second time zone, commonly used by travelers.
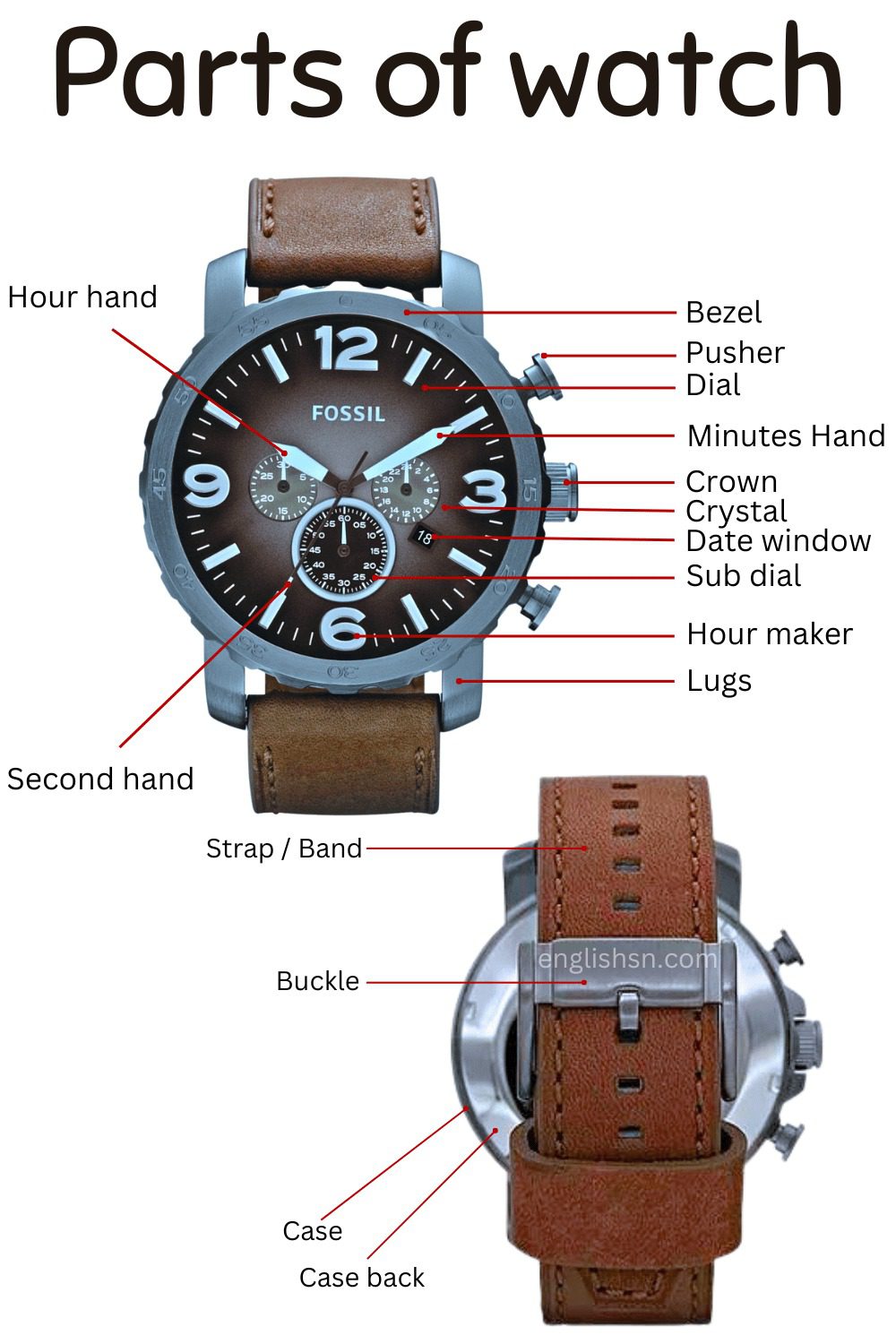
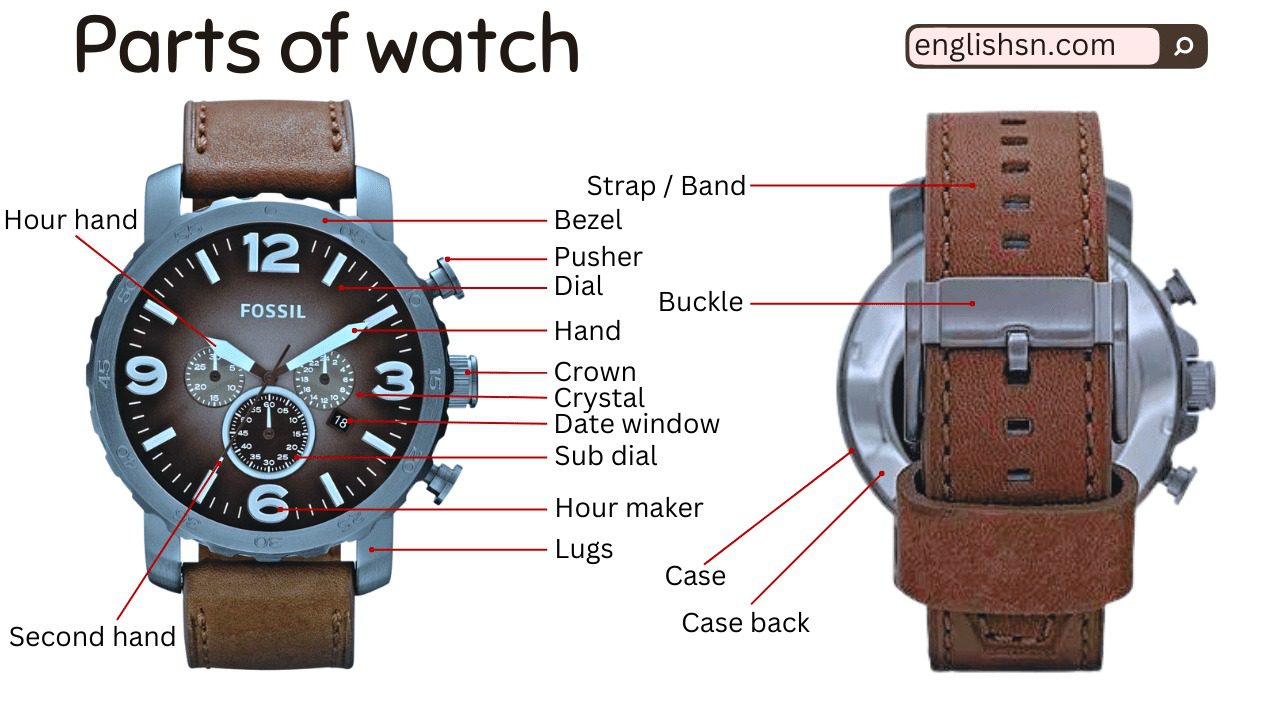
Parts of Watch
Here’s an overview of the main parts of a wristwatch:
Case:
- The outer housing that protects the internal components of the watch.
Bezel:
- The ring on the top of the case surrounding the watch crystal. It can be fixed or rotating and may serve various functions.
Dial:
- The surface displaying the time, usually marked with hour indices and hands.
Crystal:
- The transparent cover over the dial, protecting it. Common materials include sapphire, mineral glass, or acrylic.
Crown:
- A button on the side of the case used for setting the time, date, and winding the watch.
Pushers:
- Buttons on the side of the case (on some watches) used for additional functions like starting and stopping a chronograph or adjusting date and time.
Case Back:
- The cover on the back of the watch that protects the movement. It can be screw-down or snap-on.
Hands:
- Pointers on the dial that indicate the hours, minutes, and seconds.
Subdials:
- Small auxiliary dials on the main dial, used for additional features like a chronograph or date.
Strap/Bracelet:
- The band that holds the watch on the wrist, available in various materials such as leather, metal, or rubber.
Clasp or Buckle:
- The fastening mechanism for the strap or bracelet.
Lugs:
- Projections on the case to which the strap or bracelet is attached.
Water Resistance:
- The watch’s ability to resist water, measured in meters or atmospheres.
Power Reserve Indicator:
- Shows the remaining energy in a mechanical or automatic watch.
Date Window:
- A small window on the dial that displays the current date.
GMT Hand:
- An additional hand that indicates a second time zone on GMT watches.
Tachymeter:
- A scale on the bezel or dial is used to measure speed or distance based on travel time.
How to Clean a Watch
Cleaning involves different steps depending on the type of water resistance. Here’s a general guide for cleaning:
Materials Needed:
- Mild Soap or Watch Cleaning Solution
- Soft Toothbrush or Watch Cleaning Brush
- Soft Microfiber Cloth
- Water Bowl
Steps:
1. Check Water Resistance:
- Determine the water resistance level. Avoid immersing non-water-resistant watches in water.
2. Remove the Watch from the Strap/Bracelet:
- If you have a removable strap or bracelet, detach it from the case.
3. Prepare Soapy Water:
- Fill a bowl with lukewarm water and add a small amount of mild soap or use a specialized watch cleaning solution.
4. Clean the Case and Bezel:
- Dip a soft toothbrush or watch cleaning brush into the soapy water and gently scrub the case, bezel, and lugs. Pay attention to areas where dirt, sweat, or grime may accumulate.
5. Clean the Bracelet/Strap:
- If your watch is water-resistant, you can dip the bracelet or strap into the soapy water and gently scrub it. For leather straps, use a damp cloth to wipe them clean. Avoid soaking leather in water.
6. Rinse Thoroughly:
- Rinse the watch and bracelet under lukewarm running water to remove soap residue.
7. Dry with a Soft Cloth:
- Pat the watch and bracelet dry with a soft, lint-free microfiber cloth. Be thorough to remove all moisture.
8. Air Dry:
- Allow the watch and bracelet to air dry completely before reassembling.
9. Buff and Polish:
- Use a dry cloth to buff and polish the case and crystal for a shiny finish.
10. Inspect for Water Resistance:
- If your watch is water-resistant, ensure that gaskets and seals are in good condition to maintain water resistance.
Tips:
- Avoid Chemicals: Avoid using harsh chemicals, solvents, or cleaning agents that may damage the watch.
- Leather Straps: For leather straps, avoid excessive water exposure. If the strap gets wet, pat it dry immediately.
- Professional Servicing: If your watch is high-end or valuable, consider professional servicing for thorough cleaning and maintenance.
How You Can Express the Tips for Storing a Watch
To properly store and preserve your watch, especially if you won’t be wearing it for an extended period, consider the following tips:
1. Clean the Watch:
- Before storing, make sure the watch is clean. Follow the cleaning steps mentioned earlier to remove any dirt or residue.
2. Check Water Resistance:
- Ensure the watch is water-resistant, especially if you plan to store it in a humid environment.
3. Wind or Charge:
- If you have a mechanical watch, wind it or wear it for a bit to ensure it’s fully wound. If it’s an automatic watch, ensure it has sufficient power.
4. Keep Away from Magnets:
- Store the watch away from magnetic fields, as they can affect the accuracy of the movement.
5. Use a Watch Box or Case:
- Consider storing your watch in a watch box or a dedicated watch case. These typically provide a cushioned and secure environment to prevent scratches.
6. Avoid Direct Sunlight:
- Keep the watch away from direct sunlight to prevent fading of the dial and strap.
7. Temperature and Humidity:
- Store the watch in a cool, dry place. Avoid extremes in temperature and humidity.
8. Rotate Automatic Watches:
- If you have multiple automatic watches, consider using a watch winder to keep them running, especially if you won’t wear them regularly.
9. Remove the Batteries:
- If your watch is quartz and uses a battery, consider removing the battery before storing to prevent leakage.
10. Use Silica Gel Packets:
- Place silica gel packets in the storage area to help absorb moisture and prevent humidity.
11. Regular Checks:
- Even if the watch is not in use, periodically check its condition to ensure it’s functioning correctly.
Quiz:
1. What part protects the dial and hands?
- A) Bezel
- B) Crystal
2. Which component is used for setting the time, date, and winding?
- A) Crown
- B) Movement
3. What is the transparent cover over the dial called?
- A) Dial
- B) Crystal
4. Which part of the watch houses the internal components and provides protection?
- A) Movement
- B) Case
5. What is the small button on the side of the case used for additional functions like starting a chronograph?
- A) Bezel
- B) Pusher
6. Which part holds the watch on the wrist and can be made of leather, metal, or rubber?
- A) Crown
- B) Strap/Bracelet
7. What do we call the pointers on the watch that indicate the hours, minutes, and seconds?
- A) Hands
- B) Indices
8. Which part of the watch displays the current date?
- A) Subdial
- B) Date Window
9. What is the back cover called, protecting the movement inside?
- A) Bezel
- B) Case Back
10. Which type of movement is powered by the motion of the wearer’s wrist?
- A) Mechanical
- B) Quartz
11. Which part measures speed or distance based on travel time?
- A) Tachymeter
- B) GMT Hand
12. What is the term for additional dials on the watch face used for features like a chronograph or date?
- A) Indices
- B) Sub-dials
Answers:
- B) Crystal
- A) Crown
- B) Crystal
- B) Case
- B) Pusher
- B) Strap/Bracelet
- A) Hands
- B) Date Window
- B) Case Back
- A) Mechanical
- A) Tachymeter
- B) Sub-dials
FAQs
Key components include the case, dial, hands, crystal, crown, and movement.
The movement is the internal mechanism that powers. Common types include quartz (battery-powered) and mechanical (manual or automatic).
Automatic are powered by the motion of the wearer’s wrist, which winds the mainspring. They don’t require manual winding if worn regularly.
The crown is used for setting the time, date, and other functions. In some watches, it may also be used for manual winding.
The crystal is the transparent cover over the dial, protecting it from scratches and impacts. Common materials include sapphire, mineral glass, or acrylic.
The bezel is a ring around its crystal. It can be fixed or rotating and may have functions such as tracking elapsed time, especially in diver.
Indices and numerals mark the hours on the dial, aiding in time reading. They can be in the form of hour markers or numerals.
Subdials are small dials on the main dial used for additional features like a chronograph, moon phase, or date complications.
A date window displays the current date. Some also have additional complications like day and month indicators.
Read More