In every sentence, there are two main parts: the subject and the predicate. The subject tells us who or what the sentence is about, while the predicate explains what the subject is doing or describes it. This post helps learn how these parts work together to form meaningful sentences.
In English, every sentence consists of two main parts:
- Subject – Tells us who or what the sentence is about.
- Predicate – Explains what the subject does or what happens to it.
Examples:
- The dog barks. (Subject: The dog, Predicate: barks)
- Apples are tasty. (Subject: Apples, Predicate: are tasty)
By understanding subjects and predicates, you can write clearer and more effective sentences.
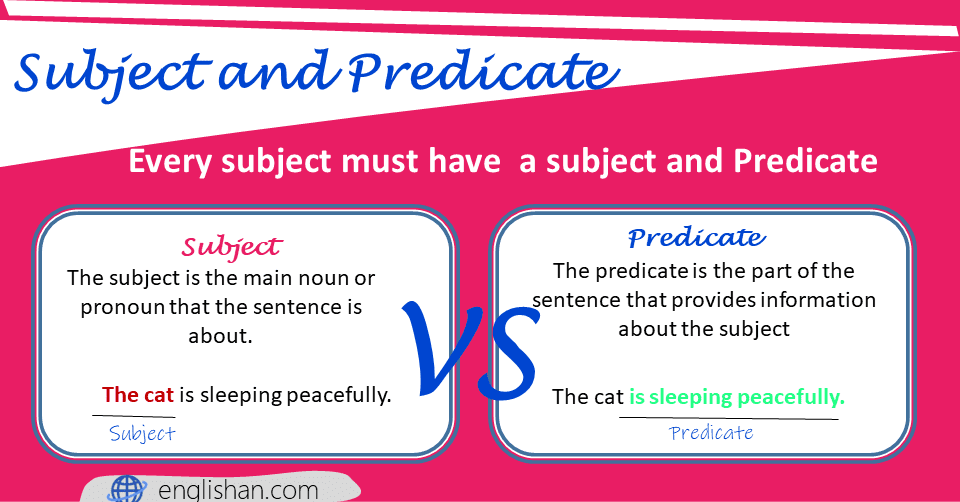
What is the Subject?
The subject is the main noun or pronoun that the sentence is about. It represents a person, thing, or idea performing an action or being described.
To identify the subject, ask:
“Who or what is the sentence about?”
Types of Subjects
Subjects can be simple, complete, or compound:
Simple Subject – The main noun or pronoun:
- The cat sleeps on the sofa.
Complete Subject – The simple subject + modifiers:
- The black and white cat sleeps on the sofa.
Compound Subject – Two or more subjects sharing the same predicate:
- John and Sarah went to the mall.
Examples
- Mary loves to play the piano.
- Dogs are loyal animals.
- The sun rises in the east.
- They went to the park together.
- My sister is a doctor.
In each sentence, the subject represents the who or what the sentence describes.
What is the Predicate?
The predicate is the part of the sentence that provides information about the subject. It includes:
- The verb
- Any other words or phrases describing the action or state of being
To identify the predicate, ask:
“What is happening or being said about the subject?”
Types of Predicates
Predicates can also be simple, complete, or compound:
Simple Predicate – The main verb or verb phrase:
- She sings beautifully.
Complete Predicate – The verb + additional details:
- She sings beautifully in the choir.
Compound Predicate – Two or more verbs sharing the same subject:
- She sings and plays the piano.
Examples
- Mary loves to play the piano.
- Dogs are loyal animals.
- The sun rises in the east.
- They went to the park together.
- My sister is a doctor.
The predicate highlights what happens to the subject in the sentence.
More Examples of Subjects and Predicates
Here are more example sentences to reinforce the concept:
| Sentence | Subject | Predicate |
|---|---|---|
| Cats sleep a lot. | Cats | sleep a lot. |
| He runs every morning. | He | runs every morning. |
| The book has an interesting plot. | The book | has an interesting plot. |
| We enjoy going to the beach. | We | enjoy going to the beach. |
| The flowers bloom in spring. | The flowers | bloom in spring. |
| She sings beautifully. | She | sings beautifully. |
| The students studied hard. | The students | studied hard. |
| I like to read books. | I | like to read books. |
| The car needs repairs. | The car | needs repairs. |
| They won the basketball game. | They | won the basketball game. |
| The baby is crying. | The baby | is crying. |
| My parents love to travel. | My parents | love to travel. |
| Heather baked a delicious cake. | Heather | baked a delicious cake. |
| The birds are chirping. | The birds | are chirping. |
| The movie starts at 8 PM. | The movie | starts at 8 PM. |
| We visited the museum yesterday. | We | visited the museum yesterday. |
| The dog barks loudly. | The dog | barks loudly. |
| The teacher explains the lesson. | The teacher | explains the lesson. |
| Sheila and Mark are best friends. | Sheila and Mark | are best friends. |
| The rain stopped abruptly. | The rain | stopped abruptly. |

FAQs
The subject and predicate are the two main parts of a sentence:
Every sentence has two parts:
1. Subject: Who or what the sentence is about.
2. Predicate: What the subject is doing or what happens.
Examples:
The cat (subject) is sleeping (predicate).
Tom (subject) plays football (predicate).
The flowers (subject) are blooming (predicate).
The subject is the “who or what,” and the predicate tells the action or description.
Here’s the simple rule for subject and predicate:
1. Every sentence needs a subject and a predicate.
2. The subject tells who or what the sentence is about.
3. The predicate tells what the subject is doing or what happens.
Example:
The dog (subject) runs fast (predicate).
Both parts are needed to make a complete sentence.
A predicate tells what the subject does or what happens to it. It usually includes the action word (verb) and other details about it.
Example:
The dog (subject) barks loudly (predicate).
Sara (subject) is reading a book (predicate).
The predicate shows the action or what is happening to the subject.
You May Also Like
Check Your Understanding by Solving the Worksheet Subject and Predicate in English