Contents
Learning English Language involves understanding not only grammar and vocabulary but also when and how to use different styles of the language. Formal and informal English serve distinct purposes and are used in different settings. English, like any language, adapts to its environment.
Formal English is the choice for professional, academic, or serious contexts, while informal English is used in casual, everyday interactions. Understanding when to use each is essential for effective communication, whether you’re writing an email to your boss or chatting with friends online.
Therefore, this guide will help you understand the key differences between formal and informal English by providing practical tips and examples so you can switch seamlessly between the two anytime.
What Is Formal English?
Formal English is structured, precise, and free from slang or contractions. It is a language style often characterized by its strict adherence to grammatical rules and its focus on delivering information clearly and unambiguously. This style is commonly used in:
- Academic writing, such as research papers and essays.
- Professional environments, including business correspondence and formal reports.
- Official documents, such as contracts, policies, and legal texts.
Using formal English demonstrates respect, professionalism, and seriousness. It’s especially important when communicating with people you do not know well or in settings where credibility is essential. So, mastering formal English can significantly enhance your ability to express complex ideas clearly and persuasively.
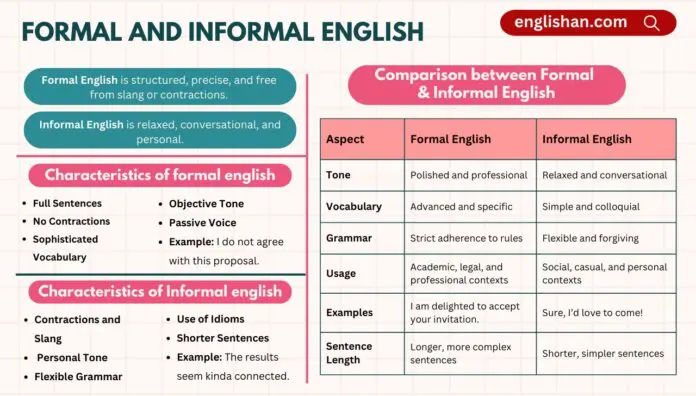
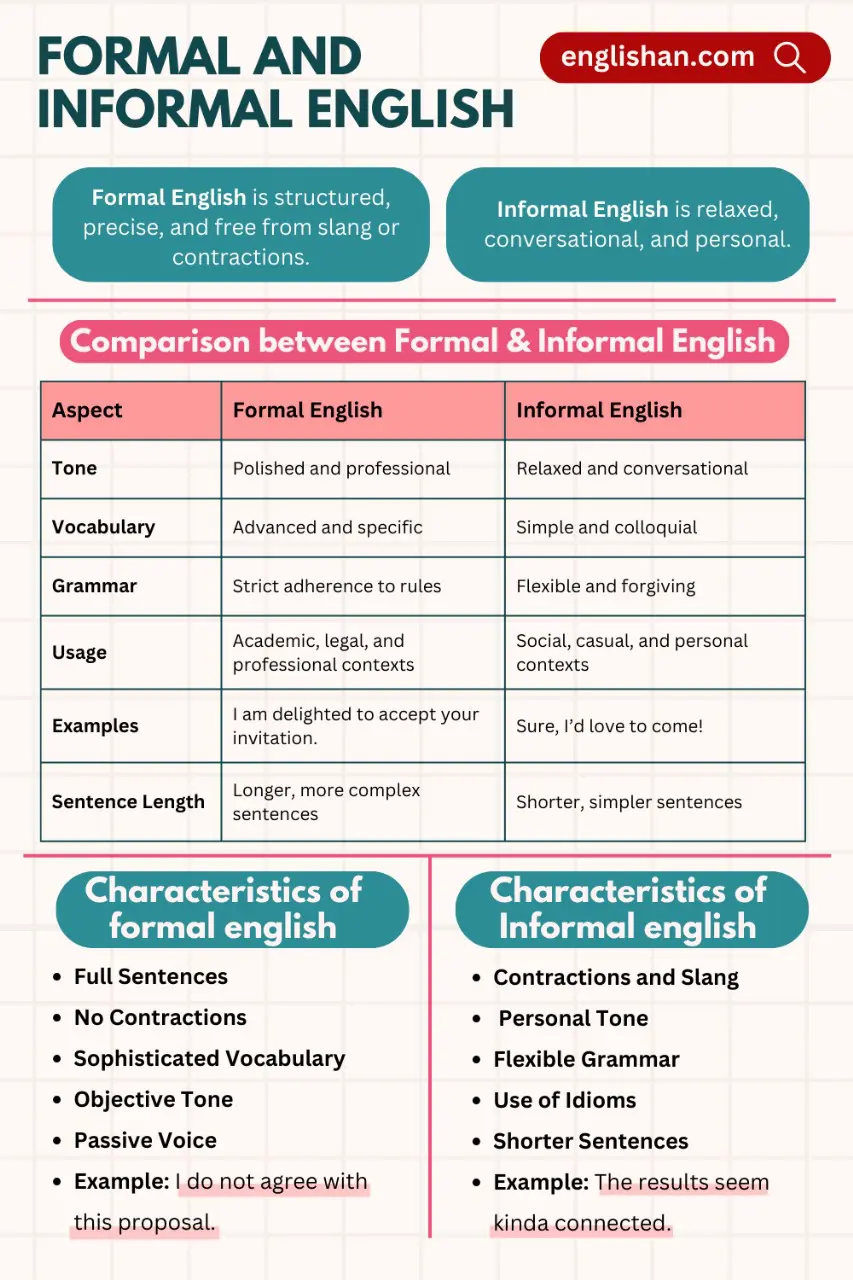
Characteristics of Formal English
Formal English is defined by several distinguishing features that set it apart from informal language:
1 – Full Sentences:
Sentences in formal English are complete and grammatically correct however fragmented sentences or incomplete ideas are avoided.
- Formal: I am writing to inquire about the available positions within your organization.
- Informal: Hey, any jobs open?
2 – No Contractions:
Words are spelled out in their entirety, avoiding contractions such as “don’t” or “can’t.”
- Formal: I do not agree with this proposal.
- Informal: I don’t agree with this.
3 – Sophisticated Vocabulary:
Additionally, formal English uses precise and advanced vocabulary to convey meaning effectively.
- Formal: The presentation demonstrated exceptional insight into the topic.
- Informal: The talk was really good.
4 – Objective Tone:
Statements are made with a focus on facts, logic, and neutrality rather than personal opinions or emotions.
- Formal: The findings indicate a significant correlation between the variables.
- Informal: The results seem kinda connected.
5 – Passive Voice:
While not always necessary, passive voice is more common in formal writing to maintain an objective tone.
- Formal: The report was completed on time.
- Informal: We finished the report on time.
Examples of Formal English in Use:
Following are a few examples in which formal English is used during conversation.
- It is imperative to adhere to the guidelines stipulated in the manual.
- The agenda for the meeting will be distributed by the end of the day.
What Is Informal English?
Informal English is relaxed, conversational, and personal. It reflects the natural way people speak in everyday life. Unlike formal English, it allows for greater flexibility in grammar and vocabulary and is used in:
- Social settings, such as chatting with friends or family.
- Casual writing, including personal emails and text messages.
- Creative contexts, like blogs or informal articles.
Informal English is characterized by its approachable tone, which makes it ideal for building rapport and fostering personal connections. Furthermore, it’s an excellent choice when you’re communicating with people you know well or in settings where a relaxed atmosphere is appropriate.
Characteristics of Informal English
Here are some key traits of informal English that distinguish it from its formal counterpart:
1 – Contractions and Slang:
First of all, contractions like “it’s” or “can’t” are frequently used in informal English, along with colloquial expressions and slang.
- Informal: Can’t wait to see you!
- Formal: I am looking forward to seeing you.
2 – Personal Tone:
Secondly, informal English often includes emotions, humor, and personal opinions.
- Informal: I’m so excited about the trip!
- Formal: I am looking forward to the trip.
3 – Flexible Grammar:
Thirdly, grammar rules are more relaxed, and sentences may be fragmented or incomplete.
- Informal: You okay?
- Formal: Are you feeling well?
4 – Use of Idioms and Expressions:
Moreover, informal language often employs idiomatic phrases to add color and expressiveness.
- Informal: Break a leg! (Good luck)
- Formal: I wish you success.
5 – Shorter Sentences:
Lastly, informal English often features shorter, simpler sentences that are easy to understand.
- Informal: It’s great. Let’s do it!
- Formal: It is an excellent opportunity, and I recommend proceeding with it.
Common Examples of Informal English in Use:
Here are some common examples of informal English used in everyday discussions.
- Wanna grab lunch?
- I can’t believe how awesome that show was!
Formal vs Informal English: A Quick Comparison
Here is a handy table to summarize the key differences between formal and informal English so you can understand them better:
| Aspect | Formal English | Informal English |
| Tone | Polished and professional | Relaxed and conversational |
| Vocabulary | Advanced and specific | Simple and colloquial |
| Grammar | Strict adherence to rules | Flexible and forgiving |
| Usage | Academic, legal, and professional contexts | Social, casual, and personal contexts |
| Examples | I am delighted to accept your invitation. | Sure, I’d love to come! |
| Sentence Length | Longer, more complex sentences | Shorter, simpler sentences |
When to Use Formal English?
You can use formal English in situations where professionalism or seriousness is expected. Here are some examples:
- In Job Applications like this, ‘I am writing to express my interest in the Marketing Manager position.’
- While writing Academic Papers like this, ‘The study indicates a significant correlation between variables.’
- In Official Correspondence like this, ‘Please find attached the requested documents.’
- During Presentations like this, ‘The purpose of this presentation is to outline the project’s milestones.’
Moreover, formal English is also used in speeches, proposals, and professional introductions where establishing credibility is vital.
When to Use Informal English?
Informal English is perfect for building personal connections and casual conversations. For instance:
- While Texting Friends like this, ‘Hey, wanna hang out later?’
- In Social Media like this, ‘Can’t wait for the weekend!’
- In Friendly Emails like this ‘Hi there! Just checking in to see how you’re doing.’
- During Everyday Chats like this ‘Guess what? I’ve got big news!’
In addition to this, informal English is also used in creative contexts like storytelling, blogging, or casual group discussions where the focus is on connection rather than precision.
Tips to Transition Between Formal and Informal English
Switching between formal and informal English can seem tricky, but with regular practice and an understanding of context, it becomes second nature. Here are additional tips to perfect your transitions:
- Know Your Audience: Consider who you are communicating with and the purpose of the interaction.
- Practice Code-Switching: Regularly practice switching between styles to become comfortable in both.
- Learn Context-Specific Phrases: Familiarize yourself with phrases suited to different situations.
- Proofread for Formal Settings: Double-check grammar and tone in professional communications.
- Observe Context Clues: Pay attention to the language others use and adapt accordingly.
- Understand Cultural Nuances: Be mindful of how cultural expectations might influence the choice between formal and informal English.
Moreover, being able to transition smoothly demonstrates language fluency and cultural awareness, enhancing both personal and professional relationships.
FAQs
Learning English grammar and mastering formal and informal English takes time, but curiosity and practice make the process enjoyable. Here are some additional insights to common queries:
1. Can I mix formal and informal English?
Mixing styles can confuse your audience so stick to one style based on the context.
2. Is slang acceptable in informal English?
Yes, but use it appropriately and ensure your audience understands the slang.
3. How can I improve my formal English?
Read academic papers, listen to professional talks, and practice writing in a formal tone.
4. Do contractions make writing informal?
Contractions are more common in informal writing but can appear in semi-formal contexts too.
5. Why is formal English harder to learn?
Formal English often involves complex grammar and vocabulary so it requires more practice and exposure.
Conclusion
Formal and informal English are two sides of the same coin, each serving distinct but equally important purposes in communication. While formal English ensures professionalism, clarity, and respect in serious contexts, informal English fosters warmth, connection, and relatability in casual settings. So, by learning their differences and practicing how to switch between them, you can equip yourself with a versatile communication toolkit.
Whether you’re drafting a business proposal or sharing a laugh with friends, the ability to use both styles confidently enhances your fluency and effectiveness as a communicator. Practice often, seek feedback, and embrace the journey of mastering English in all its forms.
You May Also Like