Infinitive verbs are the basic form of verbs, usually with the word to in front of them. The structure is to + base verb, like to go, to eat, or to write. Infinitives have different roles in sentences and are important for understanding English grammar.
Key Points About Infinitive Verbs
Formation
The infinitive form is made by adding to before the base verb, except in cases of bare infinitives (without to), like after modal verbs.
Examples:
- to run, to study, to sing
- She can run. (bare infinitive)
Functions
Infinitive verbs can have different roles in a sentence:
- Expressing Purpose: I study hard to succeed.
- After Adjectives: It is important to be honest.
- As Subjects: To swim is my favorite activity.
- In Verb Complementation: He wants to eat.
- With Modal Verbs: You should try.
Types of Infinitive Verbs
Infinitive verbs can be split into two main types based on their usage: bare infinitive and full infinitive.
1. Bare Infinitive
The base form of a verb used without to, often after modal verbs or certain other verbs.
Example: She can go to the party.
2. Full Infinitive
The base form of a verb with to, used in different situations, like after adjectives, nouns, or other verbs.
Example: It is important to study for the exam.
3. Infinitives for Purpose
Used to show the reason or intention behind an action.
Example: She studies hard to succeed.
4. Infinitives After Adjectives
Follow adjectives to add more information.
Example: It is easy to learn.
5. Infinitives After Nouns
Follow nouns to express desires or goals.
Example: I have a desire to travel.
6. Infinitives in Verb Complementation
Used to complete the meaning of certain verbs.
Example: They decided to leave.
7. Infinitives as Subjects
Can be used as the subject of a sentence to highlight an action.
Example: To err is human.
Functions of Infinitive Verbs
Infinitive verbs can serve many roles in a sentence, making them very versatile.
- Expressing Purpose:
- Example: She studies hard to succeed.
- After Adjectives:
- Example: It is easy to learn.
- After Nouns:
- Example: I have a desire to travel.
- After Certain Verbs:
- Example: They decided to leave.
- After Modifiers:
- Example: He is old enough to drive.
- As the Subject of a Sentence:
- Example: To err is human.
- In Infinitive Clauses:
- Example: I asked him to help.
- With Certain Phrases:
- Example: She is ready to begin.
- In Split Infinitives:
- Example: It is sometimes acceptable to boldly go where no one has gone before.
- In Verb Complementation:
- Example: She wants to go.
- With Modal Verbs:
- ❌ He can to swim. (Incorrect)
- ✅ He can swim. (Correct)
Examples of Infinitive Verbs in Sentences
Here are some examples of infinitive verbs in sentences:
- She hopes to travel to Europe next year.
- It’s important to exercise regularly for good health.
- He decided to learn a new language over the summer.
- We plan to visit the museum this weekend.
- She can go to the store after work.
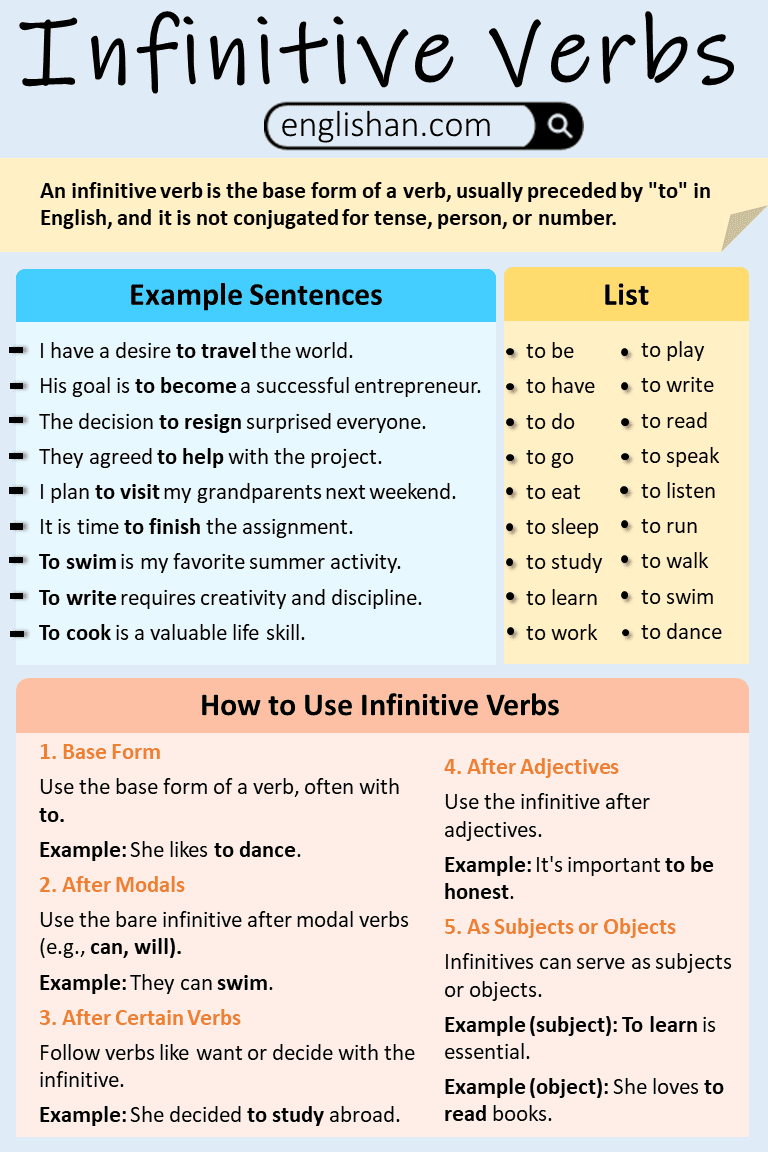
How to Use Infinitive Verbs
Using infinitive verbs correctly means knowing their different roles in a sentence. Here are some guidelines:
1. Base Form
Use the base form of a verb, usually with to.
Example: She likes to dance.
2. After Modals
Use the bare infinitive after modal verbs (e.g., can, will).
Example: They can swim.
3. After Certain Verbs
Follow verbs like want or decide with the infinitive.
Example: She decided to study abroad.
4. After Adjectives
Use the infinitive after adjectives.
Example: It’s important to be honest.
5. As Subjects or Objects
Infinitives can be subjects or objects in a sentence.
Examples:
- (Subject) To learn is essential.
- (Object) She loves to read books.
6. Expressing Purpose
Use infinitives to show why something is done.
Example: He studies hard to succeed.
7. Verb Complementation
Complete sentences with infinitives after certain verbs.
Example: They agreed to help.
8. With Certain Phrases
Pair infinitives with phrases like it’s time or it’s important.
Example: It’s time to go home.
9. Split Infinitives
Sometimes, adverbs are placed between to and the verb.
Example: She decided to boldly go where no one had gone before.
List of Infinitive Verbs
Infinitive verbs are the base form of verbs, often with to. Here’s a list of common infinitive verbs:
to love
to be
to have
to do
to go
to eat
to sleep
to study
to learn
to work
to play
to write
to read
to speak
to listen
to run
to walk
to swim
to dance
to sing
to cook
to travel
to think
to understand
to help
FAQs:
An infinitive verb is the base form of a verb, usually with “to” in front of it. It shows an action, but not when it happens.
Examples:
1. To eat
2. To play
3. To run
Here are 12 examples of infinitive verbs:
1. To eat
2. To dance
3. To sing
4. To run
5. To write
6. To jump
7. To read
8. To sleep
9. To talk
10. To swim
11. To play
12. To learn
Each of these verbs is in its basic form, with “to” in front of them!
To identify an infinitive verb, look for these signs:
1. It starts with “to” (e.g., to eat, to play).
2. It is the base form of the verb (e.g., to run, not to ran).
3. It shows an action or state (e.g., to jump, to learn).
Example:
In the sentence “She loves to sing,” “to sing” is an infinitive verb.
There are 3 types of infinitive verbs:
1. To + base verb: Example: to eat, to play
2. Bare infinitive: No “to” after verbs like can or will. Example: can go, will run
3. Perfect infinitive: To have + past verb. Example: to have eaten, to have seen
Here’s how to tell if a verb is finite or infinite:
Finite Verb:
1. Shows tense (past, present).
2. Changes based on the subject (I, he, she).
3. Stands alone in a sentence.
Example: She runs.
Infinite Verb (Infinitive):
1. Does not show tense.
2. Starts with “to” + base verb.
3. Needs other words to make sense.
Example: She wants to run.
Finite verbs change for tense and subject, while infinite verbs stay the same with ‘to.’
You May Also Like