The mouth is a vital part of the human body, serving as the entry point for food into the digestive system. It consists of various components such as the teeth, tongue, and salivary glands, each playing a crucial role in functions like chewing, speaking, and initiating digestion. Teeth break down food into smaller pieces, the tongue aids in taste and speech, while saliva helps in the digestion process. Despite its importance, the mouth is prone to issues like cavities and gum disease. Taking care of oral health is essential not just for a bright smile but for overall well-being.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Mouth?
The mouth is the part of your face that you use for eating, talking, and breathing. It includes your lips, tongue, teeth, and the opening where you put food. When you eat, your mouth helps break down food into smaller pieces, making it easier for your body to digest. Additionally, your mouth is important for talking and expressing yourself. Taking care of your mouth, like brushing your teeth, is crucial for staying healthy.
Functions
What’s my Mouth’s Function?
The mouth serves several important functions, encompassing both digestive and non-digestive roles. Your mouth has several important functions:
1. Eating (Ingestion): The primary function is to take in food and liquids, allowing your body to receive the nutrients it needs for energy and growth.
2. Chewing (Mastication): Your teeth and jaw work together to break down food into smaller, more manageable pieces, making it easier for digestion.
3. Tasting (Gustation): The tongue contains taste buds that allow you to experience different flavors like sweet, salty, sour, bitter, and umami.
4. Speaking (Speech Articulation): The movements of your tongue, lips, and palate are crucial for forming sounds and words, enabling you to communicate verbally.
5. Initiating Digestion: Salivary glands produce saliva, which contains enzymes that begin the process of breaking down carbohydrates in your food.
6. Formation of Bolus: The chewed food mixes with saliva to form a soft mass called a bolus, which is easier to swallow.
7. Swallowing (Deglutition): Coordinated muscle movements in your mouth and throat allow you to swallow food and liquids, transporting them to your stomach for further digestion.
8. Respiration (Secondary Function): The mouth can serve as an alternate air passage during breathing, especially in situations where nasal breathing is hindered.
9. Oral Hygiene: Proper care of the mouth, including brushing and flossing, is essential for maintaining oral health and preventing dental issues
Overall, your mouth plays a vital role in both the intake of nutrients and communication, highlighting its significance for overall well-being. Regular oral hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing, help maintain the health of your mouth and prevent dental issues.
Anatomy
What are the Parts of Mouth?
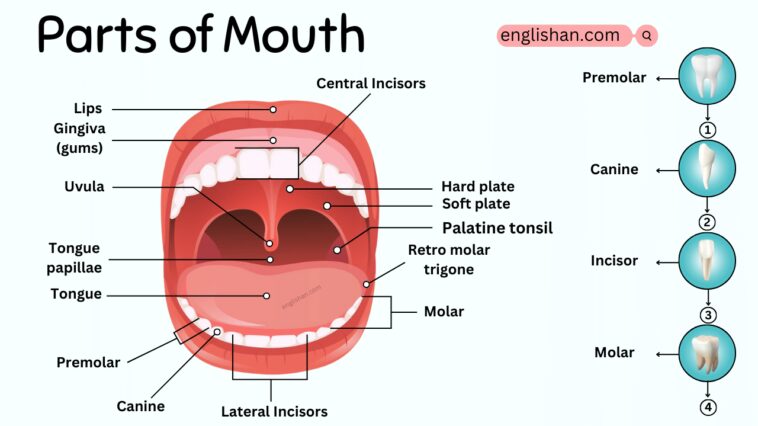
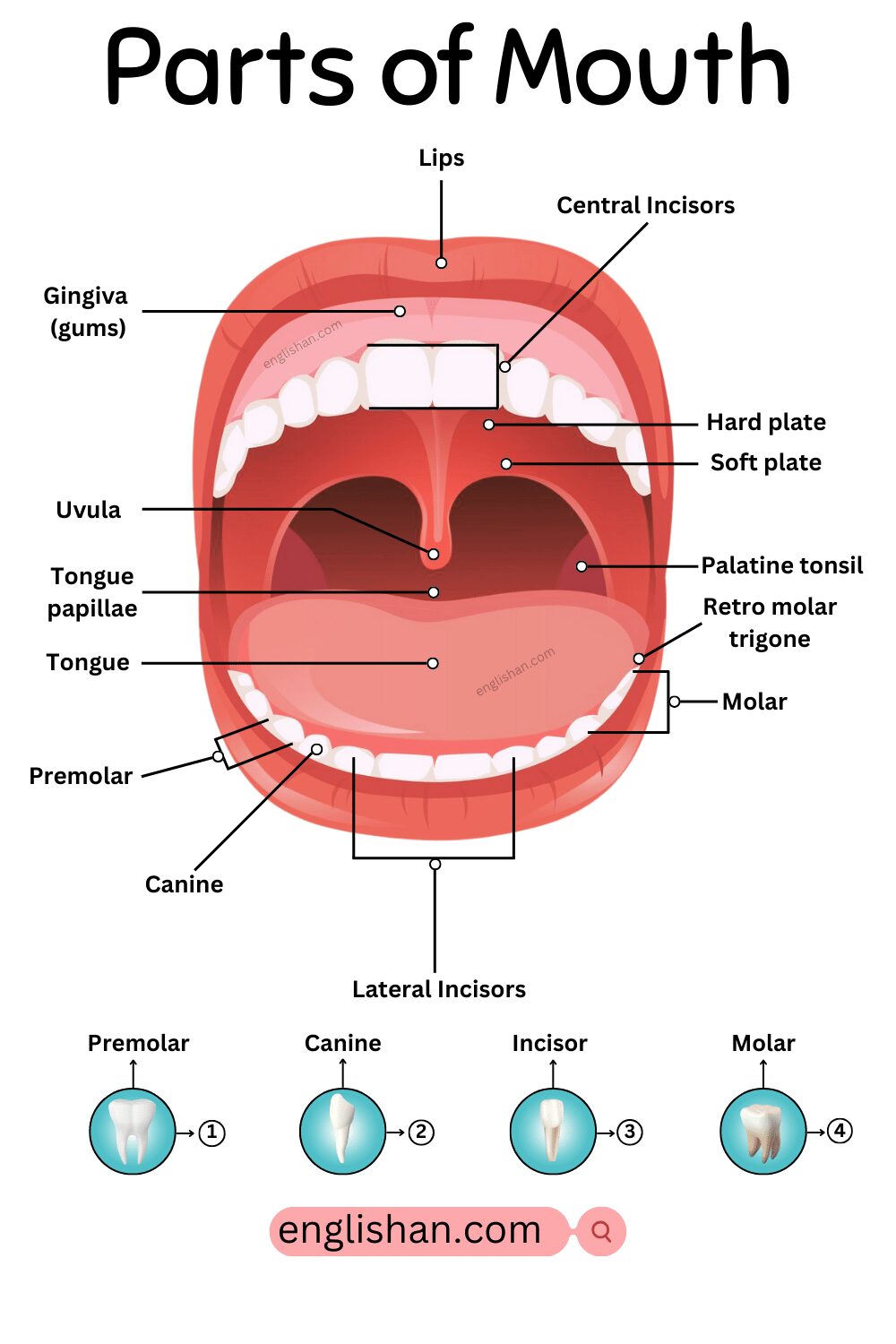
The mouth is a complex structure with various parts, each serving specific functions in the processes of digestion, communication, and respiration. Here are the main parts of the mouth:
- Lips: The fleshy structures that form the entrance to the mouth. They play a role in speech, expression, and holding food and liquids within the mouth.
- Palatine Tonsils: Clusters of lymphoid tissue located on either side of the back of the throat (oropharynx). They are part of the immune system.
- Tongue: A muscular organ with taste buds that assists in the manipulation of food, taste perception, and speech.
- Hard Palate: The front part of the roof of the mouth, composed of bone. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
- Soft Palate: The flexible, rear part of the roof of the mouth. It plays a role in speech, swallowing, and closing off the nasal passages during swallowing.
- Uvula: A small, fleshy extension hanging down from the soft palate. It contributes to speech and swallowing.
- Gums (Gingiva): The soft tissues surrounding the base of the teeth. Healthy gums are crucial for overall oral health.
- Tongue Papillae: Small bumps on your tongue that help you taste different flavors.
- Premolar: A flat tooth in the middle of your mouth, used for chewing and grinding food.
- Canine: Pointy teeth next to your front teeth, used for tearing food.
- Molar: Big, flat teeth at the back of your mouth, used for crushing and grinding food.
- Retro Molar Trigone: An area behind your last big tooth in the back of your mouth.
- Central Incisors: The two middle teeth in the front, are used for biting and cutting food.
- Lateral Incisors: The teeth next to the middle ones in the front, are also used for biting and cutting food.
Conditions and Disorders
What Conditions and Disorders can Affect your Mouth?
There are various conditions and disorders that can affect the mouth, teeth, and surrounding structures. Here are some common ones:
1. Cavities (Dental Caries):
Caused by bacteria that produce acid, cavities result in the decay of tooth enamel.
2. Gingivitis:
Inflammation of the gums, often caused by poor oral hygiene, leading to redness, swelling, and bleeding.
3. Periodontitis:
Advanced gum disease involving the inflammation and infection of the supporting structures of the teeth, leading to potential tooth loss.
4. Bad Breath (Halitosis):
Often caused by bacteria in the mouth, gum disease, or other oral health issues.
5. Tooth Sensitivity:
Discomfort or pain when consuming hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and beverages.
6. Dry Mouth (Xerostomia):
Insufficient saliva production, which can result from certain medications, medical conditions, or dehydration.
7. Oral Thrush (Candidiasis):
A fungal infection in the mouth, characterized by white patches on the tongue and inside the cheeks.
8. Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders:
Conditions affecting the jaw joint, often causing pain, clicking sounds, and difficulty in jaw movement.
9. Cleft Lip and Palate:
Congenital conditions where there is an opening or gap in the upper lip and/or the roof of the mouth.
10. Bruxism:
Teeth grinding or clenching, often occurring during sleep, which can lead to tooth wear and jaw discomfort.
11. Oral Cancer:
The development of cancerous cells in the oral cavity, including the lips, tongue, and throat.
12. Dental Abscess:
A collection of pus caused by a bacterial infection, often resulting from untreated cavities or gum disease.
It’s essential to seek professional dental care if you experience symptoms or suspect any oral health issues. Regular dental check-ups and maintaining good oral hygiene practices can help prevent many of these conditions.
Cancerous Conditions of the Mouth
Oral cancers can affect any area of your mouth. Cancerous conditions of the mouth include:
- Oral Cancer
- Lip Cancer
- Tongue Cancer
- Cheek Cancer (Buccal Mucosa Cancer)
- Gum Cancer (Gingival Cancer)
- Palate Cancer
- Floor of the Mouth Cancer
- Oropharyngeal Cancer
Care
How can I keep my Mouth Healthy?
Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential for keeping your mouth healthy. Here are some tips:
1. Brush Your Teeth:
Brush your teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and brush all surfaces of your teeth.
2. Floss Daily:
Flossing helps remove plaque and food particles between your teeth and along the gumline. Make it a daily habit.
3. Use Mouthwash:
Rinse your mouth with an antimicrobial or fluoride mouthwash to help reduce plaque, fight bacteria, and strengthen teeth.
4. Visit the Dentist:
Schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings. Your dentist can catch issues early and provide professional cleaning.
5. Limit Sugary Foods and Drinks:
Sugary foods and drinks contribute to tooth decay. Limit your intake, especially between meals.
6. Eat a Balanced Diet:
Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Nutrient-rich foods support overall oral health.
7. Stay Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water to help flush away bacteria and acids, and to keep your mouth moist.
8. Quit Smoking:
Smoking can contribute to gum disease, tooth decay, and oral cancer. Quitting improves your overall oral health.
9. Protect Your Teeth:
Wear a mouthguard if you play contact sports, and use a nightguard if you grind your teeth at night.
10. Monitor Your Oral Health:
Pay attention to changes in your mouth, such as bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, or unusual growths. If you notice anything unusual, see your dentist.
Remember, good oral health is a combination of consistent at-home care and regular professional dental visits. Taking care of your mouth contributes to your overall well-being.
When Should I Call My Healthcare Provider?
You should contact your healthcare provider if you experience any of the following:
1. Persistent Pain:
Continuous or severe pain in your mouth, teeth, or gums.
2. Bleeding Gums:
Excessive or persistent bleeding, especially during or after brushing.
3. Swelling or Lumps:
Unexplained swelling, lumps, or bumps in your mouth or on your gums.
4. Persistent Bad Breath:
Chronic bad breath that doesn’t improve with proper oral hygiene.
5. Tooth Sensitivity:
Persistent sensitivity to hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and drinks.
6. Changes in Oral Tissues:
Any changes in the color, texture, or appearance of your tongue, gums, or other oral tissues.
7. Difficulty Swallowing or Chewing:
Problems with swallowing, chewing, or moving your jaw.
8. Loose or Shifting Teeth:
Teeth that are loose or shifting out of position.
9. Jaw Pain or Clicking:
Persistent jaw pain, clicking sounds, or difficulty opening and closing your mouth.
10. Sores or Ulcers:
Non-healing sores, ulcers, or lesions in your mouth.
11. Orthodontic Concerns:
Issues related to braces or other orthodontic treatments.
12. Dental Emergencies:
Any dental emergency, such as a knocked-out tooth, a broken tooth, or severe trauma to the mouth.
Remember, regular dental check-ups are crucial for preventive care, but if you notice any of these issues between appointments, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider or dentist for guidance and appropriate care. Early intervention can often prevent more significant problems.
Conclusion
The mouth is essential for eating, speaking, and breathing. Teeth, tongue, and saliva contribute to functions like chewing and taste. Despite its importance, the mouth is prone to issues such as cavities. Simple habits like regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, along with a healthy lifestyle, are crucial for maintaining oral health and overall well-being.
Quiz:
1. What is the primary function of the mouth?
a) Speaking
b) Digestion
2. Which part of the mouth aids in forming sounds and words?
a)Teeth
b) Tongue
3. What is the main role of the uvula?
a) Initiating digestion
b) Speech articulation
4. What can excessive sugar intake contribute to in the mouth?
a) Gum disease
b) Dry mouth
5. How often should you visit the dentist for regular check-ups?
a) Once a year
b) Twice a year
6. What is the primary function of the premolar teeth?
a) Crushing and grinding food
b) Tearing food
7. What can bad breath be a sign of?
a) Cavities
b) Dry mouth
8. What is the uvula’s role during swallowing?
a) Initiating digestion
b) Closing off nasal passages
9. Which part of the mouth is responsible for detecting sweetness in food?
a) Taste buds
b) Tongue papillae
10. What is the purpose of using a mouthguard?
a) Preventing cavities
b) Protecting teeth during sports
11. What condition is characterized by a collection of pus caused by a bacterial infection? a. a) Cavities
b) Dental abscess
12. Why is regular oral hygiene crucial?
a) Only for a bright smile
b) For overall well-being
13. What is the primary function of the palatine tonsils?
a) Initiating digestion
b) Immune system support
14. What part of the mouth is responsible for tearing food?
a) Canine teeth
b) Molar teeth
Answers:
- b) Digestion
- b) Tongue
- b) Speech articulation
- a) Gum disease
- b) Twice a year
- a) Crushing and grinding food
- a) Cavities
- b) Closing off nasal passages
- a) Taste buds
- b) Protecting teeth during sports
- b) Dental abscess
- b) For overall well-being
- b) Immune system support
- a) Canine teeth
FAQs:
Q1. What is the primary function of the mouth?
The primary function of the mouth is to facilitate the intake of food and liquids, initiating the process of digestion.
Q2. How often should I visit the dentist?
It is generally recommended to visit the dentist for regular check-ups and cleanings twice a year.
Q3. Why is saliva important in the mouth?
Saliva helps in the digestion process by moistening food, making it easier to swallow. It also contains enzymes that begin breaking down carbohydrates.
Q4. What are some common oral health issues?
Common oral health issues include cavities, gum disease, bad breath, tooth sensitivity, and oral infections.
Q5. How can I maintain good oral hygiene?
Good oral hygiene practices include brushing teeth twice a day, flossing daily, using mouthwash, and visiting the dentist regularly.
Q6. What is the role of the tongue in the mouth?
The tongue assists in functions such as taste perception, speech articulation, and manipulation of food during chewing and swallowing.
Q7. How does smoking affect oral health?
Smoking can contribute to gum disease, tooth decay, bad breath, and an increased risk of oral cancer.
Q8. What conditions can affect the taste buds?
Conditions such as infections, certain medications, and aging can affect taste perception and the functionality of taste buds.
You May Also Like: