Contents
A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. In English grammar, there are different types of nouns, each with a specific role. Learning how these types work helps you write clearer sentences and use English more effectively. This guide explains the main types of nouns in English with easy definitions and simple examples.
What Is a Noun?
A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. It can be the subject or object of a sentence and is one of the eight parts of speech in English.
Role of Nouns in a Sentence
Nouns often serve as:
- Subjects: Ali plays football.
- Objects: She saw a movie.
- Objects of prepositions: He sat on the chair.
- Complements: He is a teacher.
Main Types of Nouns in English
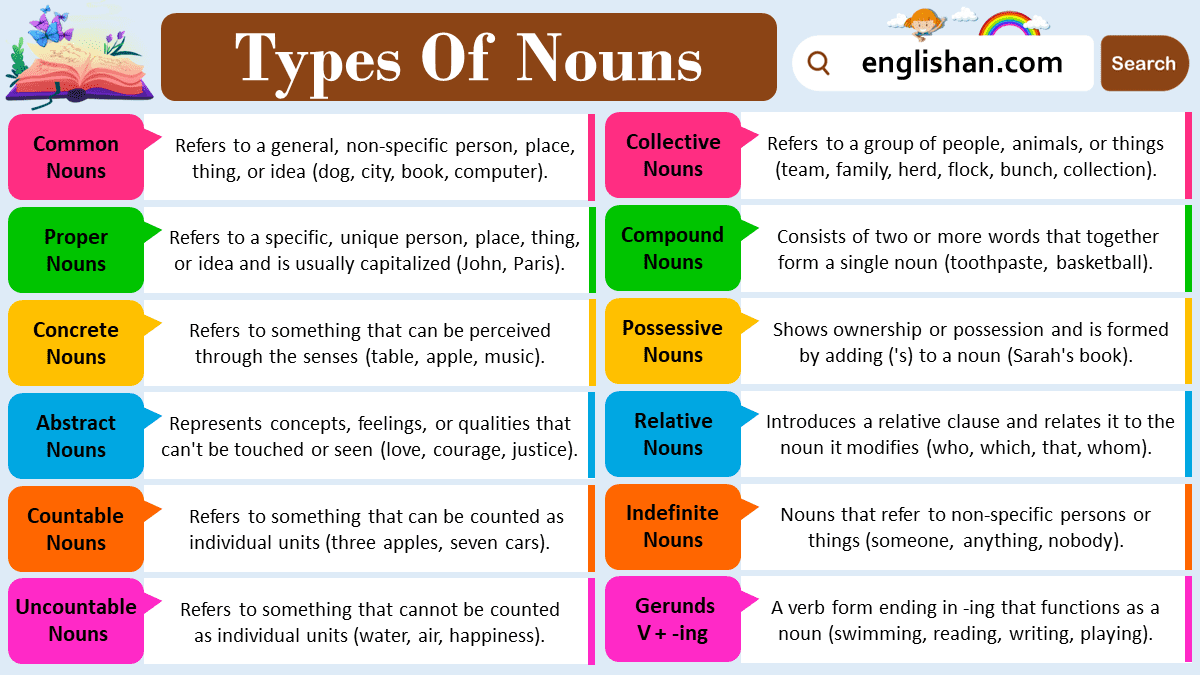
Common Nouns
A common noun refers to general names of people, places, or things.
- Examples: teacher, city, book, river
Proper Nouns
A proper noun names a specific person, place, or thing and is always capitalized.
- Examples: Maria, Lahore, Titanic, Monday
Abstract Nouns
An abstract noun refers to intangible ideas or qualities that cannot be touched.
- Examples: happiness, strength, freedom, honesty
Concrete Nouns
A concrete noun names things that can be seen, touched, heard, smelled, or tasted.
- Examples: apple, music, sand, perfume
Collective Nouns
A collective noun names a group of people or things considered as one unit.
- Examples: team, flock, class, family
Countable and Uncountable Nouns
- Countable nouns can be counted individually.
- Examples: apple, chair, car
- Uncountable nouns cannot be counted individually and often refer to mass or abstract concepts.
- Examples: water, sugar, information
Compound Nouns
A compound noun is made up of two or more words that function as a single noun.
- Examples: toothpaste, mother-in-law, swimming pool
Possessive Nouns
A possessive noun shows ownership or relationship.
- Examples: Ali’s book, the dog’s tail, children’s toys
Noun Types Chart (with Examples)
| Type of Noun | Definition | Example(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Common Noun | General name of a thing | city, dog, book |
| Proper Noun | Specific name of a noun | London, Zainab, Friday |
| Abstract Noun | Quality or idea you can’t touch | love, hope, anger |
| Concrete Noun | Things you can see or touch | table, flower, sound |
| Collective Noun | Group considered as one | class, team, herd |
| Countable Noun | Things that can be counted | apple, book, coin |
| Uncountable Noun | Things that cannot be counted | rice, milk, advice |
| Compound Noun | Noun made of multiple words | laptop, swimming pool |
| Possessive Noun | Shows ownership | Sarah’s bag, dog’s bone |
How to Identify the Type of a Noun
Quick Rules for Each Type
- Ask “Is this general or specific?” → Common vs Proper
- Ask “Can I count it?” → Countable vs Uncountable
- Ask “Is it a group?” → Collective
- Ask “Can I see or touch it?” → Concrete vs Abstract
Common Mistakes Learners Make
- Using proper nouns without capitalization
- Confusing abstract and concrete nouns
- Trying to count uncountable nouns (e.g., “informations”)
Practice Examples for Each Noun Type
- Common: A dog barked loudly.
- Proper: Ali visited Paris in summer.
- Abstract: Kindness is important.
- Concrete: She held a red ball.
- Collective: The class is going on a trip.
- Countable: I have three notebooks.
- Uncountable: Please give me some water.
- Compound: I bought a toothbrush.
- Possessive: That is Aisha’s pencil.
Quiz: Test Your Knowledge of Noun Types
- Identify the type of noun: Happiness → Abstract
- Identify the type of noun: Family → Collective
- Identify the type of noun: London → Proper
- Identify the type of noun: Book → Common / Countable
- Identify the type of noun: Laptop → Compound / Concrete
Summary: Mastering All Types of Nouns
Nouns are essential to sentence structure. Knowing how to use different types of nouns—common, proper, abstract, collective, and more—helps you communicate accurately. Keep practicing with examples and identifying how each noun functions in context.
FAQs
The 5 types of nouns are:
1. Common Nouns
2. Proper Nouns
3. Abstract Nouns
4. Concrete Nouns
5. Collective Nouns
Here are 12 types of nouns with simple examples:
1. Common Noun – A general name. Example: dog, city, book.
2. Proper Noun – A specific name. Example: John, Paris, Monday.
3. Abstract Noun – Names of things you can’t touch or see, like feelings. Example: love, happiness, freedom.
4. Concrete Noun – Things you can touch, see, or feel. Example: apple, car, house.
5. Collective Noun – A group of people or things. Example: team, family, flock.
6. Countable Noun – Things you can count. Example: apple, book, dog.
7. Uncountable Noun – Things you can’t count. Example: water, sugar, sand.
8. Possessive Noun – Shows ownership. Example: Tom’s book, the cat’s toy.
9. Singular Noun – Refers to one thing. Example: cat, child, tree.
10. Plural Noun – Refers to more than one thing. Example: cats, children, trees.
11. Compound Noun – Two words combined into one. Example: toothbrush, basketball, mailbox.
12. Material Noun – Names of materials or substances. Example: gold, wood, water.
These nouns help us talk about things, people, ideas, and groups in different ways.
Yes, there are 7 types of nouns:
1. Common Noun
2. Proper Noun
3. Abstract Noun
4. Concrete Noun
5. Collective Noun
6. Countable Noun
7. Uncountable Noun
These types help us describe different things.
Here are 10 common nouns:
1. Dog
2. Cat
3. Book
4. Car
5. School
6. House
7. Teacher
8. Friend
9. City
10. Food
These are general names for things, animals, or people that we encounter every day.
You May Also Like