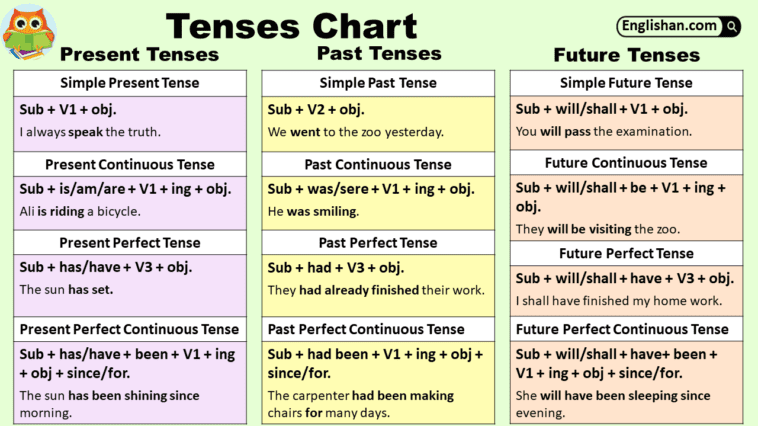
A tenses chart is a visual representation or table that displays the various verb tenses in a language along with their structures, examples, rules, and common usage. It serves as a concise reference guide for learners and users of the language to understand how verbs change to convey different time frames—past, present, and future.
Definition Of Tense From Different Dictionaries
Merriam-Webster: “A category of verbal inflection that serves chiefly to specify the time of the action or state expressed by the verb.”
Oxford English Dictionary (OED):“ Set of forms taken by a verb to indicate the time, and sometimes also the continuance or completeness, of the action about the time of the utterance.”
Cambridge Dictionary:“ Any of the forms of a verb which show the time at which an action happened.”
Dictionary.com: “A set of forms taken by a verb to indicate the time of action or state.”
Lexico (powered by Oxford): “A set of forms taken by a verb to show the time of an action.”
Types Of Tense Chart
There are three main types of tense:
- Present Tense
- Past Tense
- Future Tense
Further, there are four subforms:
- Simple
- Perfect
- Continuous
- Perfect Continuous
Tenses Chart with Examples
Below is a chart summarizing different English tenses along with examples:
| Tenses | Tense Forms |
|---|---|
| Present Tense | 1. Simple Present Tense
2. Present Perfect Tense 3. Present Continuous Tense 4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense |
| Past Tense | 1. Simple Past Tense
2. Past Perfect Tense 3. Past Continuous Tense 4. Past Perfect Continuous Tense |
| Future Tense | 1. Simple Future Tense
2. Future Perfect Tense 3. Future Continuous Tense 4. Future Perfect Continuous Tense |
Tenses Rules Chart with Examples in English
Here’s the chart with different examples:
| Tense | Rules and Formula | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Present Tense | Subject + Verb (base form/third person singular) + Rest of the sentence | She Wears new clothes. |
| Present Continuous Tense | Subject + Helping Verb (am/is/are) + Main verb + -ing + Rest of the sentence | The birds are chirping. |
| Present Perfect Tense | Subject + Helping Verb (have/has) + Past participle + Rest of the sentence | Sarfraz has won the prize. |
| Present Perfect Continuous Tense | Subject + Have/Has + Been + Verb + -ing + Rest of the sentence | I have been reading in this school since 2000. |
| Simple Past Tense | Subject + Verb (ed or past tense) + Rest of the sentence | She boiled the eggs. |
| Past Continuous Tense | Subject + Helping Verb (was/were) + Main verb + -ing + Rest of the sentence | You were performing ablutions. |
| Past Perfect Tense | Subject + Helping Verb (had) + Past participle of the main verb + the rest of the sentence along with the time frame. | He had reached here till 2 o’clock. |
| Past Perfect Continuous Tense | Subject + Had + Been + Verb + -ing + Rest of the sentence | My friend had been looking for services for several months. |
| Simple Future Tense | Subject + Will/Shall + Verb1 + Rest of the sentence | You will pass the examination. |
| Future Continuous Tense | Subject + Will be/Shall be + Verb1 + -ing + Rest of the sentence | Pakistan will be progressing. |
| Future Perfect Tense | Subject + Will have/Shall have + Verb3 + Rest of the sentence | Our teacher will have taught us a lesson. |
| Future Perfect Continuous Tense | Subject + Will have been + Verb1 + -ing + Rest of the sentence | Birds will have been chirping since morning. |
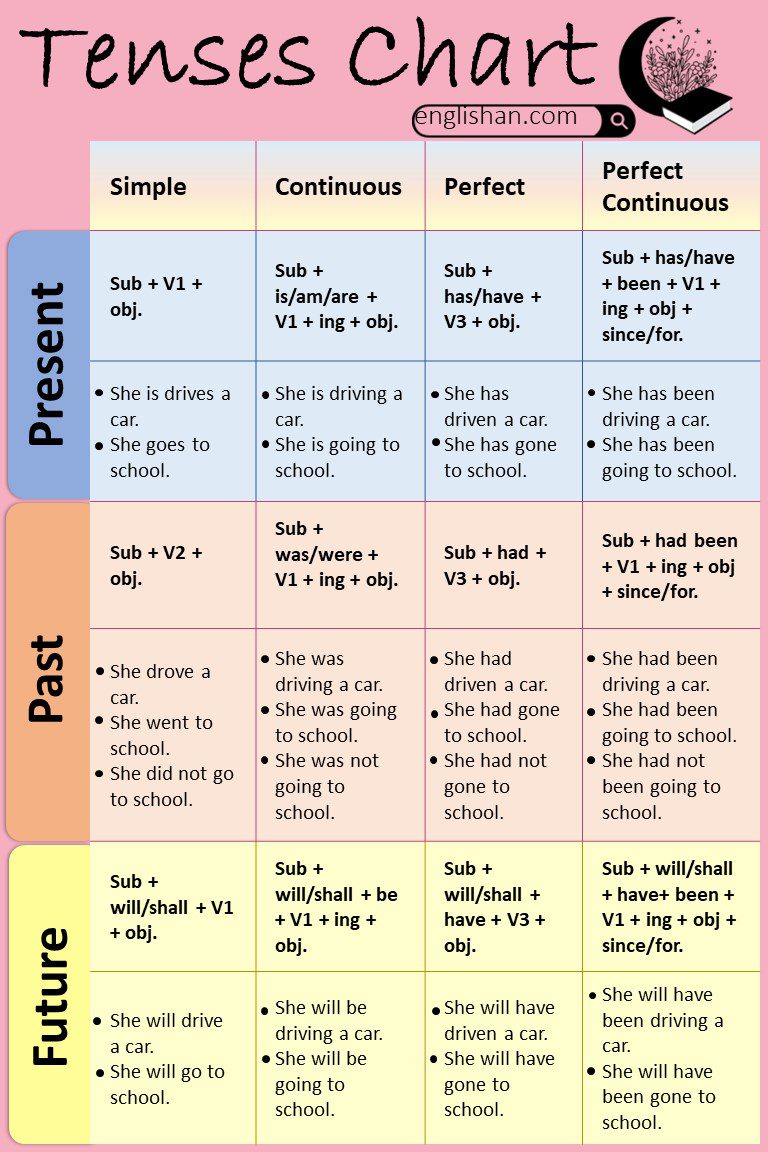
Tenses Chart With Examples, Rules
All Tenses Formulas
- Sub(subject) + v1 + Obj(object).
- Sub +do not/does not + v1 + obj.
- Do/Does + sub + v1 + obj?
2. Present Continuous Tense
- Sub + is/am/are + v1 + ing + obj.
- Sub + is/am/are + not + v1 + ing + obj.
- Is/am/are + Sub + v1 + ing + obj?
3. Present Perfect Tense
- Sub + has/have + v3 + obj.
- Sub + has/have + not v3 + obj.
- Has/ Have + sub + v3 + obj?
4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Sub + (has/have)been + (v1) ing + obj + since/for.
- Sub + has/have + not + been + (v1) ing + obj + since/for.
- Has/have + Sub + been + (v1) ing + obj + since/for.
5. Simple Past Tense
- Sub + v2 + obj.
- Sub + did not + v1 + obj.
- Did + sub + v1 + obj?
6. Past Continuous Tense
- Sub + was/were + (v1) ing + obj.
- Sub + was/ were + not + (v1) ing + obj.
- Was/ were + sub + (v1) ing + obj?
7. Past Perfect Tense
- Sub + had + v3 + obj.
- Sub + had + not + v3 + obj.
- Had + sub + v3 + obj?
8. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- Sub + had been + (v1) ing + obj + since/for.
- Sub + had + not + been + (v1) ing + obj + since/for.
- Had + sub+ been + (v1) ing + obj + since/for?
9. Simple Future Tense
- Sub + will/shall + v1 + obj.
- Sub + will/shall + not + v1 + obj.
- Shall/Will + sub + v1 + obj?
10. Future Continuous Tense
- Sub + will be/shall be + (v1) ing + obj.
- Sub + (will/shall) not + be + (v1) ing + obj.
- Will/shall + sub + be + (v1) ing + obj?
11. Future Perfect Tense
- Sub + will have/shall have + v3 + obj.
- Sub + will/shall + not + have + v3 + obj.
- Will/shall + sub + have + v3 + obj?
12. Future Perfect Continuous Tense
- Sub + will have/shall have been + (v1) ing + obj + since/for.
- Sub + will/shall + not + have + been + (v1) ing + obj + since/for.
- Will/shall + sub + have + been + (v1) ing + obj + since/for?
Tenses Example Sentences Chart
Present Simple Tense:
- I play tennis every Saturday.
- Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.
- The sun rises in the east.
- Plants need sunlight to grow.
- I wake up at 6:00 AM.
Past Simple Tense:
- I finished my homework yesterday.
- They visited Paris last summer.
- She woke up, had breakfast, and went to work.
- We used to play hide and seek as children.
- Once upon a time, there was a brave knight.
Present Continuous Tense:
- I am studying for my exams.
- They are playing basketball in the park.
- She is working on a project this week.
- The weather is getting colder.
- She is always interrupting me.
Past Continuous Tense:
- I was studying when the phone rang.
- He was cooking dinner when the doorbell rang.
- While I was working, he was watching TV.
- It was raining, and people were running for cover.
- The sun was setting as they reached the summit.
Future Simple Tense:
- I think it will rain tomorrow.
- The phone is ringing; I’ll answer it.
- The concert will start at 8:00 PM.
- I will help you with your homework.
- Our flight will depart in two hours.
Present Perfect Tense:
- I have visited London before.
- She has never eaten sushi.
- We have lived in this city for five years.
- They have just finished their project.
- He has already seen that movie.
Past Perfect Tense:
- I had already eaten when they arrived.
- She realized she had forgotten her keys at home.
- By the time I got there, they had already left.
- He had read the book before watching the movie.
- They had known each other for years before they got married.
Future Continuous Tense:
- This time next week, I will be relaxing on the beach.
- At 8:00 PM tomorrow, we will be attending the concert.
- She will be cooking dinner when you arrive.
- They will be studying for their exams all night.
- By this time next year, I will be working in a new job.
Future Perfect Tense:
- By the end of the month, I will have finished the book.
- She will have completed her degree by the time she turns 25.
- In two years, they will have been married for a decade.
- By next week, he will have traveled to five different countries.
- By the time you read this, I will have already left for the airport.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense:
- I have been studying for hours.
- She has been working on the project all day.
- They have been living in this city since last year.
- We have been waiting for the bus for 30 minutes.
- He has been practicing the guitar for weeks.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense:
- I had been reading for hours when she called.
- They had been working on the report before the deadline.
- By the time I arrived, they had been waiting for ages.
- She realized she had been driving in the wrong direction.
- Before the event, they had been rehearsing for days.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense:
- By 5:00 PM, I will have been working for eight hours.
- They will have been traveling for a week by the time they return.
- By the end of the year, she will have been living here for a decade.
- He will have been studying English for two years next month.
- By the time you arrive, I will have been waiting for an hour.
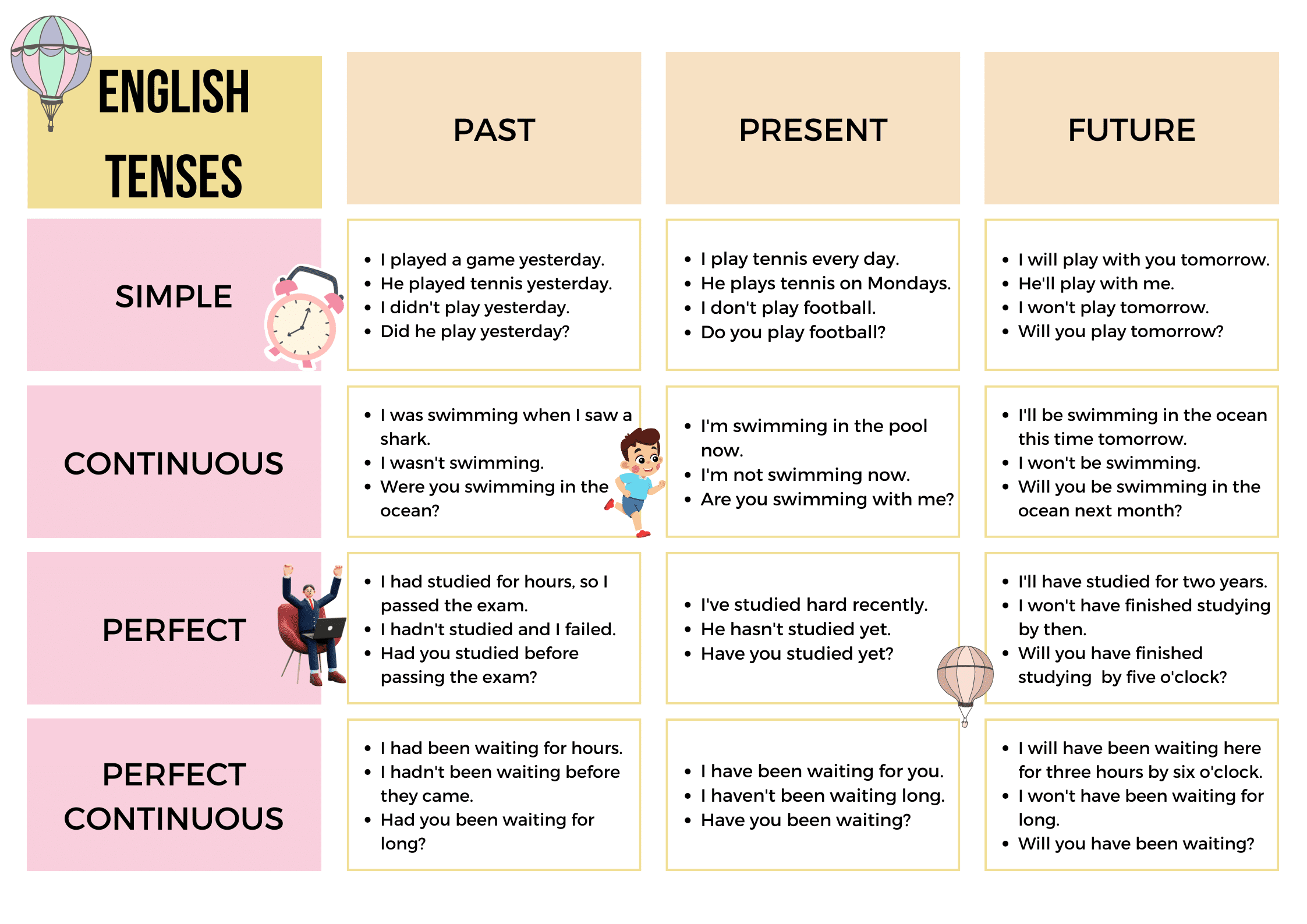
Tenses Quiz:
- She ___ (finish) her work when I called.
- By the time you arrive, I ___ (read) the book.
- I ___ (visit) my grandparents every summer.
- They ___ (be) friends since kindergarten.
- Next week, we ___ (go) on a vacation.
- The sun ___ (set) by the time they reach the beach.
- He ___ (work) on this project for three hours.
- We ___ (wait) for the bus when it started raining.
- I ___ (never/eat) sushi before last night.
- By this time next year, they ___ (graduate) from college.
- Yesterday, she ___ (buy) a new car.
- They ___ (travel) to Paris twice already.
- She ___ (study) for the exam all day.
- We ___ (live) in this city for ten years.
- When I was a child, I ___ (love) to play in the park.
- The concert ___ (start) by the time we get there.
- I ___ (have) lunch when you called me.
- They ___ (play) tennis every Sunday.
- She ___ (complete) her assignment by tomorrow.
- We ___ (not/see) that movie yet.
Answers:
- had finished
- will have read
- used to visit
- have been
- will go
- will have set
- has been working
- were waiting
- had never eaten
- will have graduated
- bought
- have traveled
- has been studying
- have lived
- loved
- will start
- had
- play
- will have completed
- have not seen
FAQS:
Q1: What are verb tenses?
Verb tenses indicate the time of an action or state of being. There are three primary tenses: past, present, and future.
Q2: How many tenses are there in English?
There are three main tenses: past, present, and future. Each of these can be further divided into simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous forms.
Q3: What is the difference between simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous tenses?
Simple tenses express a straightforward action or state. Continuous tenses emphasize the duration of an action. Perfect tenses show completion and perfect continuous tenses highlight the duration leading up to a point in time.
Q4: When do I use the past simple tense?
Past simple is used for completed actions or states in the past.
Q5: What is the past continuous tense used for?
Past continuous is used for actions that were ongoing at a specific point in the past.
Q6: How do I form the past perfect tense?
The past perfect is formed with “had” + the past participle of the main verb and is used to show that one action in the past happened before another.
Q7: When do I use the present simple tense?
Present simple is used for general truths, habits, and scheduled events.
Q8: What is the present continuous tense used for?
Present continuous is used for actions happening at the present moment.
You May Also Like:
- Present Indefinite Tense Worksheets and Exercises
- Present Continuous Tense Worksheets
- Present Perfect Tense Worksheets
- Present Perfect Continuous Worksheets
- Past Continuous Tense Worksheets
- Worksheet Tenses: Use of Tenses in Sentences
- Choose the Correct Direct Narration | Exercise with Solution