Contents
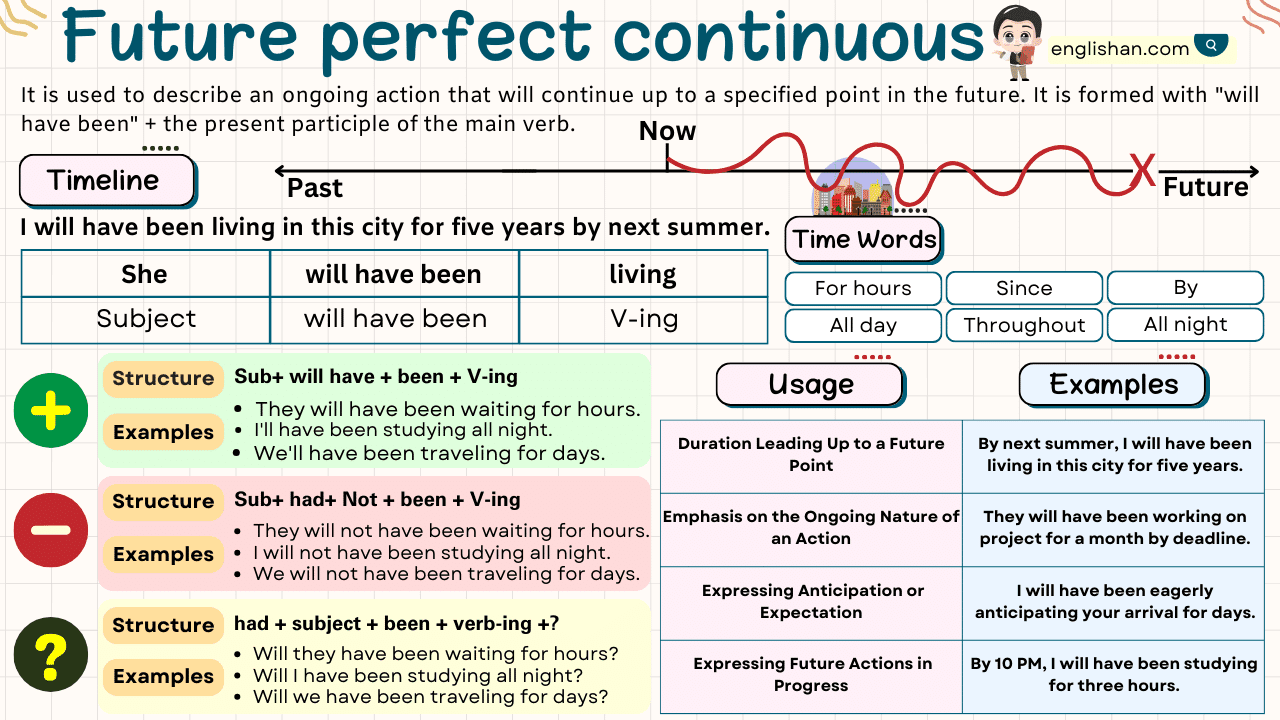
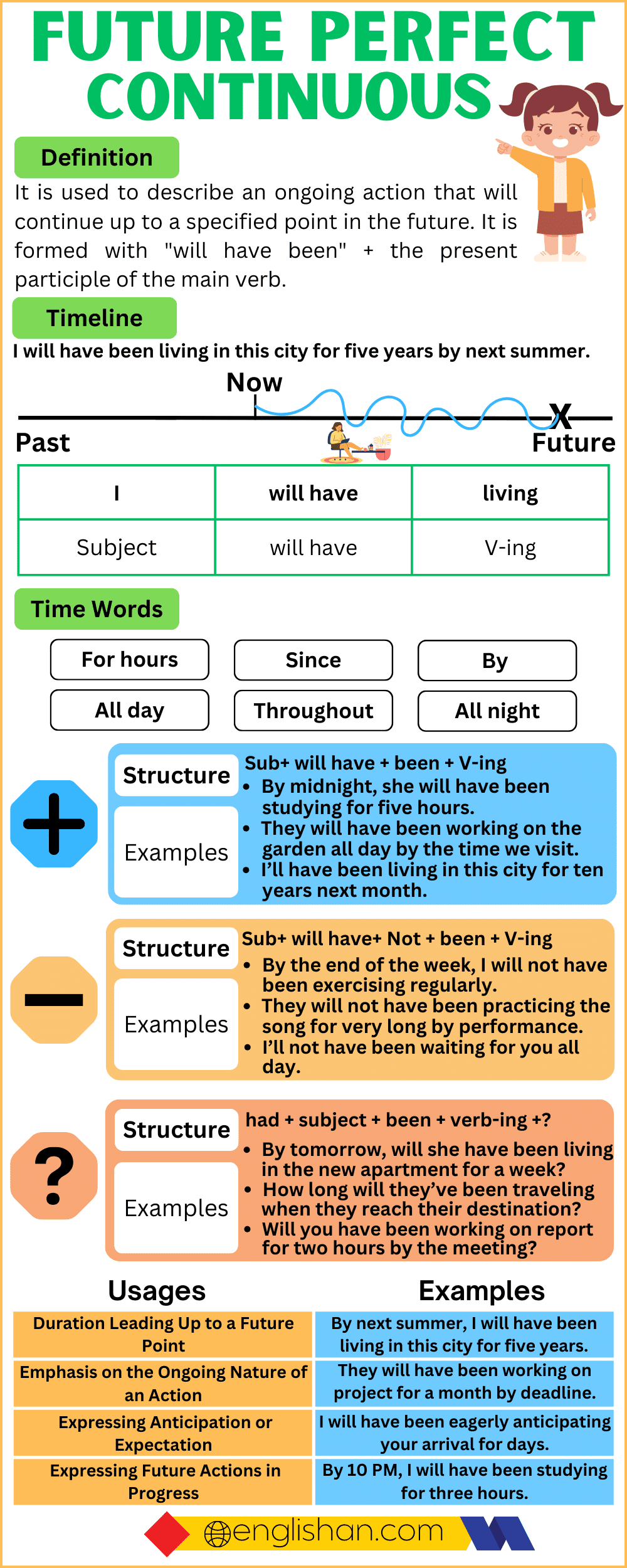
The future perfect continuous tense is used to talk about actions that will continue until a specific point in the future. It focuses on how long an action will have been happening by a certain time. Learning this tense can help you explain ongoing events that will continue in the future.
Structure of the Future Perfect Continuous Tense
To use the future perfect continuous tense, it’s important to know how to form affirmative, negative, interrogative, and double interrogative sentences. Here is how you can create sentences using this tense:
Affirmative Structure
Subject + will have been + verb-ing + object
Examples:
- Ahmed will have been working on his project for three hours.
Ahmed will still be working on his project until the given time.
- The children will have been playing in the garden all afternoon.
The children will keep playing until a certain time in the future.
Negative Structure
Subject + will not have been + verb-ing + object
Examples:
- Aisha will not have been attending the seminar by that time.
Aisha will not be at the seminar when the time comes.
- My parents will not have been traveling by bus for long.
The travel will not have lasted very long by that point.
Interrogative Structure
Will + subject + have been + verb-ing + object
Examples:
- Will Sara have been studying for her exams for two hours?
Asking if Sara will have already been studying for two hours.
- Will the workers have been fixing the road all day?
Asking if the workers will have been fixing the road for the whole day.
Double Interrogative Structure
Wh-word + will + subject + have been + verb-ing + object
Examples:
- Why will he have been driving for ten hours straight?
Asking why he will be driving for ten hours without stopping.
- Where will they have been staying during the trip?
Asking where they will be staying during their trip.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense Chart
Subject-Verb Agreement
Subject and verb agreement is important for making correct sentences. The following table shows how subjects match with the helping verbs.
| Subject | Helping Verb | Verb-ing Form Example |
| He | will have been | studying |
| They | will have been | working |
| The teachers | will have been | explaining |
| A father | will have been | supporting |
| Dogs | will have been | barking |
Time Expressions
In the future perfect continuous tense, certain time words and phrases are used to show how long an action will continue.
- For two hours: The cat will have been sleeping for two hours.
- By next year: By next year, they will have been running this business for five years.
- Since morning: He will have been waiting since morning.
- Until midnight: We will have been studying until midnight.
Adverb Placement
Correct adverb placement is important in the future perfect continuous tense. Adverbs usually go between the helping verb “will” and “have been” or after the “verb-ing” form.
- Always: She will always have been helping the poor by that time.
- Probably: They will probably have been working on the new software by then.
- Never: I will never have been spending so much time on a task.
Uses of the Future Perfect Continuous Tense
The future perfect continuous tense is used:
To show an action that will be ongoing for a period of time in the future.
- By December, Bilal will have been teaching at the school for ten years.
To show expected actions and their length at a specific time in the future.
- At 8 PM, she will have been practicing her presentation for two hours.
To make predictions about actions involving time.
- By then, it will have been raining for five hours continuously.
Short Answers
The future perfect continuous tense can also be used to give short answers to questions.
Examples:
- Will you have been cooking for long?
- Yes, I will have.
- No, I won’t have.
- Will she have been waiting there?
- Yes, she will have.
- No, she won’t have.
Question Tags
To make question tags with this tense, we add a short question after the statement to check information.
Examples:
- You will have been working late, won’t you?
- She will not have been eating junk food, will she?
Examples of the Tense in Use
Affirmative:
- I will have been writing for three hours by then.
- The students will have been preparing for exams for a month.
- He will have been jogging for five kilometers.
- Maryam will have been cooking since noon.
- The kids will have been playing outside for hours.
Negative:
- He will not have been exercising long enough.
- They will not have been traveling for a year by then.
- She will not have been teaching at that school.
- We will not have been using the same computer for five years.
- Ahmed will not have been working late.
Interrogative:
- Will they have been watching the movie all night?
- Will you have been studying for your degree?
- Will Sarah have been practicing for the competition?
- Will the players have been training in the morning?
- Will Hina have been reading the novel for a week?
Common Mistakes with the Future Perfect Continuous Tense
- Incorrect: He will have be running for an hour. ❌
- Correct: He will have been running for an hour. ✅
- Incorrect: They will has been working all day. ❌
- Correct: They will have been working all day. ✅
- Incorrect: She will been writing a book. ❌
- Correct: She will have been writing a book. ✅
FAQs
The future perfect continuous tense is used to describe an action that will keep going until a certain point in the future, focusing on how long it will have lasted.
Use “will have been” followed by the “verb-ing” form. For example: She will have been working on her project.
Common time expressions include “for two hours,” “by next year,” “since morning,” and “until midnight.”
Avoid mistakes by remembering to use “will have been” before the verb-ing form and making sure the subject and verb agree.
Yes, the future perfect continuous tense can be used in negative forms (e.g., She will not have been working.) and question forms (e.g., Will they have been working?).
The future perfect continuous tense is rarely used in the passive voice because it focuses on the duration of an action. Instead, the active voice is generally preferred for this tense.Yes, the future perfect continuous tense can be used in negative forms (e.g., She will not have been working.) and question forms (e.g., Will they have been working?).
Free Grammar and Vocabulary Worksheets Resources
- Worksheet Tenses
- Since and For Worksheets
- English Worksheets
- Action Verbs Worksheets
- Future Perfect Continuous Worksheets
You May Also Like