Contents
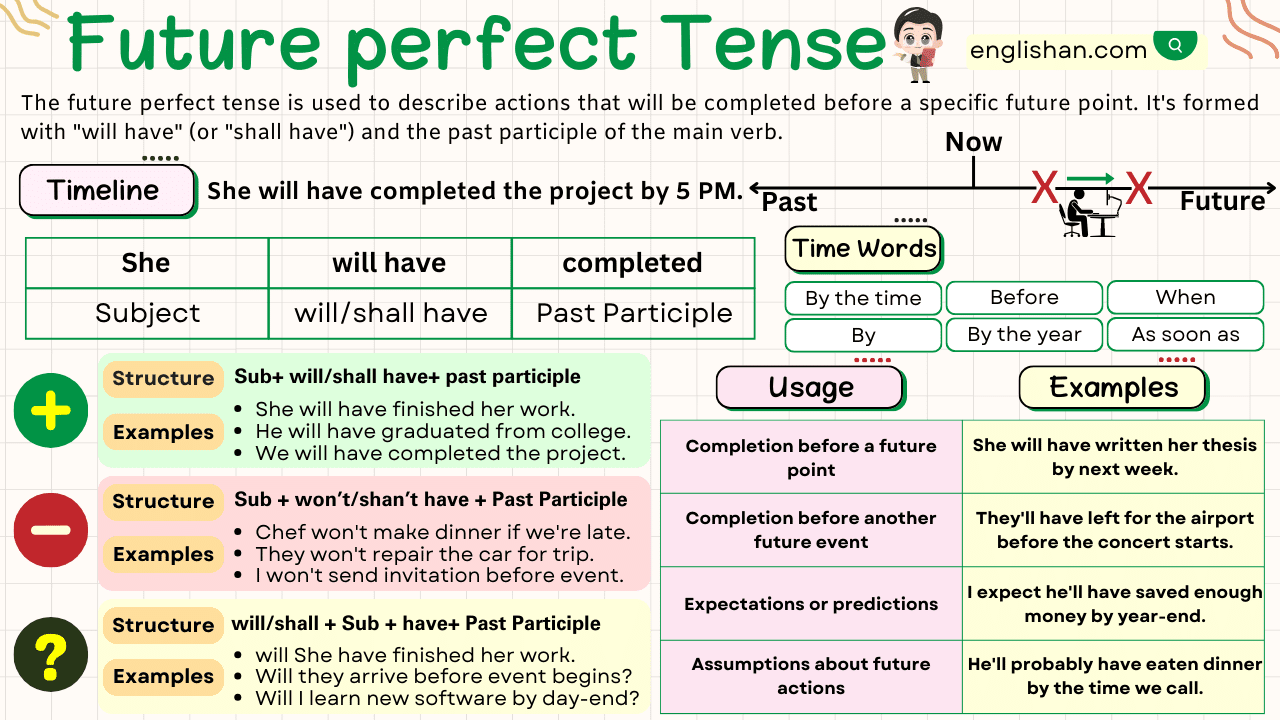
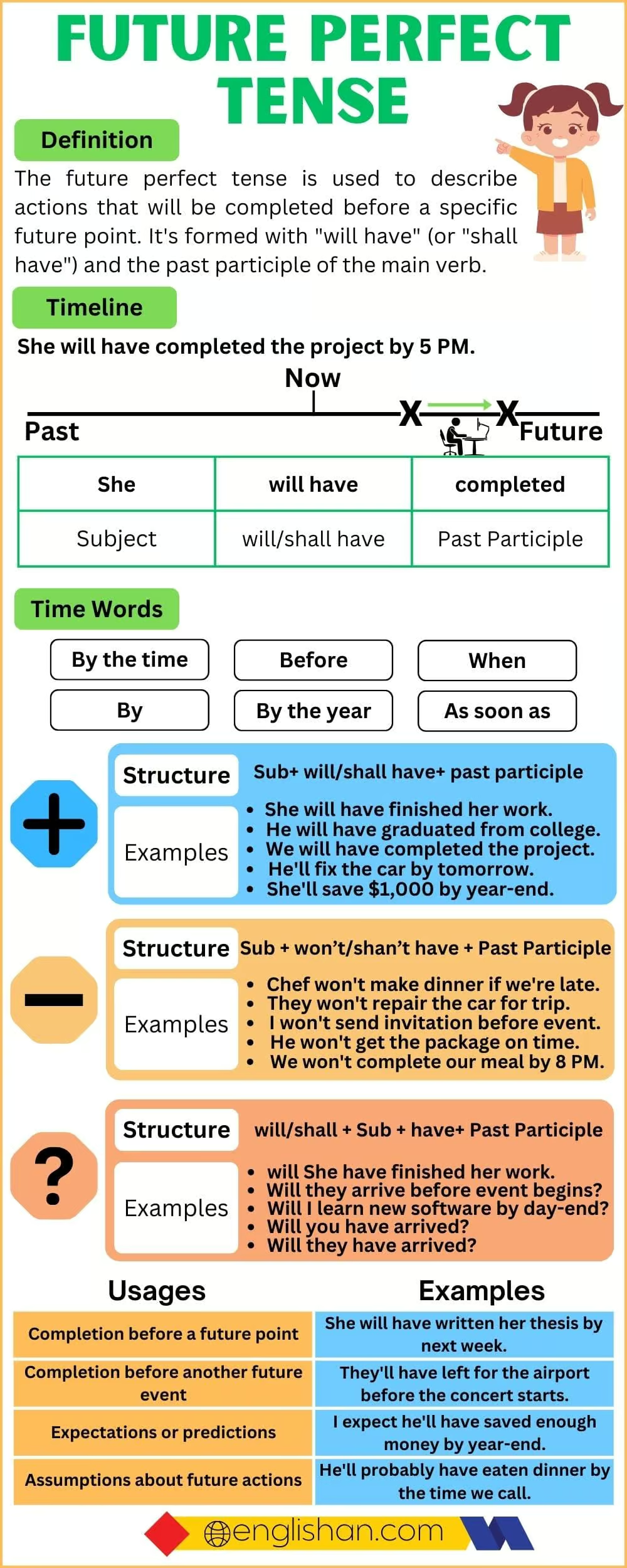
The Future Perfect Tense is used to talk about actions that will be completed before a specific time in the future. It is formed using the auxiliary verbs will have followed by the past participle of the main verb. This tense emphasizes the completion of an action before a particular time or event in the future.
For example:
- By next week, I will have finished the project.
In this sentence, the action of finishing the project will be completed before a future time (next week).
Structures of the Tense
Affirmative Sentence Structure
Structure:
Subject + will have + past participle
Examples:
- She will have completed her degree by next year.
- By 10 p.m., they will have arrived at the airport.
Negative Sentence Structure
Structure:
Subject + will not have + past participle
Examples:
- He will not have finished the book by tomorrow.
- They won’t have left by the time we arrive.
Interrogative Sentence Structure
Structure:
Will + subject + have + past participle?
Examples:
- Will you have completed the report by next week?
- Will she have arrived before the meeting starts?
Double Interrogative Sentence Structure
Structure:
Wh-word + will + subject + have + past participle?
Examples:
- What will you have achieved by the end of this year?
- How long will they have studied English by the time they graduate?
Subject-Verb Agreement
In the Future Perfect Tense, the auxiliary verbs will have are used for all subjects (singular and plural). The past participle of the verb remains the same regardless of the subject.
Examples:
- I will have traveled to five countries by the end of the year.
- They will have learned Spanish by next summer.
Time Expressions
Time expressions are crucial in the Future Perfect Tense because they indicate when the action will be completed. Here are some common time expressions:
| Time Expression | Example Sentence |
| By tomorrow | I will have finished the assignment by tomorrow. |
| By next week | She will have graduated by next week. |
| By the end of the day | We will have cleaned the house by the end of the day. |
| In a few hours | They will have arrived in a few hours. |
| Before | He will have left before you get home. |
Adverb Placement in Future Perfect Tense
Adverbs such as already, just, and never are usually placed between will and have.
Examples:
- She will already have finished the task when you arrive.
- They will never have completed the project by the deadline.
Uses of the Future Perfect Tense
- To express actions that will be completed before a specific time in the future:
- By 2025, we will have built 50 new schools.
- To show the result of an action by a certain time in the future:
- I will have saved enough money by the end of this year to buy a car.
- To describe expectations or assumptions about something in the future:
- She will have finished her homework by now.
- To indicate an action completed before another future event:
- They will have eaten dinner before we arrive.
Examples of the Future Perfect Tense in Use
Here are 10 examples showing how the Future Perfect Tense is used in different contexts:
- By 8 p.m., they will have finished watching the movie.
- We will have painted the house by next weekend.
- She will have studied English for five years by the time she moves abroad.
- You will have left by the time I get home.
- I will have worked here for ten years by next month.
- He will have driven 500 miles by the time the sun sets.
- They will have moved to their new house by next Monday.
- The team will have practiced hard by the time the competition starts.
- By this time tomorrow, we will have arrived at our destination.
- She will have written her first novel by the end of the year.
Common Mistakes with the Future Perfect Tense
When learning the Future Perfect Tense, students often make some common mistakes. Let’s highlight these errors and provide the correct usage.
- Using the wrong tense for future events:
- ❌ By next week, I will finished the course.
- ✅ By next week, I will have finished the course.
- Confusing the Future Perfect with other future tenses:
- ❌ They will be finished the work by tomorrow.
- ✅ They will have finished the work by tomorrow.
- Forgetting the auxiliary verb “have”:
- ❌ We will finished by noon.
- ✅ We will have finished by noon.
- Incorrect placement of adverbs:
- ❌ They will have never completed the project by the deadline.
- ✅ They will never have completed the project by the deadline.
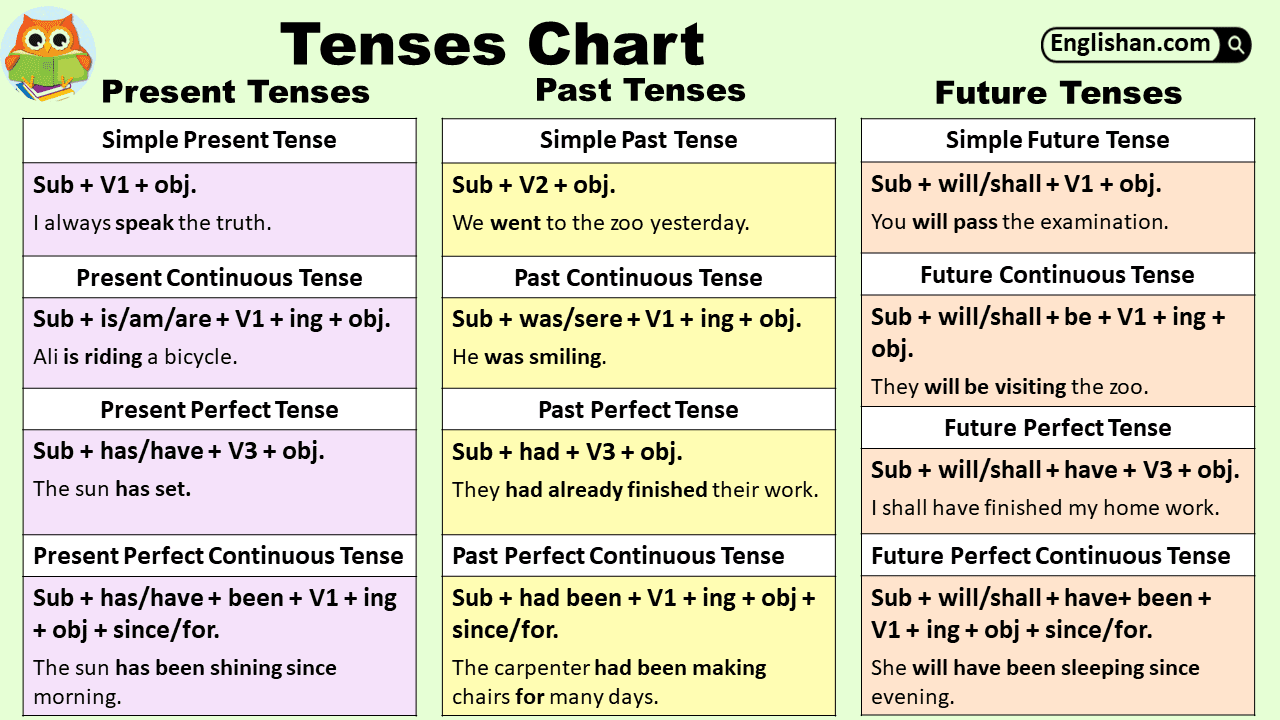
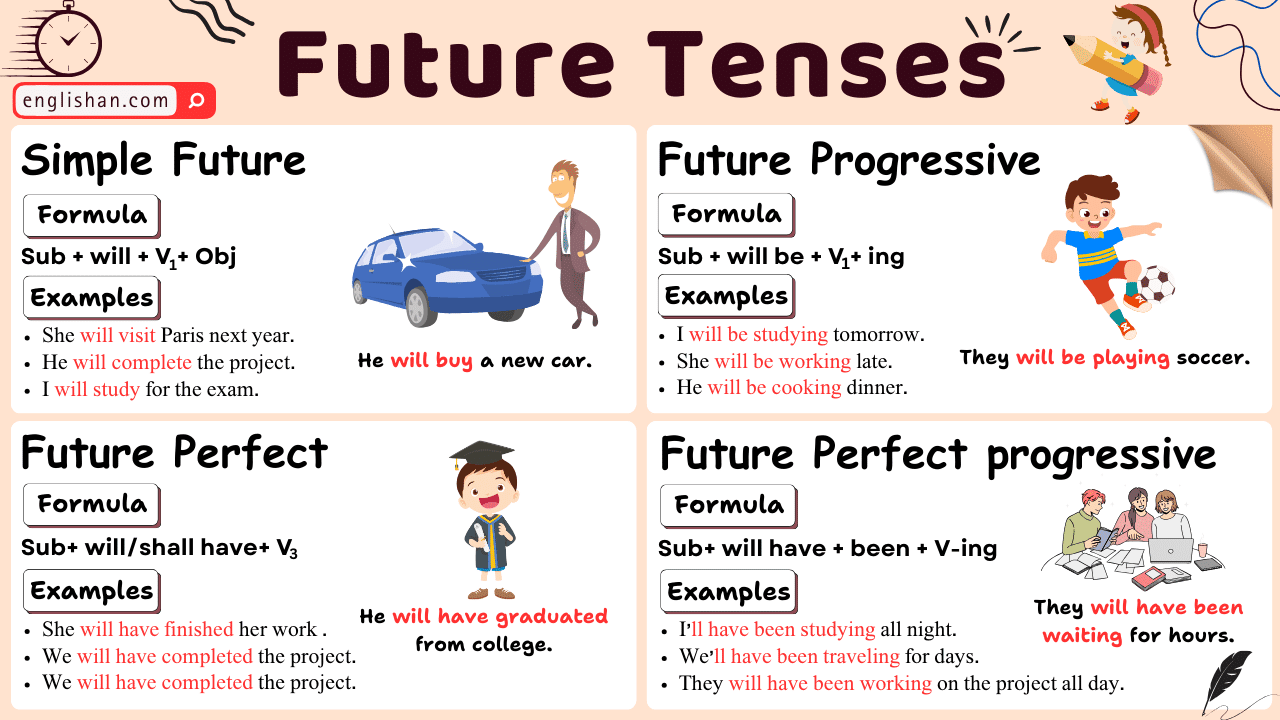
Future Perfect Tense Chart
FAQs:
The future perfect tense is used to describe an action that will be completed at a specific time in the future. It shows that something will be finished before another action or event happens.
The structure is: will have + past participle
Here are 12 simple examples of future perfect continuous tense:
1. By next month, I will have been studying for two years.
2. She will have been working here for five years by December.
3. They will have been traveling for a week when they reach Paris.
4. We will have been waiting for an hour when the bus comes.
5. He will have been running for an hour by 5 PM.
6. I will have been cooking for two hours when you arrive.
7. By next week, I will have been reading this book for a month.
8. She will have been practicing for weeks before the competition.
9. We will have been working on the project for three days by tomorrow.
10. They will have been playing football for hours when it gets dark.
11. I will have been living here for ten years by 2025.
12. By next summer, he will have been studying for five years.
This tense shows an action that will be happening for some time before a future point.
The future perfect tense is used to talk about actions that will be completed before a certain time in the future.
The rule for forming the future perfect tense:
will + have + past participle of the verb
Example:
1. I will have finished my homework by 8 PM.
2. She will have left by the time you arrive.
Steps:
1. Use “will” for future.
2. Add “have” after “will”.
3. Use the past participle of the main verb (e.g., ‘finished,’ ‘left,’ ‘eaten’).
This tense shows that something will be completed in the future before another event happens.
To teach the future perfect tense:
Explain the Use: It talks about something that will be finished by a certain time in the future.
1. Show the Structure: will + have + past participle
Example: I will have finished my homework by 6 PM.
2. Use a Timeline: Show that the action happens before a future time.
3. Practice: Give examples for students to complete, like:
By 5 PM, I will have eaten lunch.
4. Ask Real-Life Questions:
What will you have done by tomorrow?
This makes the tense easy to understand and practice!
Free Grammar and Vocabulary Worksheets Resources
- Worksheet Tenses
- English Worksheets
- Action Verbs Worksheets
- Future Perfect Tense Worksheets
- Future Perfect Continuous Worksheets
Read More