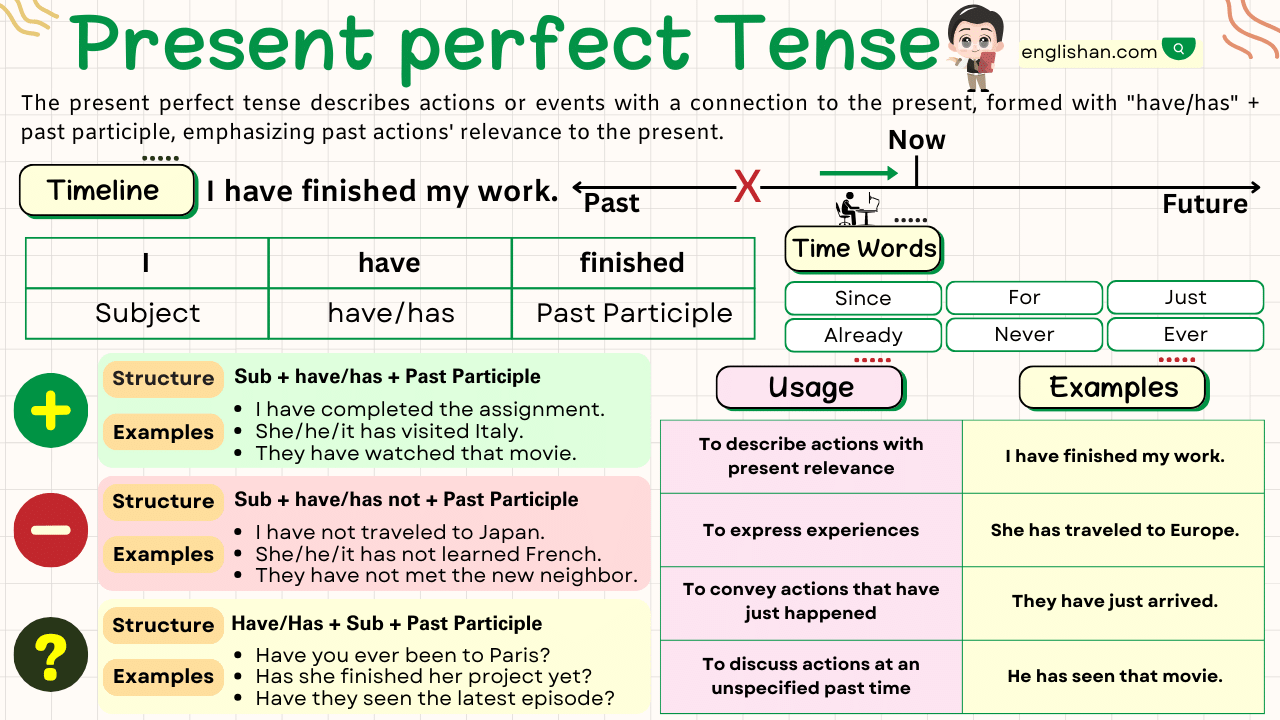
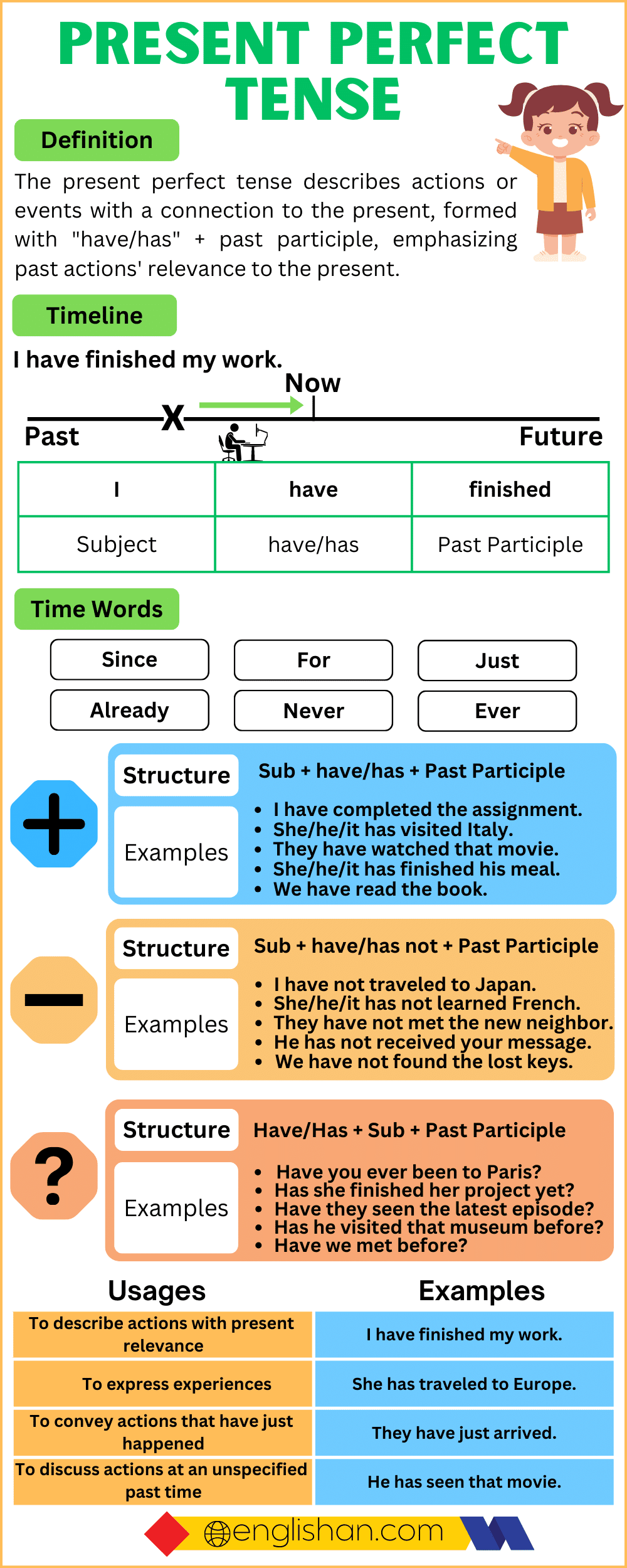
The present perfect tense describes actions or events with a connection to the present, even if they happened in the past. It’s formed with have or has + past participle.
Examples:
- She has visited Paris.
- They have finished their project.
- He has never tasted sushi before.
- She hasn’t seen the movie yet.
- They haven’t been to the new restaurant.
- He hasn’t received the email.
- Have you ever been to London?
- Has she completed the assignment?
- Have they seen this movie before?
Usages of the Present Perfect Tense
Actions that happened at an unspecified time in the past
“Actions that happened at an unspecified time in the past” refer to events that occurred before now, but the exact timing isn’t specified or isn’t important. This is often conveyed using the present perfect tense.
Examples:
- She has visited Paris.
- They have studied Spanish.
- He has eaten sushi before.
- he hasn’t visited Paris.
- They haven’t studied Spanish.
- He hasn’t eaten sushi before.
- Has she ever visited Paris?
- Have they ever studied Spanish?
- Has he ever eaten sushi before?
Actions that have a connection to the present moment
“Actions that have a connection to the present moment” refer to events or activities that occurred at some point before the present time and are relevant or significant in the current context. These actions may have an impact on the present situation, or they may be recent events that continue to influence the current situation. This connection to the present moment is often expressed using the present perfect tense in English.
Examples:
- She has just finished her work.
- They have already seen the movie.
- He has recently moved to a new city.
- She hasn’t started her assignment yet.
- They haven’t visited the new museum exhibit.
- He hasn’t met his new neighbors yet.
- Has she finished her work yet?
- Have they seen the movie already?
- Has he met his new neighbors?
Past actions with present relevance
“Past actions with present relevance” refer to actions or events that occurred in the past but still have some significance or impact on the present moment. These actions are relevant or important in the context of the current situation or discussion.
Examples:
- She has written a report that we can use.
- They have completed the project on time.
- He has learned a valuable skill for his job.
- She hasn’t sent the email with the important information yet.
- They haven’t received the feedback from the client.
- He hasn’t applied the new technique correctly.
- Has he applied the new technique correctly?
- Has the company implemented the new policy?
- Have I shared the updated guidelines?
Emphasizing the result or completion of an action
“Emphasizing the result or completion of an action” means highlighting the successful or finished aspect of an activity. It focuses on the outcome, not the process. This is often expressed using language that emphasizes achievement or completeness.
Examples:
- She has successfully completed the project.
- They have beautifully decorated the room.
- He has perfectly cooked the dinner.
- She hasn’t finished reading the book yet.
- They haven’t resolved the issue.
- I haven’t fixed the broken laptop.
- Has she finished reading the book?
- Have they resolved the issue yet?
- Have I fixed the broken laptop?
Present Perfect Tense Chart
Signal Words
Signal words in the present perfect tense are words or phrases that indicate the use of this specific tense. They often suggest a connection between the past and the present. Like Already, Just, Ever, Never, Not yet, So far, Have… ever, Have… yet, How long, etc.
Examples:
- She has already finished her homework.
- They have just arrived at the party.
- Have you ever visited London?
- I have recently bought a new car.
- He has never traveled abroad.
- They have not yet received the package.
- We have not encountered any problems so far.
- They have not yet finished reading the book.
- He hasn’t seen that movie yet.
- Have they ever met the CEO?
- Have you finished the report yet?
- How long have they been living in this city?
- Has the company announced the winner?
- Have they seen the latest episode of the show?
Time Expressions
Time expressions play a crucial role in providing context to actions or events described in the present perfect tense. They help indicate when the action took place or for how long it has been occurring.
Examples:
- I have just finished my work. (A very recent action)
- She has already eaten breakfast. (The action has happened earlier than expected)
- Have you finished your homework yet? (Asking about completion up to now)
- Have you ever been to Paris? (In your entire life)
- I have never tasted sushi before. (At any time in the past)
- They have lived here for five years. (Indicates duration up to now)
- She has been working here since 2010. (Specifies the starting point of an action)
- He has recently moved to a new city. (Not long ago)
- They have been studying a lot lately. (Recently, in the recent period)
- We have seen a lot of changes in the company in the past few years. (Recent years leading up to now)
Forming the Present Perfect Tense
Affirmative Sentences
Affirmative sentences in present perfect tense describe actions that happened at an unspecified time in the past with a connection to the present. They use have (for plural subjects and I ) or has (for singular subjects like he, she, it ) followed by the past participle form of the main verb.
Subject + has/have + verb(3rd form) + object.
Examples:
- She has eaten breakfast.
- They have visited the museum.
- He has watched the movie.
- The cat has slept all day.
- I have read a book.
- We have cooked dinner.
- She has cleaned her room.
- He has finished his homework.
- They have played soccer.
- The sun has set.
- I have taken a shower.
- They have painted the walls.
- She has written a letter.
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
| Subject | has/have | Verb (3rd Form) | Object |
|---|---|---|---|
| She | has | eaten | breakfast |
| They | have | visited | the museum |
| He | has | watched | the movie |
| The cat | has | slept | all day |
| I | have | read | a book |
| We | have | cooked | dinner |
| She | has | cleaned | her room |
| He | has | finished | his homework |
| They | have | played | soccer |
| The sun | has | set | (none) |
| I | have | taken | a shower |
| They | have | painted | the walls |
| She | has | written | a letter |
| He | has | fixed | the car |
| The dog | has | chased | its tail |
| I | have | learned | a new word |
| They | have | bought | a new car |
| She | has | danced | in the rain |
| We | have | planted | flowers |
| He | has | sung | a song |
Negative Sentences
Negative sentences in the present perfect tense indicate that actions or events have not happened up to the present moment. They use haven’t (for plural subjects and I) or hasn’t (for singular subjects like he, she, it ) followed by the past participle form of the main verb.
Subject + has/have + not + verb (3rd form) + object.
Examples:
- She hasn’t eaten breakfast.
- They haven’t visited the museum.
- He hasn’t watched the movie.
- The cat hasn’t slept all day.
- I haven’t read a book.
- We haven’t cooked dinner.
- She hasn’t cleaned her room.
- He hasn’t finished his homework.
- They haven’t played soccer.
- The sun hasn’t set.
- I haven’t taken a shower.
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
| Subject | has/have + not | Verb (3rd Form) | Object |
|---|---|---|---|
| She | hasn’t | eaten | breakfast |
| They | haven’t | visited | the museum |
| He | hasn’t | watched | the movie |
| The cat | hasn’t | slept | all day |
| I | haven’t | read | a book |
| We | haven’t | cooked | dinner |
| She | hasn’t | cleaned | her room |
| He | hasn’t | finished | his homework |
| They | haven’t | played | soccer |
| The sun | hasn’t | set | (none) |
| I | haven’t | taken | a shower |
| They | haven’t | painted | the walls |
| She | hasn’t | written | a letter |
| He | hasn’t | fixed | the car |
| The dog | hasn’t | chased | its tail |
| I | haven’t | learned | a new word |
| They | haven’t | bought | a new car |
| She | hasn’t | danced | in the rain |
| We | haven’t | planted | flowers |
| He | hasn’t | sung | a song |
Interrogative Sentences
Interrogative sentences in the present perfect tense ask questions about actions that have a connection to the present moment. They start with Have (for plural subjects and b) or Has (for singular subjects like he, she, it ), followed by the subject, and then the past participle form of the main verb.
Has/have + subject + verb (3rd form) + object?
Examples:
- Has she eaten breakfast?
- Have they visited the museum?
- Has he watched the movie?
- Has the cat slept all day?
- Have I read a book?
- Have we cooked dinner?
- Has she cleaned her room?
- Has he finished his homework?
- Have they played soccer?
- Has the sun set?
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
| Has/Have | Subject | Verb (3rd Form) | Object? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Has | She | eaten | breakfast? |
| Have | They | visited | the museum? |
| Has | He | watched | the movie? |
| Has | The cat | slept | all day? |
| Have | I | read | a book? |
| Have | We | cooked | dinner? |
| Has | She | cleaned | her room? |
| Has | He | finished | his homework? |
| Have | They | played | soccer? |
| Has | The sun | set | -? |
| Have | I | taken | a shower? |
| Have | They | painted | the walls? |
| Has | She | written | a letter? |
| Has | He | fixed | the car? |
| Has | The dog | chased | its tail? |
| Have | I | learned | a new word? |
| Have | They | bought | a new car? |
| Has | She | danced | in the rain? |
| Have | We | planted | flowers? |
| Has | He | sung | a song? |
Contrast with Simple Past Tense
- When to use simple past
- When to use present perfect
Here’s a more clear and concise table contrasting the Simple Past Tense with the Present Perfect Tense:
| Aspect | Simple Past Tense | Present Perfect Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Time of Action | Specific point in the past. | Unspecified time in the past, with a connection to the present. |
| Emphasis | When the action happened. | Result or completion of the action, relevance to the present. |
| Examples | She visited Paris last summer. | She has visited Paris. (Emphasizing the visit, not when.) |
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when using the present perfect tense:
1. Mixing up ‘have’ and ‘has’:
Use have with pronouns like I, you, we, and they. Use has with he, she, and it.
Example: Incorrect – “He have finished the task.” Correct – “He has finished the task.”
2. Forgetting the past participle form:
Use the past participle form of the verb after have or has.
Example: Incorrect – “She has went to the store.” Correct – “She has gone to the store.”
3. Using the present perfect for specific times:
Avoid using the present perfect when you want to specify a particular time in the past.
Example: Incorrect – “They have visited the museum yesterday.” Correct – “They visited the museum yesterday.”
4. Using present perfect with time expressions that require past tense:
Some time expressions like yesterday, last week, and in 2005 require past tense, not present perfect.
Example: Incorrect – “I have seen that movie last night.” Correct – “I saw that movie last night.”
5. Confusing present perfect with past continuous:
Be clear about whether you want to emphasize the result (present perfect) or the ongoing action (past continuous).
Example: Incorrect – “She has been cooking when I arrived.” Correct – “She had been cooking when I arrived.” (past continuous)
Present Perfect Tense Example Sentences
Affirmative Sentences:
- We have bought fruit.
- It has ceased raining.
- The bell has rung.
- The sun has set.
- The child has slept.
- The clock has struck four.
- Sana has won the prize.
- The students have taken the examination.
- Our army has defeated the enemy.
- We have revised our lesson.
- The bird has flown away.
- I have seen that movie.
- They have completed the puzzle.
- She has visited her grandparents.
- He has called his friend.
- We have played a board game.
- The cake has been baked.
- I have ridden a bike.
- They have taken a photo.
- She has finished her painting.
Negative Sentences:
- He has not cheated you.
- The sun has not set.
- The train has not steamed off.
- We have not taken tea.
- The hen has not laid an egg.
- You have not kept your promise.
- It hasn’t rained today.
- He hasn’t met his new neighbor.
- We haven’t had lunch yet.
- She hasn’t opened the package.
- They haven’t found their keys.
- I haven’t visited Paris.
- They haven’t finished their work yet.
- She hasn’t seen that movie.
- We haven’t traveled to Europe.
- He hasn’t met his new neighbors.
- The hen hasn’t laid an egg.
- They haven’t studied Spanish.
- She hasn’t learned to play the guitar.
- He hasn’t read that book.
Interrogative Sentences:
- Why have you not waited for me?
- Why have you come so late?
- Where have you come from?
- Have you received the parcel?
- Have you locked your bicycle?
- Have you ever traveled to Asia?
- Has she finished reading the novel?
- Have they visited the new art gallery?
- Have you learned any new languages recently?
- Has he met the famous author?
- Have we received any updates on the project?
- Has the company released their latest software?
- Have you tried the new restaurant in town?
- Has she seen the latest superhero movie?
- Have they ever been to a live concert?
- Have you painted any new artwork lately?
- Has he bought a new car this year?
- Have they completed the challenging puzzle?
- Have you taken any exciting trips recently?
- Has she won any awards for her writing?
Quiz:
1. Have you ever __________ to Paris?
a) been b) be
2. She __________ her homework already.
a) has finished b) finished
3. They __________ the new restaurant downtown.
a) have tried b) tried
4. He __________ in that company for five years.
a) has worked b) worked
5. We __________ to the beach this summer.
a) have not been b) not been
6. Has she __________ her book yet?
a) finished b) finish
7. I __________ this movie before.
a) have seen b) saw
8. They __________ a new car recently.
a) have bought b) bought
9. The team __________ the championship last year.
a) won b) have won
10. She __________ English for three years.
a) has studied b) studied
11. Have they __________ to the new exhibit?
a) been b) be
12. He __________ the report just now.
a) has submitted b) submitted
13. I __________ my keys. I can’t find them.
a) have lost b) lost
14. They __________ to that concert twice.
a) have been b) was
15. She __________ a great job on the presentation.
a) has done b) did
16. Has the company __________ the new product yet?
a) released b) release
17. We __________ a lot of progress in our project.
a) have made b) made
18. Have you __________ dinner yet?
a) had b) have
19. They __________ their flight on time.
a) have caught b) caught
20. She __________ to many countries in Europe.
a) has traveled b) traveled
Answers:
- a) been
- a) has finished
- a) have tried
- a) has worked
- a) have not been
- a) finished
- a) have seen
- a) have bought
- a) won
- a) has studied
- a) been
- a) has submitted
- a) have lost
- a) have been
- a) has done
- a) released
- a) have made
- a) had
- a) have caught
- a) has traveled
FAQS:
- What is the present perfect tense?
- The present perfect tense is a verb form used to describe actions or events that have a connection to the present moment, even though they may have occurred at an unspecified time in the past.
- How is the present perfect tense formed?
- It is formed using the auxiliary verbs “have” or “has” with the past participle form of the main verb.
- What is the difference between “have” and “has” in the present perfect tense?
- “Have” is used with plural subjects (e.g., I, you, we, they), while “has” is used with singular subjects (e.g., he, she, it).
- What are some common signal words for the present perfect tense?
- Ever, never, just, already, yet, since, for, recently, lately.
- Can I use specific time expressions with the present perfect tense?
- It’s generally better to avoid specific time expressions like “yesterday” or “last year” with the present perfect tense, as it is more suited for unspecific time references.
- How does the present perfect tense differ from the simple past tense?
- The simple past tense is used for actions with a specific time in the past, while the present perfect tense emphasizes actions with a connection to the present, even if the exact timing is not specified.
Free Grammar and Vocabulary Worksheets Resources
You May Also Like
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Present Perfect Continuous Worksheets
- Past Perfect Tense With Examples