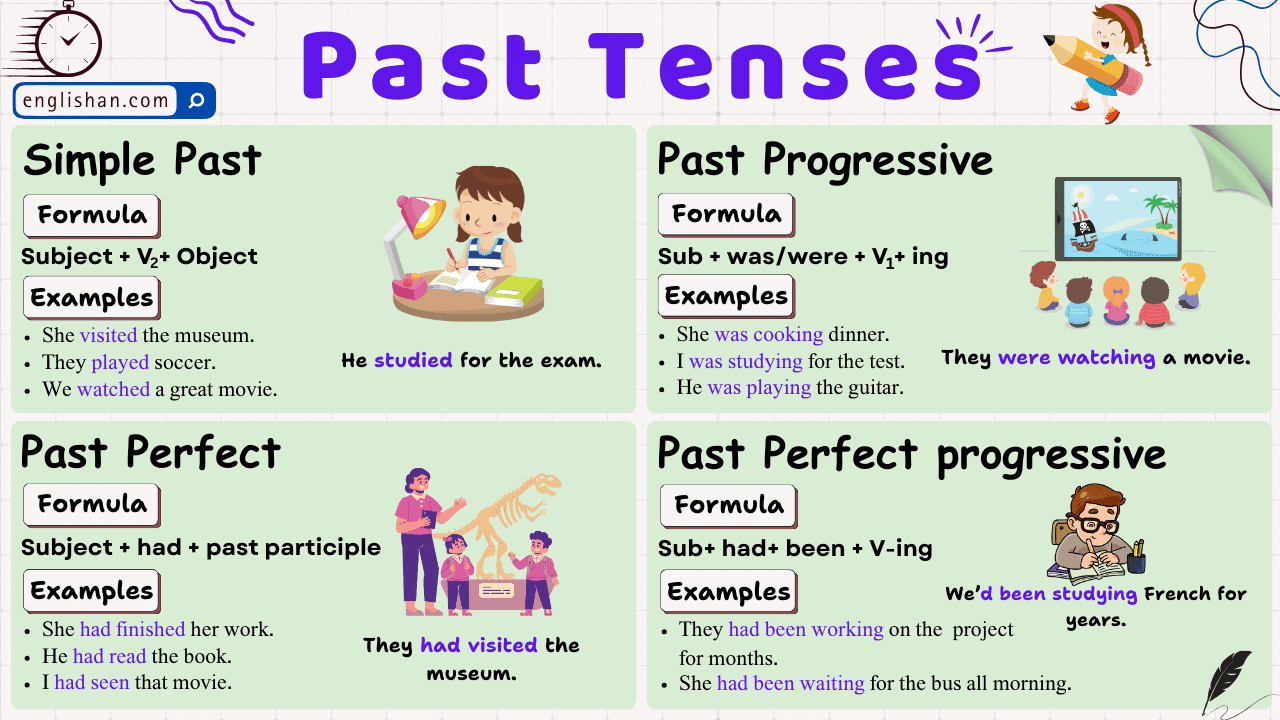
Contents
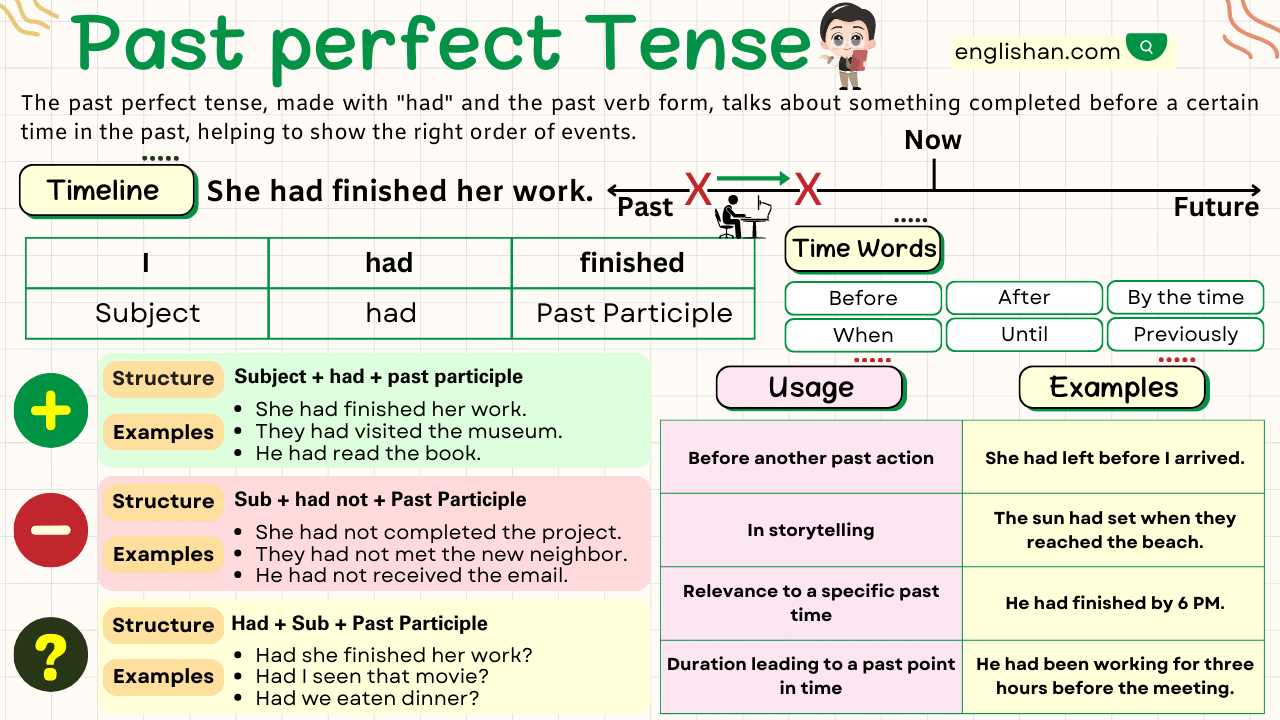
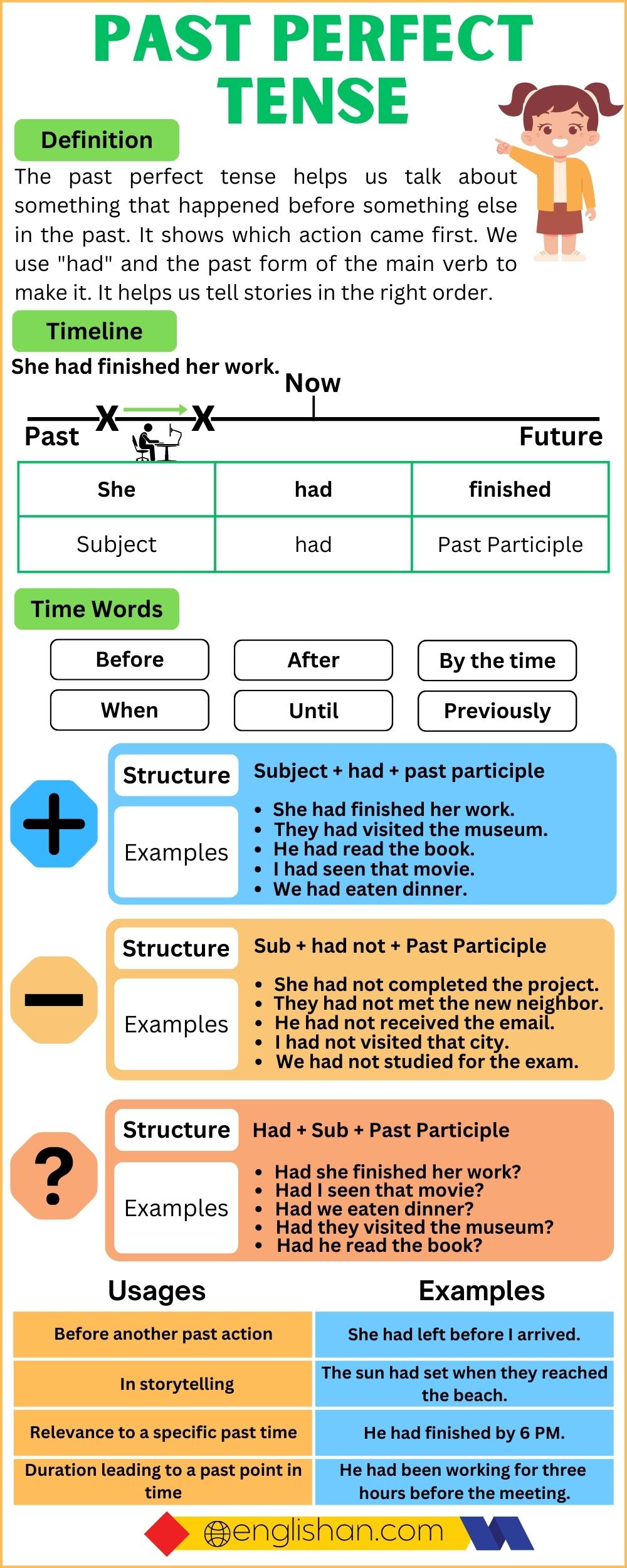
The past perfect tense is a grammatical form used to describe actions that were completed before a specific point in the past. It is formed by using the auxiliary verb “had” followed by the past participle of the main verb.
Examples:
- She had finished the work.
- They had visited the museum last summer.
- They had not seen the movie.
- He had never been to Paris before this vacation.
- Had you studied for the test before it was announced?
- Had the mail arrived before you left the house?
Forming the Past Perfect Tense
Affirmative Sentences
Affirmative sentences in past perfect tense are statements that express an action that was completed before a specific point in the past. They are structured using the following formula.
Subject + had +verb(3rd form) + object.
Examples:
- She had already finished her breakfast.
- They had watched the movie before bedtime.
- He had visited the new museum in town.
- The children had played in the park all afternoon.
- By the time I arrived, they had already eaten dinner.
- She realized she had forgotten her keys at home.
- We had never been to this restaurant before.
- The teacher had explained the lesson before the test.
- He told me he had already seen the new movie.
- The sun had set by the time we reached the beach.
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
| Subject | Had | Verb (3rd form) | Object | Complement. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| She | had | finished | her breakfast | already. |
| They | had | watched | the movie | before bedtime. |
| He | had | visited | the new museum | in town. |
| The children | had | played | in the park | all afternoon. |
| We | had | been | to this restaurant | before. |
| The teacher | had | explained | the lesson | before the test. |
| The sun | had | set | by the time | we reached the beach. |
| The bakery | had | sold out | of pastries | by noon. |
Negative Sentences
Interrogative sentences in past perfect tense are questions that inquire about actions or events that occurred before a specific point in the past. They are formed by using the auxiliary verb “had” followed by the subject and the past participle of the main verb.
Subject + had + not + verb(3rd form) + object.
Examples:
- She hadn’t finished her chores before dinner.
- They hadn’t visited the park in months.
- He hadn’t heard that song until yesterday.
- The team hadn’t practiced enough before the match.
- We hadn’t met our new neighbors until last week.
- The store hadn’t restocked the shelves by noon.
- He hadn’t tried sushi before last night.
- She hadn’t watched that TV series until now.
- They hadn’t seen that movie before last night.
- He hadn’t spoken to his cousin in years.
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
| Subject | Had not/hadn’t | Verb (3rd form) | Object | Complement. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| She | hadn’t | finished | her chores | before dinner. |
| They | hadn’t | visited | the park | in months. |
| He | hadn’t | heard | that song | until yesterday. |
| The team | hadn’t | practiced | enough | before the match. |
| The store | hadn’t | restocked | the shelves | by noon. |
| The bakery | hadn’t | sold out | of pastries | by noon. |
| The children | hadn’t | played | in the garden | before dusk. |
| We | hadn’t | heard | that joke | before today. |
Interrogative Sentences
Interrogative sentences in past perfect tense are questions about actions or events that happened before a specific point in the past. They start with “Had” followed by the subject and the past participle of the main verb.
Had + subject + verb(3rd form) + object?
Examples:
- Had she eaten breakfast before leaving for work?
- Had they visited the museum before the trip?
- Had he finished his chores before going out to play?
- Had you heard the news before we told you?
- Had they cleaned the house before the party?
- Had she read the book before watching the movie?
- Had we met our new neighbors before the event?
- Had he seen that movie before last night?
- Had they played any games before the picnic?
- Had she finished her work by the time you called?
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
| Had | Subject | Verb (3rd form) | Object | Complement? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Had | she | eaten | breakfast | before leaving for work? |
| Had | they | visited | the museum | before the trip? |
| Had | he | finished | his chores | before going out to play? |
| Had | you | heard | the news | before we told you? |
| Had | they | cleaned | the house | before the party? |
| Had | you | traveled | abroad | before last summer? |
| Had | they | studied | for the exam | before the test? |
| Had | we | heard | that song | before yesterday? |
Usages of the Past Perfect Tense
Describing Completed Actions Before Another Past Action
Describing Completed Actions Before Another Past Action” is one of the key uses of the past perfect tense. It helps establish a clear sequence of events in the past.
Examples:
- By the time we arrived, they had already finished their meal.
- She had completed the project before the deadline.
- The train had left the station before we reached it.
- They hadn’t started the meeting before the boss arrived.
- The bakery hadn’t sold out of croissants when we got there.
- She hadn’t visited that museum before last summer.
- Had you finished your homework before the teacher collected it?
- Had they seen that movie before it won an award?
- Had she ever traveled to Europe before this trip?
Narrating Past Events in a Sequence
“Narrating Past Events in a Sequence” is another important use of the past perfect tense. It helps in presenting a series of past events in the order in which they occurred.
Examples:
- She had breakfast, then went for a walk, and finally read a book.
- They had a picnic, then played games, and afterwards shared stories.
- She didn’t have time to finish her drawing, so she left it for tomorrow.
- They didn’t find any ripe apples, so they postponed making the pie.
- Had she already finished her snack before going for a walk?
- Had they played any games before having the picnic?
Expressing Regrets or Hypothetical Scenarios in the Past
Expressing regrets or hypothetical scenarios in the past involves using the past perfect tense to discuss situations that didn’t happen, or to express a sense of regret or longing for different outcomes in the past.
Examples:
- If I had known you were coming, I would have baked a cake.
- She wishes she had taken that job offer last year.
- He believes he would have won the race if he had trained harder.
- If she had arrived earlier, she wouldn’t have missed the train.
- He wishes he hadn’t sold his antique collection.
Reporting Past Actions or Speech
Reporting past actions or speech” involves conveying what someone said or did in the past. This is typically done through indirect or reported speech, where the original statement or action is reported using a different verb tense (often the past perfect tense) to indicate that it happened in the past.
Examples:
- She told me, I finished the report.
- He said, She has already left.
- They mentioned, We visited the museum.
- She told me that she hadn’t finished the report.
- He said that she had already left.
- They mentioned that they hadn’t visited the museum.
- Did she tell you she had finished the report?
- Had he mentioned that she had already left?
- Did they ask if we had visited the museum?
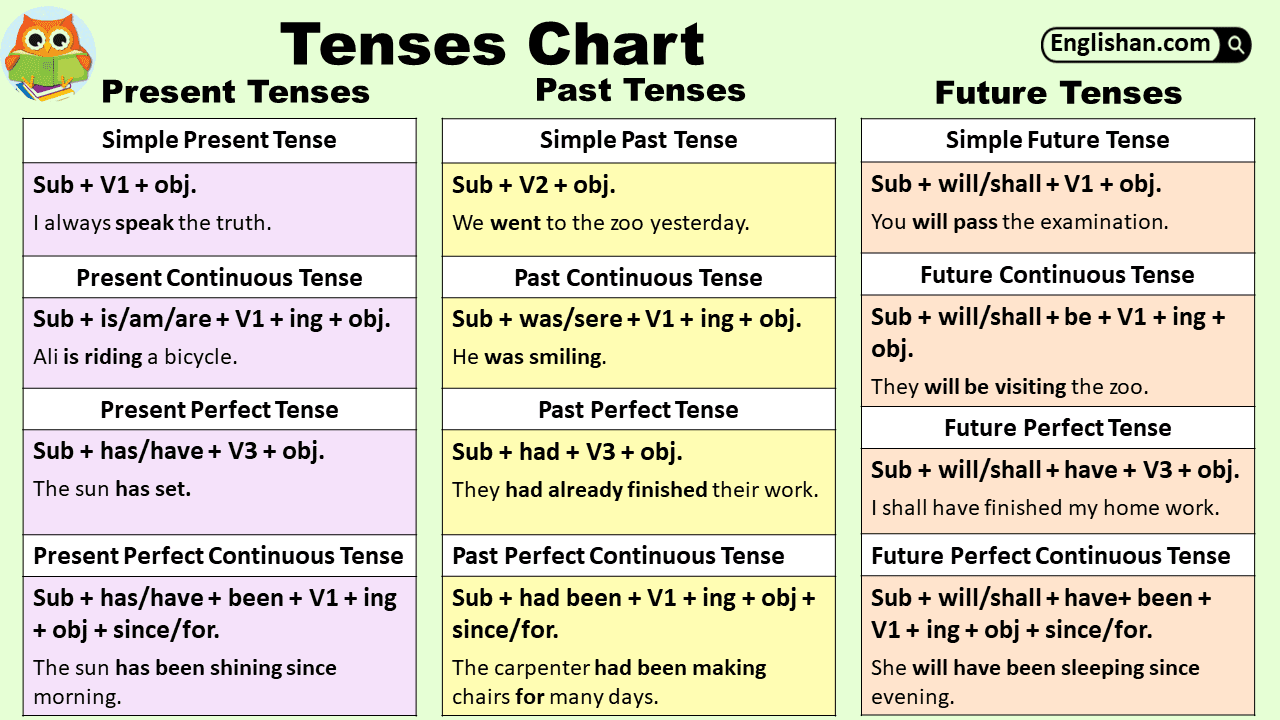
Past Perfect Tense Chart
Signal words for Past Perfect Tense
Signal words for Past Perfect Tense indicate that an action or event occurred before another action in the past.
Examples:
- She had finished her work before the meeting started.
- They had already eaten when I arrived.
- By the time we got to the cinema, the movie had already begun.
- She hadn’t seen the movie until last night.
- After they had left, I realized I forgot my keys.
- He hadn’t heard the news before we told him.
- She had never visited that city before.
- She didn’t taste that type of food until today.
- No sooner had they finished the project than the deadline arrived.
- Had you finished your work before the call?
- Hadn’t they seen the movie before last night?
- Had you ever been to this city before your trip?
- Had they finished the project by the deadline?
- Before we arrived, had they already played the game?
Time Expressions
Time expressions are words or phrases that indicate when an action or event took place. In the context of past perfect tense, they help establish the relationship between different past actions.
Examples:
- She finished her homework before dinner.
- He had known her since kindergarten.
- By morning, the rain had stopped.
- They had watched the movie twice already.
- She had read the book before bedtime.
- He hadn’t eaten breakfast yet.
- She realized she hadn’t studied in a while.
- They hadn’t seen that show since last year.
- He hadn’t visited the museum in years.
- She hadn’t traveled abroad before last summer.
- Had you finished your chores by the time I called? (Time Expression)
- When did they first meet each other? (Time Expression)
- By what time had they completed the project? (Time Expression)
- Had they ever been to this city before? (Time Expression)
- Since when had he known about this new technology? (Time Expression)
Past Perfect vs. Simple Past Tense
Differentiating Between Past Perfect and Simple Past
Here’s a table comparing Past Perfect Tense and Simple Past Tense
| Feature | Past Perfect Tense | Simple Past Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Use | Indicates an action that was completed before another action or point in time in the past. | Indicates an action that happened at a specific time in the past. |
| Structure | had + past participle (e.g., had walked, had eaten) | Verb in the past form (e.g., walked, ate) |
| Key Words | before, after, by the time, until, when, by | yesterday, last week, in 1990, ago, when |
| Example | I had finished my homework before the movie started. | I finished my homework yesterday. |
Past Perfect Tense Example Sentences
Affirmative Sentences
- The mother had cooked food before the sun rose.
- I had recited the Holy Quran before you came.
- The bell had rung when we reached the school.
- The train had gone when I reached the station.
- They had taken tea when I reached there.
- The patient had died before the doctor came.
- They had already finished their work.
- He had reached here till 2’O clock.
- The girl had already sung songs.
- The teacher had already taught us lesson.
- By then, he had finished all his work.
- They were tired because they had walked a lot.
- We were surprised because they hadn’t told us.
- The movie was over because they had watched it.
- She knew the answer because she had studied.
- They were happy because they had won the prize.
- He was full because he had eaten a big meal.
- The students were tired because they had studied.
- She had a great time because she had danced a lot.
- They were sleepy because they had stayed up late.
Negative Sentences
- He had not taken breakfast before you came.
- They had not bought tickets before the train came.
- Aslam had not heard this good news yet.
- It had not rained yet.
- I had never eaten such a delicious fruit before.
- He hadn’t visited his grandparents in a long time.
- She hadn’t tried that new restaurant yet.
- They hadn’t met their new neighbors before the party.
- By the time they arrived, the show hadn’t started yet.
- He hadn’t seen a shooting star until last night.
- She hadn’t been to the beach in years.
- We hadn’t seen each other in a long time.
- The cat hadn’t eaten its food yet.
- She hadn’t visited the museum in a while.
- They hadn’t finished the puzzle by bedtime.
- He hadn’t cooked dinner before the guests arrived.
- She hadn’t heard the news until now.
- They hadn’t bought groceries for the week.
- By the time they left, the party hadn’t even started.
- He hadn’t taken a vacation in years.
Interrogative Sentences
- Had you finished your work before the sun set?
- Had the police already dispersed the crowd?
- Had they already left for Lahore?
- Why had you not posted the letter before you went to school?
- Had they already reached the school?
- Had he fixed the car before the road trip?
- Had she learned to swim before the summer?
- Had they packed their bags before the vacation?
- Had we finished all the tasks before leaving?
- Had he visited his grandparents before the holidays?
- Had you met the new neighbors before the barbecue?
- Had they chosen a restaurant before the reservation?
- Had she attended any classes before the conference?
- Had we booked the tickets before they were sold out?
- Had he heard about the new job before the interview?
- Had they received the package before leaving home?
- Had she completed the assignment before the deadline?
- Had we packed our bags before the trip started?
- Had he visited that museum before it closed down?
- Had you tried that dish before today?
Avoiding Common Mistakes
Avoiding common mistakes in language use is crucial for effective communication.
Here are some tips to help you steer clear of frequent errors:
- Watch Subject-Verb Agreement: Ensure that the subject and verb in a sentence agree in number (singular or plural).
- Avoid Double Negatives: Using two negatives in a sentence can lead to confusion. For example, “I can’t hardly wait” should be “I can hardly wait.”
- Be Consistent with Verb Tenses: Stick to one tense throughout a piece of writing, unless there’s a specific reason for a shift.
FAQS:
- What is the Past Perfect Tense?
- The Past Perfect Tense is a verb form that is used to describe an action that took place before another action or a specific point in the past.
- How is the Past Perfect Tense formed?
- The Past Perfect Tense is formed using the auxiliary verb “had” followed by the past participle form of the main verb (e.g., had + eaten).
- What are some common time expressions used with the Past Perfect Tense?
- Time expressions like “before,” “by the time,” “already,” “until,” and “hadn’t” are commonly used with the Past Perfect Tense.
- How is the Past Perfect Tense different from the Simple Past Tense?
- The Simple Past Tense describes an action that happened at a specific point in the past, while the Past Perfect Tense describes an action that occurred before another past action.
- What is the difference between “hadn’t” and “didn’t” in the Past Perfect Tense?
- “Hadn’t” is the contraction of “had not” and is used in negative sentences (e.g., “She hadn’t finished her work.”). “Didn’t” is the contraction of “did not” and is used in negative sentences in the Simple Past Tense (e.g., “She didn’t finish her work.”).
- Can the Past Perfect Tense be used for reported speech?
- Yes, the Past Perfect Tense can be used in reported speech to convey information that was said or thought in the past (e.g., “He said he had already seen the movie.”).
- Is it possible to use adverbs with the Past Perfect Tense?
- Yes, adverbs like “already,” “just,” “never,” “yet,” and others can be used with the Past Perfect Tense to provide additional information about the timing of the action.
Free Grammar and Vocabulary Worksheets Resources
You May Also Like