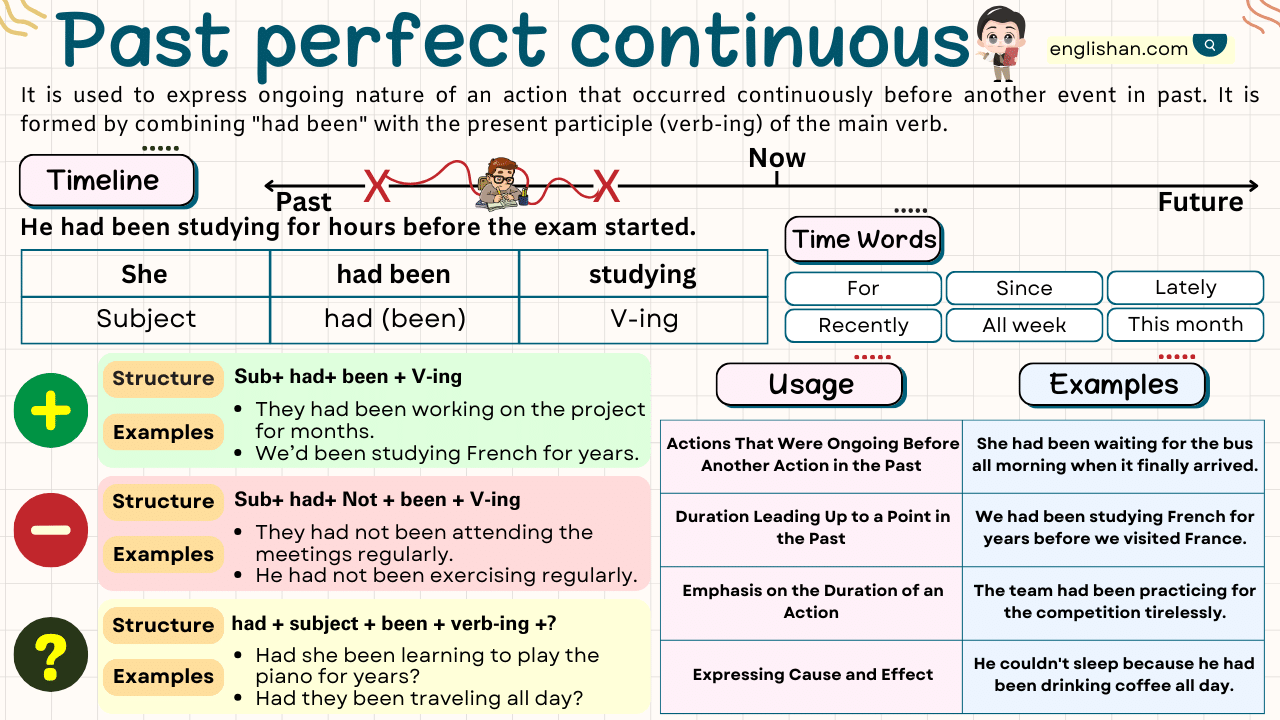
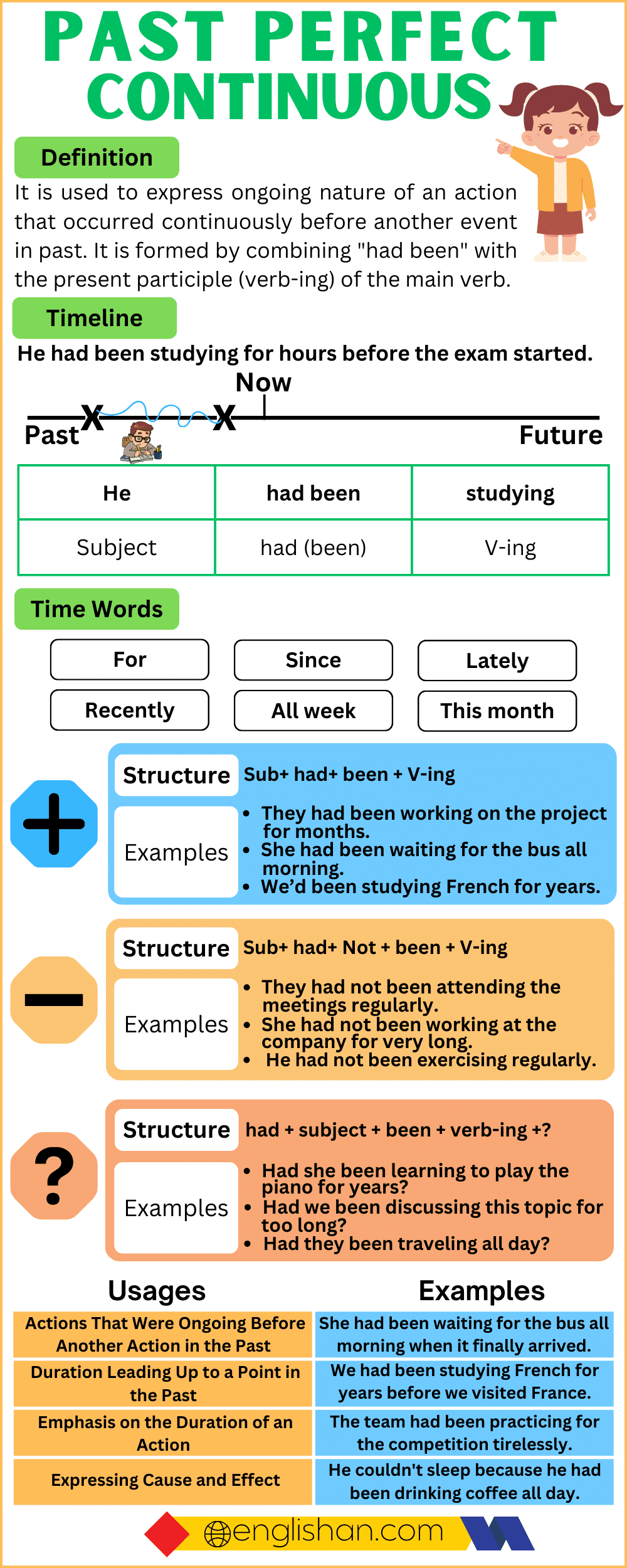
The Past Perfect Continuous Tense is a verb form that expresses an ongoing action that was happening before another action took place in the past. This tense is formed by using the past perfect of the auxiliary verb “to have” (had) and the past participle of the main verb, along with the present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
Examples:
- I had been working on the project for three hours before the meeting started.
- She had been practicing the piano for months before the concert.
- I realized I had not been paying attention during the entire lecture.
- Had you been waiting for a long time before the bus finally arrived?
- How long had they been working on the project before they completed it?
Usages of the Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Ongoing Action in the Past
An “ongoing action in the past” refers to an activity that was happening continuously at a specific point in the past, emphasizing its duration. Past Continuous or Past Perfect Continuous tenses are commonly used to express such ongoing actions.
Examples:
- She was reading a novel when the power went out.
- We were playing tennis at the park all afternoon.
- They had been studying chemistry for hours before the experiment.
- I wasn’t watching TV when the big news broke.
- She had not been practicing the piano before the recital.
- They weren’t playing video games the whole evening.
- Were you studying when the phone rang?
- Had they been working on the project for a long time before finishing it?
- Was she practicing the guitar when you called her?
Cause and Effect
“Cause and effect” describe a relationship where one ongoing action (expressed in Past Perfect Continuous) leads to another action (expressed in the past simple), indicating a direct influence or consequence.
Examples:
- They had been waiting for hours (cause), so she arrived at the party (effect).
- He had been practicing guitar for weeks, so his performance at the concert was outstanding.
- After they had been saving money diligently, they could finally afford a dream vacation.
- Because he hadn’t been paying attention in class, he failed the surprise quiz.
- She had not been managing her time well, so she missed the deadline for the project.
- As they hadn’t been communicating effectively, misunderstandings arose in their relationship.
- Had you been practicing the presentation before delivering it at the conference?
- Had they been working on the proposal for a while before submitting it?
- Was the team practicing hard before the crucial match?
Emphasis on Duration
“Emphasis on Duration” in the context of verb tenses, specifically the Past Perfect Continuous Tense, refers to the focus on the extended period during which an action was continuously happening in the past. This tense is particularly useful when you want to highlight the duration of an ongoing activity that took place leading up to a specific point in the past.
Examples:
- She had been practicing the piano for hours before the recital.
- They had been renovating the house for months when it was finally complete.
- We had been hiking all day before reaching the summit.
- I realized I had not been paying attention during the entire lecture.
- She hadn’t been practicing her guitar regularly, so her performance suffered.
- They had not been exercising consistently, leading to a decline in fitness.
- Had you been working on the project for a long time before submitting it?
- Were they practicing the dance routine for hours before the performance?
- Had she been living in the city for a while before finding a job?
Past Perfect Continuous Tense Chart
Signal Words
Signal words are words or phrases that indicate the use of a specific verb tense or help convey the relationship between different events in a sentence. In the case of the Past Perfect Continuous Tense, certain signal words or phrases are commonly used to provide context and indicate the ongoing and continuous nature of the action leading up to a specific point in the past. like by the time, before, already, for, since, how long, etc.
Examples:
- By the time the movie started, they had been waiting in line for tickets.
- She realized she had already been baking for hours when guests arrived.
- Before the trip, we had been planning itineraries for weeks.
- Before the rescue team arrived, they had not been receiving any signals.
- She was upset because her car hadn’t been running smoothly for weeks.
- They had not been practicing regularly, so the performance suffered.
- By the time you arrived, how long had they been waiting for you?
- Had she already been preparing for the exam when you called?
- How long had you been learning French before your trip to Paris?
Time Expressions
Time expressions are words or phrases that provide information about the duration or specific period during which the ongoing action occurred. These expressions help to set the timeframe for the continuous action leading up to a particular point in the past. Like for, since, all day/night/week/month/year, how long, by the time etc.
Examples:
- They had been working on the project for weeks before they presented it.
- She realized she had been practicing the piano all day before the concert.
- Before the guests arrived, I had been decorating the house all night.
- Before the repair, the car hadn’t been running smoothly for weeks.
- He failed the exam because he hadn’t been studying effectively all week.
- The garden suffered because it had not been receiving water for several days.
- For how long had you been waiting before the train arrived?
- Since when had they been planning the surprise party for you?
- All morning, what had they been discussing in the meeting?
Forming the Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Affirmative Sentences
Affirmative sentences in the Past Perfect Continuous Tense express an action that was ongoing and continuous for a duration leading up to a specific point in the past. The structure of affirmative sentences in this tense involves the use of the past perfect form of the auxiliary verb “to have” (had), the past participle of the main verb, and the present participle (base verb + -ing).
Subject + had been + verb(1st form) ing + object +since/for.
Examples:
- I had been working on the report for hours before the deadline.
- By the time they arrived, we had been waiting for ages.
- She had been practicing the piano all morning.
- The kids had been playing outside for hours.
- We had been living in that city for ten years.
- Before the guests came, I had been preparing dinner.
- He had been running marathons for years.
- They had been studying hard for the exam.
- By the time I got there, they had been rehearsing the play.
- She had been gardening since early morning.
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
| Subject | Had Been | Verb (1st form) ing | Object | Since/For. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | had been | working | on the report | for hours before the deadline. |
| we | had been | waiting | for ages | By the time they arrived. |
| She | had been | practicing | the piano | all morning. |
| The kids | had been | playing | outside | for hours. |
| We | had been | living | in that city | for ten years. |
| I | had been | preparing | dinner | Before the guests came. |
| He | had been | running | marathons | for years. |
| They | had been | studying | hard for the exam | . |
| They | had been | rehearsing | the play | By the time I got there. |
| She | had been | gardening | since early morning. | |
| We | had been | traveling | through Europe | for months. |
| The weather | had been | changing | rapidly | Before the storm hit. |
| He | had been | biking | across the country | . |
| The sun | had been | shining | By the time I woke up for hours. | |
| They | had been | renovating | the house | throughout the summer. |
| She | had been | writing | her novel | for a long time. |
| I | had been | searching | everywhere | Before I found my keys. |
| We | had been | attending | the same school | for years. |
| He | had been | fishing | at the lake | all day. |
| The band | had been | rehearsing | for weeks | By the time the concert started. |
Negative Sentences
Negative sentences in the Past Perfect Continuous Tense express actions that were not ongoing or were not continuous for a specified duration leading up to a particular point in the past. The structure of negative sentences in this tense involves the use of the past perfect form of the auxiliary verb “to have” (had not or hadn’t), the past participle of the main verb, and the present participle (base verb + -ing).
Subject + had + not + been + verb(1st form)ing object + since/for.
Examples:
- She hadn’t been studying for the test for weeks.
- We had not been working on the project since last month.
- He hadn’t been practicing the guitar for a long time.
- They had not been exercising regularly since the beginning of the year.
- By the time they called for help, they hadn’t been hiking for very long.
- I had not been taking breaks since I started working on the assignment.
- Before the storm hit, the weather hadn’t been changing for weeks.
- She had not been attending dance classes since she moved to the new city.
- The students hadn’t been using the laboratory for experiments for months.
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
| Subject | Had Not Been | Verb (1st form) ing | Object | Since/For. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| She | hadn’t been | studying | for the test | for weeks. |
| We | had not been | working | on the project | since last month. |
| He | hadn’t been | practicing | the guitar | for a long time. |
| They | had not been | exercising | regularly | since the beginning of the year. |
| By the time they | hadn’t been | hiking | for very long. | |
| I | had not been | taking | breaks | since I started working on the assignment. |
| Before the storm hit, the weather | hadn’t been | changing | for weeks. | |
| She | had not been | attending | dance classes | since she moved to the new city. |
| The students | hadn’t been | using | the laboratory | for experiments for months. |
| We | had not been | living | in the neighborhood | for a long time.. |
| Before the news broke, the researchers | hadn’t been | making | significant progress for months. | |
| He | had not been | repairing | his car | for a while. |
| They | hadn’t been | discussing | the issue | for an extended period. |
| I | had not been | attending | the gym | since the fitness classes became less effective. |
| By the time they reached the concert venue, the band | hadn’t been | rehearsing | for weeks | . |
| The garden | had not been | receiving | for a long time. | |
| She | hadn’t been | wearing | her glasses | since she got a new prescription. |
| Before the guests arrived, the chef | had not been | preparing | for an extended period. | |
| We | hadn’t been | seeing | each other | for years. |
| He | had not been | coaching | the team | since the disappointing season. |
Interrogative Sentences
Interrogative sentences in the Past Perfect Continuous Tense are formed by using the auxiliary verb “had” (the past tense of “have”), followed by “been,” and then the present participle form of the main verb with “-ing.”
Had + subject + been + verb(1st form)ing + object + since/for?
Examples:
- Had she been waiting for a long time before the concert started?
- Had they been traveling throughout Europe for months?
- Had he been working on the assignment since yesterday?
- Had the team been practicing for the championship match for weeks?
- Had you been learning Spanish for several months?
- Had it been raining since morning before you arrived?
- Had they been renovating the house for the entire summer?
- Had she been playing the piano all afternoon since she got home?
- Had we been discussing the plan for weeks before making a decision?
- Had the children been playing outside for hours before it started raining?
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
| Had | Subject | Been | Verb (1st form)ing | Object | Since/For? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Had | She | Been | waiting | for a long time | Before the concert started? |
| Had | They | Been | traveling | throughout Europe | For months? |
| Had | He | Been | working | on the assignment | Since yesterday? |
| Had | The team | Been | practicing | for the championship match | For weeks? |
| Had | You | Been | learning | Spanish | For several months? |
| Had | It | Been | raining | since morning | Before you arrived? |
| Had | They | Been | renovating | the house | For the entire summer? |
| Had | She | Been | playing | the piano | All afternoon since she got home? |
| Had | We | Been | discussing | the plan | For weeks before making a decision? |
| Had | The children | Been | playing | outside | For hours before it started raining? |
| Had | He | Been | running | marathons | For years before his injury? |
| Had | The weather | Been | changing | rapidly | Since morning before the storm hit? |
| Had | They | Been | rehearsing | the play | For a long time before the performance? |
| Had | You | Been | searching | everywhere | Since morning? |
| Had | The students | Been | studying | hard for the exam | For weeks? |
| Had | The project | Been | progressing | smoothly | For several months before the setback? |
| Had | She | Been | gardening | since early morning | Before the guests arrived? |
| Had | You | Been | working | at the company | For a decade before the promotion? |
| Had | He | Been | fishing | at the lake | All day before the sunset? |
| Had | We | Been | attending | the same school | For years before graduating? |
Spelling Rules
Spelling rules in English, including those related to the past perfect continuous tense, primarily involve maintaining consistency in verb forms and following standard rules for adding suffixes and endings.
- Verb Form:
- For regular verbs, add -ed to the base form of the verb to create the past participle.
- Example: work → worked, play → played
- For irregular verbs, the past participle can vary, and there may not be a consistent rule. Common irregular past participles include eaten, taken, and driven.
- For regular verbs, add -ed to the base form of the verb to create the past participle.
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense Spelling:
- The past perfect continuous tense is formed using had been + the present participle (base verb + -ing).
- Example: She had been studying for hours.
- The past perfect continuous tense is formed using had been + the present participle (base verb + -ing).
- Spelling Changes with -ing:
- For verbs ending in e, remove the e before adding -ing.
- Example: dance → dancing, write → writing
- For one-syllable words with a single vowel followed by a single consonant, double the final consonant before adding -ing.
- Example: run → running, hop → hopping
- For verbs ending in e, remove the e before adding -ing.
- Verbs Ending in -ie:
- For verbs ending in -ie, change the -ie to -y before adding -ing.
- Example: die → dying, lie → lying
- For verbs ending in -ie, change the -ie to -y before adding -ing.
- Exceptions:
- Some irregular verbs may have different forms in the past perfect continuous tense.
- Example: go → had been going, see → had been seeing
- Some irregular verbs may have different forms in the past perfect continuous tense.
Past Perfect vs. Past Perfect Continuous Tense
| Aspect | Past Perfect Tense | Past Perfect Continuous Tense |
|---|---|---|
| Formation | Subject + had + past participle | Subject + had been + present participle (verb + -ing) |
| Positive Structure | She had eaten. | She had been eating. |
| Negative Structure | She had not eaten. | She had not been eating. |
| Interrogative Structure | Had she eaten? | Had she been eating? |
| Use | Completed action before another past action | Duration before another past action |
| Example | She had finished her homework before the party started. | She had been studying for hours when the phone rang. |
Avoiding Common Mistakes
Incorrect Verb Form:
- ❌ Incorrect: She had been study for hours.
- ✅ Correction: She had been studying for hours.
Unnecessary Use:
- ❌ Incorrect: By the time I arrived, they had been waiting for an hour.
- ✅ Correction: By the time I arrived, they had waited for an hour.
Unnecessary “Since” with Duration:
- ❌ Incorrect: She had been working on the project since three hours.
- ✅ Correction: She had been working on the project for three hours.
Missing Time Expression:
- ❌ Incorrect: They had been practicing the song.
- ✅ Correction: They had been practicing the song for an hour.
Using it for Single, Completed Actions:
- ❌ Incorrect: She had been cooked dinner by the time I arrived.
- ✅ Correction: She had cooked dinner by the time I arrived.
Confusing Past Perfect and Past Perfect Continuous:
- ❌ Incorrect: I had been lived in that city for five years.
- ✅ Correction: I had lived in that city for five years.
Incorrect Placement of “For” and “Since”:
- ❌ Incorrect: She had been reading since two hours.
- ✅ Correction: She had been reading for two hours.
Omitting “Been” with “Have”:
- ❌ Incorrect: Had you studying all day?
- ✅ Correction: Had you been studying all day?
Past Perfect Continuous Tense Example Sentences
Affirmative Sentences:
- He had been saying his prayers since childhood.
- The clouds had been thundering since midnight.
- The people had been sitting under the trees since 11’o clock.
- She had been Knitting a sweater for an hour.
- My friend had been looking for several months.
- The washer man had been washing the clothes since morning.
- It had been raining since Monday.
- The boys had been playing a friendly match since 4’o clock.
- The villagers had been taking a bath in the canal since noon.
- We had been drawing maps since noon.
- My brother bad been preparing for the examination for many days.
- The carpenter had been making chairs for many days.
- They had been reading the newspaper for two hours.
- The mail had been plucking flowers for two hours.
- The girls had been playing with toys for many hours.
- She had been skiing since early morning.
- They had been volunteering at the shelter for a long time.
- Before the technology upgrade, the system had been malfunctioning regularly.
- He had been coaching the team for several seasons.
- By the time the news broke, the journalists had been investigating for months.
Negative Sentences:
- The boys had not been making a notice since morning.
- The fishermen had not been catching fish for many days.
- The gardener had not been plucking flowers since morning.
- The cattle had not been eating fodder since yesterday.
- Zaid had not been learning tables for many hours.
- You had not been working in this office for four months.
- Students had not been wasting their time for many days.
- They hadn’t been communicating effectively for a considerable time before the conflict arose.
- By the time the repairman arrived, the appliance hadn’t been working properly for weeks.
- She had not been taking medication for a long time, leading to health issues.
- We hadn’t been attending the language classes since the instructor changed.
- Before the event, the organizers had not been planning adequately for the large crowd.
- He had not been enjoying his job for months, so he decided to resign.
- They hadn’t been saving money for a considerable period before the unexpected expenses.
- She had not been updating her resume since she started her current job.
- Before the pandemic, people had not been practicing social distancing for a long time.
- He hadn’t been attending family gatherings for years, creating a sense of estrangement.
Interrogative Sentences:
- Had the birds been chirping since morning?
- For how many years had they been living in that house before moving?
- Had she been cooking all day before the family arrived?
- Since when had he been playing the guitar before the concert?
- Had she been writing the novel for years before publishing it?
- How long had they been watching movies before going to bed?
- For how many months had you been working on the project before completing it?
- Had they been practicing for weeks before the big game?
- Since when had she been learning French before the trip to Paris?
- Had Ahmad been living here since childhood?
- For how long had he been exercising before feeling more energetic?
- Had it been snowing for days before the roads were cleared?
- Since when had they been renovating the kitchen before the party?
- How long had she been singing before her voice became hoarse?
- Had he been coming here for two weeks?
- Where had you been playing since morning?
- For how many hours had they been discussing the plan before deciding?
- Since when had he been playing video games before the console broke?
- Had they been traveling for months before reaching their destination?
- For how long had you been waiting for the bus before it arrived?
Quiz:
- Had she been waiting for a long time before the concert started?
- a) Yes, she waits
- b) Yes, she had been waiting
- Why was the house messy? They ____________ it for hours.
- a) had cleaned
- b) had been cleaning
- Had you been practicing the piano ____________?
- a) since yesterday
- b) since morning
- By the time they arrived, we ____________ for ages.
- a) had waiting
- b) had been waiting
- Why were they tired? They ____________ all day.
- a) had been working
- b) were working
- How long ____________ at the airport before the flight was canceled?
- a) had you been waiting
- b) were you waiting
- She realized she ____________ the wrong address.
- a) had given
- b) had been giving
- The kids ____________ outside for hours before it started raining.
- a) had played
- b) had been playing
- Had it been snowing ____________?
- a) since last night
- b) since last week
- How long ____________ on the novel before she finished it?
- a) had she been working
- b) was she working
- We ____________ the same school for years before graduating.
- a) attended
- b) had attended
- Before the storm hit, the weather ____________ rapidly.
- a) had been changing
- b) changed
- He ____________ marathons for years before his injury.
- a) had been running
- b) ran
- Had she been gardening ____________?
- a) since early morning
- b) since the weekend
- How long ____________ at the company before the promotion?
- a) had you been working
- b) were you working
- They ____________ hard for the exam for weeks.
- a) had been studying
- b) were studying
- Before the guests came, I ____________ dinner.
- a) was preparing
- b) had been preparing
- Had he been fishing at the lake ____________?
- a) all day
- b) since yesterday
- The project ____________ smoothly for several months before the setback.
- a) had been progressing
- b) progressed
- She ____________ her novel for a long time before completing it.
- a) had been writing
- b) was writing
Answers:
- b) Yes, she had been waiting
- b) had been cleaning
- a) since yesterday
- b) had been waiting
- a) had been working
- a) had you been waiting
- b) had been giving
- b) had been playing
- a) since last night
- a) had she been working
- a) had attended
- a) had been changing
- a) had been running
- a) since early morning
- a) had you been working
- a) had been studying
- b) had been preparing
- a) all day
- a) had been progressing
- a) had been writing
FAQS:
- What is the structure of the past perfect continuous tense?
- Use “had been” + present participle (verb + -ing).
- Example: “She had been studying for hours.”
- Use “had been” + present participle (verb + -ing).
- When do we use the past perfect continuous tense?
- To describe ongoing actions in the past up to a specific moment.
- Example: “He had been running before he tripped.”
- To describe ongoing actions in the past up to a specific moment.
- How do we form negative sentences in the past perfect continuous tense?
- Add “not” between “had” and “been.”
- Example: “She had not been working for long.”
- Add “not” between “had” and “been.”
- What are common time expressions used with the past perfect continuous tense?
- Use “for” and “since” for duration and start time.
- Example: “They had been traveling for weeks.”
- Use “for” and “since” for duration and start time.
- Can the past perfect continuous tense be used for single, completed actions?
- It’s for ongoing/repeated actions, not single events.
- How do we form interrogative sentences in the past perfect continuous tense?
- Start with “Had,” then the subject, “been,” and the present participle.
- Example: “Had she been waiting long?”
- Start with “Had,” then the subject, “been,” and the present participle.
- What is the emphasis on duration in the past perfect continuous tense?
- It emphasizes how long an action was happening in the past.
- Example: “They had been working on the project for hours.”
- It emphasizes how long an action was happening in the past.
- Can “since” be used with a duration in the past perfect continuous tense?
- “Since” for a specific start time; “for” for duration.
- Correct: “for three hours.”
- “Since” for a specific start time; “for” for duration.
Free Grammar and Vocabulary Worksheets Resources
- Worksheet Tenses
- Since and For Worksheets
- English Worksheets
- Action Verbs Worksheets
- Past Perfect Continuous Worksheets
You May Also Like
- Present Tenses With Examples
- Present Perfect Tense With Examples
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense With Examples
- Differentiate Till, Until and Unless in English
- Time Expressions in English
- Future Perfect Tense With Examples
- Tenses