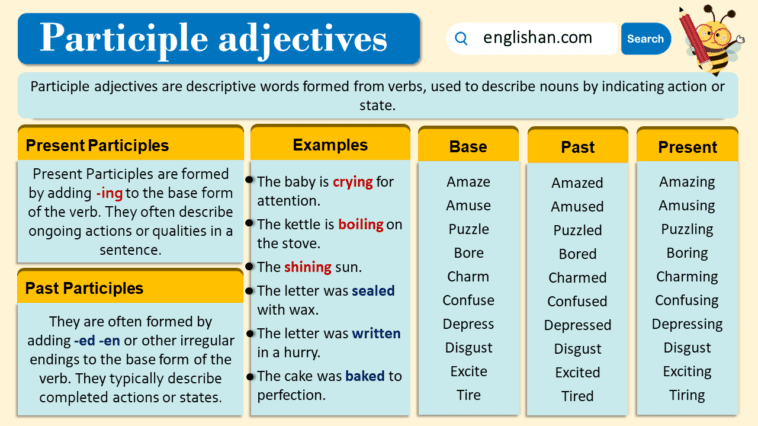
Participle adjectives are special words in English that help describe things by adding action or a state of being. They’re formed from verbs and come in two types: present participles (ending in ‘-ing’) and past participles (ending in ‘-ed’, ‘-en’, ‘-d’, ‘-t’, or irregular forms).
What are Participle adjectives?
Participle adjectives are words that are formed from verbs and used to describe nouns. They often end in “-ed” or “-ing” and convey a passive or active sense, adding more information about the state or characteristics of the noun they modify.
Importance of Participle Adjectives
Participle adjectives play a significant role in English grammar as they add depth, detail, and nuance to descriptions. Here are some reasons why they are important:
- Making Things Clear: Participle adjectives help describe things in a more interesting and clear way. Instead of just saying “a tired person,” you can say “a tired-looking person,” which gives a better picture.
- Short and Sweet: They help you say things in a shorter way by combining a verb and an adjective into one word. This can be really handy when you want to keep things brief.
- Getting Specific: Participle adjectives give you more options to describe things accurately. You can use them to show specific actions or qualities, making your writing more colorful.
- Making Language Fun: They make your writing more lively by implying action or movement. Instead of just saying what something is, you can show what it’s doing.
- Keeping It Interesting: Using different types of adjectives keeps your writing from sounding boring or repetitive. It adds variety and keeps readers engaged.
- Showing Why Things Happen: Sometimes, participles can hint at why something happened. Like saying “a broken window” suggests something caused it to break.
Types of Participle Adjectives
Participle adjectives come in two main types: present participles and past participles.
Present Participles
These are formed by adding -ing to the base form of the verb. They often describe ongoing actions or qualities.
Examples:
The running water.
The singing birds.
The shining sun.
Formation (ending in ‘-ing’)
Participles ending in “-ing” are called present participles. They are formed by adding “-ing” to the base form of the verb. Here’s how you do it:
Regular Verbs: For regular verbs, you simply add “-ing” to the base form of the verb.
Examples:
- Base form: walk
- Present participle: walking
Irregular Verbs: Some irregular verbs have different forms for their present participles.
Examples:
- Base form: swim
- Present participle: swimming
- Base form: run
- Present participle: running
- Base form: sing
- Present participle: singing
Past Participles
These are often formed by adding “-ed,” “-en,” “-d,” “-t,” or other irregular endings to the base form of the verb. Past participles typically describe completed actions or states.
For example:
The painted house.
The broken vase.
The fallen leaves.
Formation (ending in ‘-ed’, ‘-en’, or irregular forms)
Participles ending in “-ed,” “-en,” “-d,” “-t,” or irregular forms are called past participles. Here’s how they’re formed:
1. Regular Verbs:
For regular verbs, you typically add “-ed” to the base form of the verb.
Example:
- Base form: play
- Past participle: played
For base verbs ending in ‘e’, just add “-d”.
- Base form: bake
- Past participle: baked
If the base verb ends in a consonant after a vowel, double the consonant and add “-ed”.
- Base form: stop
- Past participle: stoped
If the base verb ends in a consonant after a stressed vowel, simply add “-ed”.
- Base form: enter
- Past participle: entered
2. Irregular Verbs:
Irregular verbs have unique forms for their past participles.
Examples:
- Base form: eat
- Past participle: eaten
- Base form: go
- Past participle: gone
- Base form: write
- Past participle: written
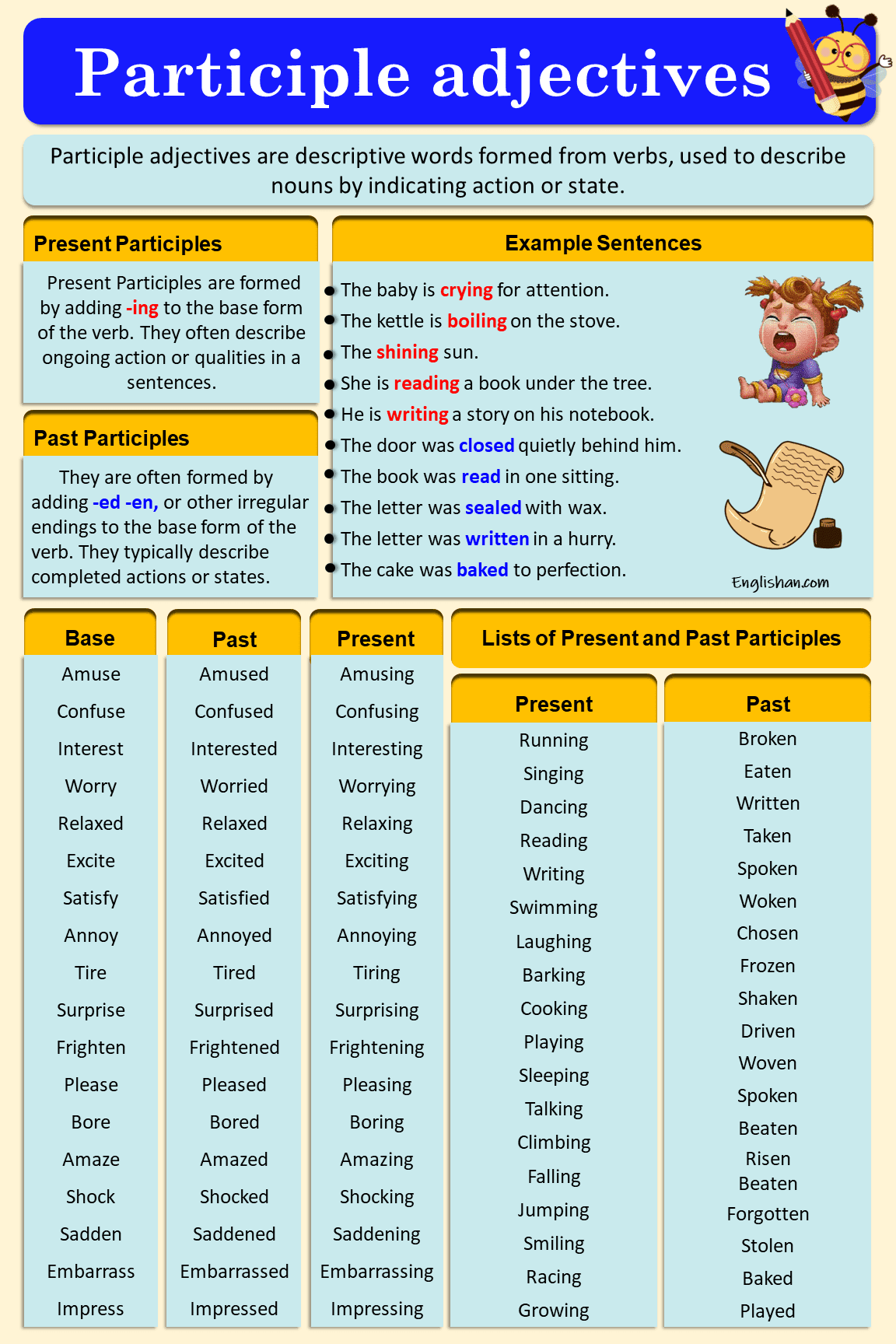
Example Sentences:
Present Participles:
- The water is flowing gently down the river.
- Birds are singing sweetly in the morning.
- The fire is burning brightly in the fireplace.
- She is reading a book under the tree.
- He is writing a story on his notebook.
- Kids are swimming happily in the pool.
- Children are laughing at the funny clown.
- The dog is barking loudly at the mailman.
- Mom is cooking dinner in the kitchen.
- They are playing with their toys in the yard.
- The wind is blowing softly through the trees.
- Flowers are blooming beautifully in the garden.
- Students are studying hard for their exams.
- The cat is purring contentedly on the sofa.
- Dad is fixing the broken chair in the garage.
- The clock is ticking rhythmically on the wall.
- People are walking briskly in the park.
- The baby is crying for attention.
- The kettle is boiling on the stove.
- They are talking excitedly about their vacation plans.
- The sun is shining brightly in the sky.
- The engine is roaring as the car speeds up.
- Leaves are falling from the trees in autumn.
- The dog is digging a hole in the backyard.
- The children are skipping happily down the street.
- The teacher is explaining the lesson to the class.
- The rain is pouring heavily outside.
- The baby is sleeping peacefully in the crib.
- The birds are chirping cheerfully in the morning.
- The painter is brushing strokes onto the canvas.
Past Participles:
- The cake was baked to perfection.
- The window was broken during the storm.
- The letter was written in a hurry.
- The vase was shattered into pieces.
- The meal was cooked by a professional chef.
- The toys were played with by the children.
- The door was closed quietly behind him.
- The book was read in one sitting.
- The dishes were washed and put away.
- The computer was fixed by a technician.
- The picture was painted by a famous artist.
- The tree was cut down for firewood.
- The car was parked in the garage.
- The cake was eaten by everyone at the party.
- The flowers were arranged beautifully in a vase.
- The road was paved with asphalt.
- The message was delivered to the recipient.
- The room was cleaned thoroughly.
- The fish was caught by the fisherman.
- The fence was mended after it broke.
- The laundry was folded and put away.
- The story was told by the old storyteller.
- The problem was solved by a team of experts.
- The package was wrapped with care.
- The cake was decorated with icing and sprinkles.
- The house was painted a bright shade of blue.
- The letter was sealed with wax.
- The project was completed ahead of schedule.
- The seeds were planted in the garden.
- The fence was painted to match the house.
Participle Adjectives List
Present Participles:
- Accepting
- Achieving
- Adapting
- Alluring
- Alarming
- Amusing
- Annoying
- Appealing
- Appalling
- Astonishing
- Astounding
- Balancing
- Bewildering
- Boring
- Calming
- Captivating
- Charming
- Comforting
- Compelling
- Confounding
- Convincing
- Dazzling
- Delighting
- Demanding
- Depressing
- Despairing
- Disappointing
- Disarming
- Disconcerting
- Disgusting
- Distressing
- Distracting
- Disturbing
- Draining
- Easing
- Electrifying
- Enchanting
- Encouraging
- Endearing
- Energizing
- Engaging
- Enthralling
- Enveloping
- Exasperating
- Exhilarating
- Fascinating
- Fatiguing
- Frightening
- Frustrating
- Gratifying
- Heartening
- Heartbreaking
- Hilarious
- Horrifying
- Humiliating
- Illuminating
- Impelling
- Impressing
- Inflaming
- Infuriating
- Inspiring
- Intensifying
- Intoxicating
- Involving
- Irking
- Irritating
- Jolting
- Joyful
- Maddening
- Mesmerizing
- Mystifying
- Overwhelming
- Paralyzing
- Persuading
- Pleasing
- Provoking
- Quenching
- Reassuring
- Rejuvenating
- Relieving
- Repelling
- Repulsing
- Rewarding
- Saddening
- Satisfying
- Scintillating
- Shocking
- Soothing
- Spellbinding
- Stimulating
- Stirring
- Straining
- Stupefying
- Subduing
- Submerging
- Subsuming
- Surrendering
- Terrifying
- Tiring
Past Participles:
Compound participle adjectives
Compound participle adjectives are just words made by joining two smaller words together. Here are some simple examples:
- Well-known: Familiar to many people.
- Example: She is a well-known actress.
- High-flying: Ambitious or successful, especially in a career.
- Example: He leads a high-flying corporate lifestyle.
- Red-faced: Embarrassed or ashamed.
- Example: He left the room feeling red-faced after his mistake.
- Fast-growing: Increasing rapidly in size or importance.
- Example: The company is a fast-growing startup.
- Long-lasting: Enduring for a long time.
- Example: They have a long-lasting friendship.
- Heavy-handed: Using too much force or authority.
- Example: The politician’s heavy-handed approach to the situation caused controversy.
- Wide-eyed: Showing surprise or innocence.
- Example: She looked around the room with wide-eyed wonder.
- Cold-blooded: Lacking emotion or empathy.
- Example: The killer was described as cold-blooded by the witnesses.
- Hard-working: Diligent and industrious.
- Example: She is a hard-working student who always strives for excellence.
- High-heeled: Having high heels on shoes.
- Example: She wore a pair of high-heeled boots to the party.
Participle Adjectives Examples
| Past Participles | Present Participles |
|---|---|
| amused | amusing |
| confused | confusing |
| interested | interesting |
| worried | worrying |
| relaxed | relaxing |
| excited | exciting |
| satisfied | satisfying |
| annoyed | annoying |
| tired | tiring |
| surprised | surprising |
| frightened | frightening |
| pleased | pleasing |
| bored | boring |
| amazed | amazing |
| shocked | shocking |
| saddened | saddening |
| embarrassed | embarrassing |
| impressed | impressing |
| frustrated | frustrating |
| humiliated | humiliating |
| inspired | inspiring |
| satisfied | satisfying |
| motivated | motivating |
| fascinated | fascinating |
| disgusted | disgusting |
| encouraged | encouraging |
| energized | energizing |
| enchanted | enchanting |
| captivated | captivating |
| entertained | entertaining |
| encouraged | encouraging |
| charmed | charming |
| concerned | concerning |
| horrified | horrifying |
| mesmerized | mesmerizing |
| mystified | mystifying |
| provoked | provoking |
| relaxed | relaxing |
| refreshed | refreshing |
| stunned | stunning |
| terrified | terrifying |
| intrigued | intriguing |
| uplifted | uplifting |
| vexed | vexing |
| thrilled | thrilling |
| reassured | reassuring |
| uplifted | uplifting |
| exhilarated | exhilarating |
| invigorated | invigorating |
| astonished | astonishing |
| bewildered | bewildering |
| captivated | captivating |
| enchanted | enchanting |
| enticed | enticing |
| enraptured | enrapturing |
| frustrated | frustrating |
| gratified | gratifying |
| electrified | electrifying |
| fascinated | fascinating |
| captivated | captivating |
| invigorated | invigorating |
| overwhelmed | overwhelming |
| captivated | captivating |
| captivated | captivating |
| frightened | frightening |
| disgusted | disgusting |
| perplexed | perplexing |
| flattered | flattering |
| dismayed | dismaying |
| concerned | concerning |
| comforted | comforting |
| confounded | confounding |
| discouraged | discouraging |
| enchanted | enchanting |
| encouraged | encouraging |
| exhilarated | exhilarating |
| fascinated | fascinating |
| horrified | horrifying |
| intrigued | intriguing |
| overwhelmed | overwhelming |
| reassured | reassuring |
| shocked | shocking |
| thrilled | thrilling |
| troubled | troubling |
| unsettled | unsettling |
Usage of Participle Adjectives
Participle adjectives play a versatile role in English grammar, enriching sentences with descriptive nuances. Here’s a comprehensive overview of their usage:
- Describing Nouns: Participle adjectives modify nouns to convey their attributes or qualities.
- Example: The excited children eagerly awaited the arrival of Santa Claus.
- Attributive Position: They often precede the noun they modify.
- Example: He admired the beautiful sunset over the horizon.
- Predicative Position: Participle adjectives can follow linking verbs like “be,” “seem,” or “appear” to describe the subject.
- Example: The cake smells delicious.
- Compound Nouns: They form compound nouns to create new terms.
- Example: A broken-hearted person may find it difficult to move on.
- Participial Phrases: They enrich sentences within participial phrases.
- Example: Sitting quietly in the corner, the cat watched the birds outside.
- Reduced Relative Clauses: Participle adjectives are used in reduced relative clauses for conciseness.
- Example: The woman sitting at the table is my aunt.
- Appositives: They function as appositives to rename or provide additional information about a noun.
- Example: The athlete, running fast, crossed the finish line first.
- Verb Complements: They complement verbs, offering additional information about the action.
- Example: She found the movie boring.
- Present and Past Participles: Both present (-ing) and past (-ed, -en, -t) participles serve as adjectives, indicating ongoing or completed actions/states.
- Example: The dancing couple captivated the audience. (Present participle)
- Example: The broken vase lay on the floor. (Past participle)
- Emotional States: They can convey emotional states or reactions.
- Example: The surprised expression on her face told us she wasn’t expecting the gift.
Quiz:
- What is a Participle Adjective?
- A) A type of noun
- B) An action verb
- C) An adjective formed from a verb
- D) An adverbial phrase
- Which suffix is commonly used to form present participles?
- A) -ing
- B) -ed
- C) -ly
- D) -er
- How do you form a past participle from a base verb ending in ‘e’?
- A) Add “-d”
- B) Double the consonant and add “-ed”
- C) Just add “-ed”
- D) Remove the ‘e’ and add “-ing”
- In which position do participle adjectives typically appear in a sentence?
- A) Before the noun
- B) After the noun
- C) Between the subject and the verb
- D) At the end of the sentence
- Which of the following is a past participle?
- A) Running
- B) Stopped
- C) Exciting
- D) Swimming
- What role do participle adjectives play in a sentence?
- A) They modify nouns
- B) They act as verbs
- C) They link two clauses
- D) They describe adverbs
- How are participle adjectives used in reduced relative clauses?
- A) They serve as appositives
- B) They follow linking verbs
- C) They enrich sentences with descriptive details
- D) They replace pronouns
- Which verb form is typically used for ongoing actions or states?
- A) Present participle
- B) Past participle
- C) Infinitive
- D) Gerund
- What is the participle adjective in the sentence: “The book, written by a famous author, became a bestseller”?
- A) Written
- B) Book
- C) Famous
- D) Author
- How do you form a past participle from a base verb ending in a consonant after a stressed vowel?
- A) Add “-ed”
- B) Double the consonant and add “-ed”
- C) Add “-d”
- D) Add “-ing”
Answers:
- An adjective formed from a verb
- -ing
- Just add “-ed”
- Before the noun
- Stopped
- They modify nouns
- They enrich sentences with descriptive details
- Present participle
- Written
- Double the consonant and add “-ed”
FAQs:
- What are participle adjectives?
- Participle adjectives are adjectives formed from verbs. They typically end in “-ing” (present participle) or “-ed” (past participle) and describe the characteristics or qualities of nouns.
- How are participle adjectives different from regular adjectives?
- Participle adjectives are formed from verbs, while regular adjectives are independent words. Participle adjectives often indicate ongoing actions or states (present participles) or completed actions or states (past participles).
- Can you provide examples of participle adjectives?
- Sure! Examples include “exciting” (present participle), “bored” (past participle), “fascinating” (present participle), and “surprised” (past participle).
- How do you form participle adjectives?
- The formation of participle adjectives depends on the verb’s base form. For example, verbs ending in “-e” simply add “-d” to form the past participle (e.g., “bake” becomes “baked”). Verbs ending in a consonant after a vowel double the consonant and add “-ed” (e.g., “stop” becomes “stopped”). Verbs ending in a consonant after a stressed vowel just add “-ed” (e.g., “enter” becomes “entered”).
- Where are participle adjectives used in sentences?
- Participle adjectives can be used before nouns (attributive position) or after linking verbs like “be” (predicative position). They add descriptive detail to sentences and enhance the reader’s understanding of the noun.
- What is the difference between present and past participles in participle adjectives?
- Present participles (-ing) typically indicate ongoing actions or states, while past participles (-ed, -en, -t) indicate completed actions or states. For example, “the running dog” (present participle) versus “the tired dog” (past participle).
You May Also Like:
- Simple Past Tense With Examples, Rules, Usage
- 60 Examples of Adjectives in Sentences
- Irregular Verbs in English with Examples
- 500 Verbs Forms List A to Z in English
- Music Notes Names and HTML Codes