Contents
Are you confused about when to use Will and Be going to in English? Don’t worry, you’re not alone! These two words might seem similar, but they’re used in different situations to talk about the future. “will” is used for decisions made at the moment of speaking or for predictions about the future, while “be going to” is used for plans or intentions already decided before the moment of speaking. Let’s explore these concepts further to understand how to use them correctly in everyday English!
When to Use Will
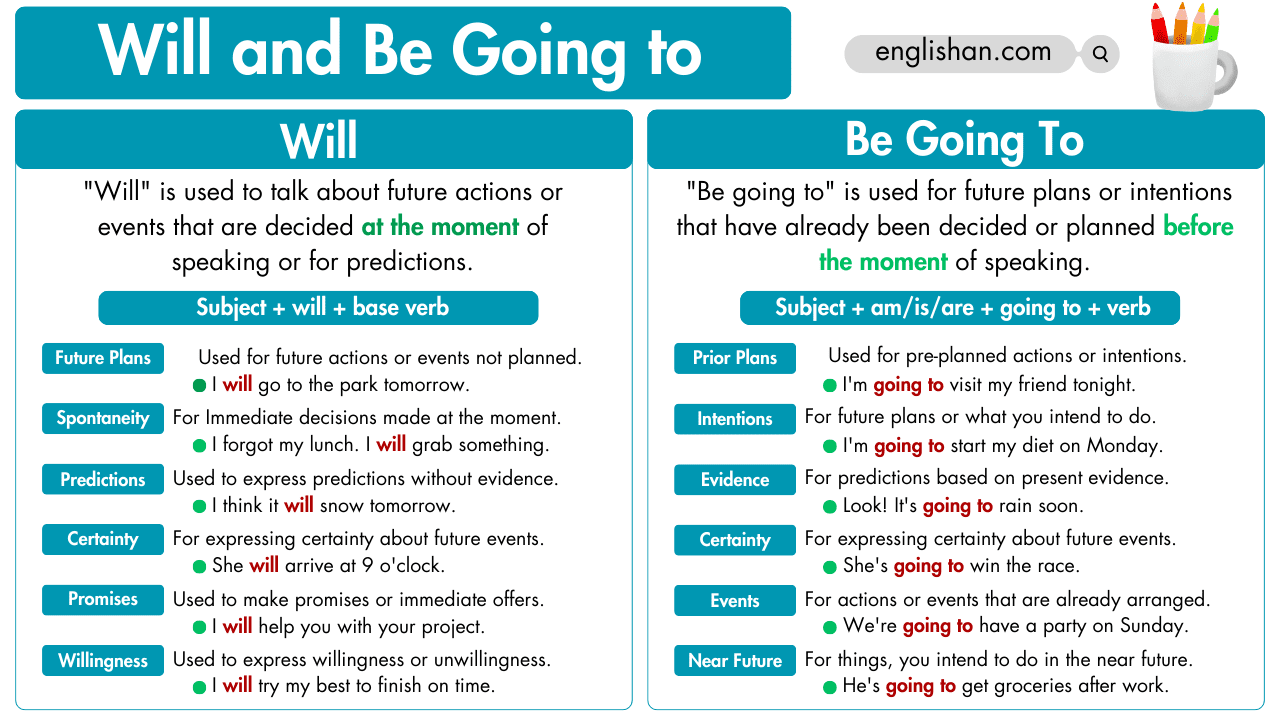
We use will to talk about future actions or events that we decide at the moment of speaking. For example: “I will call you later.” Here, the decision to call is made at the moment of speaking.
Future Tense: Use “will” to talk about actions or events that will happen in the future.
-
- Example: I will go to the park tomorrow.
Spontaneous Decisions: Use “will” to make decisions at the moment of speaking.
-
- Example: Oh no! I forgot my umbrella. I will buy one.
Promises or Offers: Use “will” to make promises or offers.
-
- Example: I will help you with your homework.
Predictions or Assumptions: Use “will” to express predictions or assumptions about the future.
-
- Example: I think it will rain later.
Expressions of Certainty: Use “will” when you are certain about something happening in the future.
-
- Example: She will be here soon.
Habitual Actions: Sometimes “will” is used to describe habitual actions, but this is less common and usually used in narratives or storytelling.
-
- Example: Every morning, he will go for a run.
Conditional Statements (First Conditional): Use “will” in the first part of conditional sentences to express a possible future action.
-
- Example: If it rains, I will bring an umbrella.
Expressions of willingness: Use “will” to express willingness or unwillingness to do something.
-
- Example: I will try my best.
When to Use Going To
We use “be going to” to talk about future plans or intentions that we have already decided or arranged before the moment of speaking. For example: “I am going to visit my grandmother tomorrow.” Here, the plan to visit the grandmother was made before the moment of speaking.
Future Plans: Use “going to” to talk about future plans or intentions that you have already decided before speaking.
-
- Example: I am going to visit my friend. (Pre-planned action)
Intentions: Use “going to” to express your intentions or what you plan to do in the future.
-
- Example: She is going to start a new job next month.
Predictions Based on Evidence: Use “going to” to make predictions about the future based on present evidence or signs.
-
- Example: Look at those dark clouds. It‘s going to rain soon.
Expressions of Future Events: Use “going to” to indicate future events or outcomes that seem likely to happen.
-
- Example: The bus is late. I‘m going to be late for class.
Expressions of Certainty: Use “going to” when you’re quite certain about something happening shortly.
-
- Example: He is going to win the race.
Casual Speech and Informal Writing: “Going to” is commonly used in everyday conversations and informal writing.
-
- Example: I‘m going to make some tea. Would you like some?
Planned Actions or Arrangements: Use “going to” to talk about actions or events that are already planned or arranged.
-
- Example: We are going to have a party on Saturday.
Intentions in the Near Future: Use “going to” to talk about things you intend to do in the near future.
-
- Example: I‘m going to clean my room this afternoon.
Rules for Using Will and Going To
Will and going to are both used to talk about future events, but they are used in slightly different contexts. Here are the basic rules for using each:
- Will:
- Form: Subject + will + base verb (e.g., I will go).
- Use will for decisions made at the moment of speaking.
- Use will for future actions not planned beforehand.
- Use will for promises, offers, or expressions of certainty.
- Use will for predictions or assumptions about the future.
- Use will in conditional sentences (first conditional) for possible future actions.
- Use will for expressing willingness or unwillingness.
- Example: I will go to the store. (I am deciding right now to go to the store.)
- Going To:
- Form: Subject + am/is/are + going to + base verb.
- Use going to for future plans or intentions decided before speaking.
- Use going to for predictions based on current evidence or signs.
- Use going to for discussing near future plans or intentions.
- Use going to for expressing intentions or goals for the future.
- Use going to for describing events likely to happen in the future.
- Use going to for actions or events that are already arranged.
- Example: I am going to visit my friend tomorrow. (I have already made plans to visit my friend tomorrow.)
Difference Between Will and Be Going To
The difference between will and be going to lies in their usage and the context in which they are used:
- Will is used to talk about future actions or events that we decide at the moment of speaking. It’s like making a decision in the present about something we will do in the future. For example:
- I will call you later.
- She will arrive at 8 o’clock.
- Be going to is used to talk about future plans or intentions that we have already decided or arranged to do. It’s like having a plan in mind already. For example:
- I’m going to study for the exam.
- They are going to buy a new car.
Will vs Be Going to Chart
Key differences between will and be going to:
| Aspect | Will | Be Going to |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Will + base verb | Am/Is/Are + going to + base verb |
| Usage | Used for decisions made at the moment of speaking | Used for plans or intentions made before the moment of speaking |
| Example | I will call you tomorrow. | She is going to visit her parents this afternoon. |
| Decision Time | At the moment of speaking | Pre-planned or intention already decided |
| Certainty | Can express willingness or uncertainty | Suggests a stronger intention or plan |
| Predictions | Based on current knowledge or intuition | Based on current evidence or plans |
| Informal Situations | Common in casual conversations | Also common but often in slightly formal contexts |
| Future Events | Actions or events not necessarily planned | Actions or events with prior intent |
| Spontaneity | Used for quick, on-the-spot decisions | Used for planned actions and intentions |
| Response to Request | Often used for promises or offers | Often used for answering “What are you going to do?” or “What are you planning to do?” |
Will and Be Going to Example Sentences
Here are some simple example sentences using will and be going to:
Will:
- I will call you later.
- The sun will set soon.
- I will go to the store later.
- Will you join us for dinner?
- He will finish his work soon.
- Will it rain tomorrow?
- Will they arrive on time?
- She will cook dinner for us.
- We will watch a movie tonight.
- The sun will rise in the east.
- We will go for a walk in the park.
- He will start his new job next month.
- Will you please turn off the lights?
- She will study for her test tonight.
- Will you be at the party tomorrow?
Be Going To:
- I am going to cook dinner tonight.
- The bus is going to arrive soon.
- I am going to call my friend later.
- We are going to have lunch together.
- I am going to visit my friend tomorrow.
- She is going to learn Spanish.
- He is going to fix his car tomorrow.
- Are you going to attend the meeting?
- He is going to buy a new car next week.
- Am I going to see you later?
- She is going to plant flowers in the garden.
- He is going to study abroad next year.
- Is she going to finish her project on time?
- She is going to start a new job in the city.
- She is going to bake a cake for her birthday.
- They are going to buy groceries this evening.
Will and Be Going to Exercises
Choose the correct future form (will or be going to) to complete each sentence.
- I think it ______ rain later.
- She _________ visit her grandmother tomorrow.
- They ___________ buy a new car next month.
- He _________ call you as soon as he arrives.
- We ____________ have a barbecue this weekend.
- Sarah ________ go to the gym after work.
- Tom _________ help you with your homework tonight.
- The company _________ launch a new product next year.
- I ____________ see that movie when it comes out.
- They ___________ travel to Europe next summer.
- It ________ be a sunny day tomorrow.
- She _________ start her new job next Monday.
- We ____________ have pizza for dinner tonight.
- He ___________ study harder if he wants to pass the exam.
- My parents ____________ come to visit us next weekend.
Answer Key:
- will
- is going to
- are going to
- will
- are going to
- is going to
- will
- will
- will
- are going to
- will
- is going to
- are going to
- will
- are going to
FAQs
We use will to express a decision made at the moment of speaking or to make predictions about the future based on current observations or beliefs. For example:
1. I will call you later.
2. It will rain tomorrow.
“Be going to” is used to express a planned intention or future event that is already decided upon or expected to happen based on evidence or current circumstances. For example:
1. I am going to start my diet next week.
2. She is going to visit her parents later.
“Will” is used to express future actions or states that are not planned or decided at the moment of speaking, whereas “be going to” is used to talk about future plans or intentions that have already been decided or prepared.
She will buy a new dress.
They are going to buy a new car.
I will study for the exam tomorrow.
I am going to cook dinner tonight.
They will visit Paris next summer.
Read More