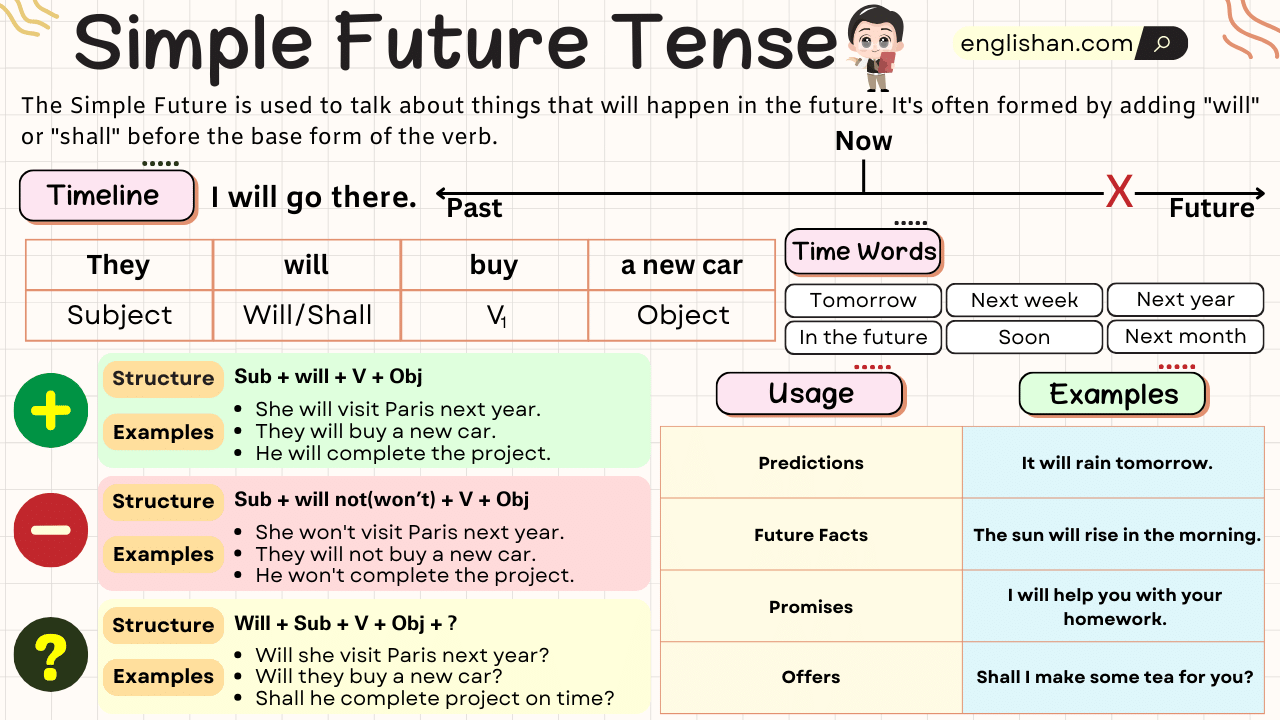
The Simple Future Tense is a verb form used to describe an action or event that will happen after the present moment. It is one of the ways to express the future in English. The Simple Future Tense is formed using the auxiliary verb “will” (or “shall” in some cases) followed by the base form of the main verb.
Examples:
- Positive: I will study for my exam.
- Negative: She will not (won’t) attend the party.
- Interrogative: Will they arrive on time?
Usages of the Simple Future Tense
Predictions and Statements about the Future
- Predictions
These are statements that provide information about future events or situations without relying on empirical evidence or specific reasons.
Examples:
- The weather forecast predicts rain tomorrow.
- The cake will be delicious.
- He will probably pass the exam.
- It will rain later today.
- She thinks he will like the gift.
- The bus will arrive soon.
- The team won’t win the championship this year.
- She doesn’t think it will snow in April.
- I doubt he will pass the exam without studying.
- According to the forecast, it won’t be sunny tomorrow.
- They believe the project won’t be completed on time.
- Will it rain tomorrow?
- Do you think she’ll win the game?
- Will he get the job?
- Do you believe the team will score a goal?
- Will the movie be interesting?
Statements about the Future
These are statements that declare forthcoming events, actions, or situations. They are based on reliable sources or announcements.
Examples:
- I will visit my grandparents next weekend.
- The sun will shine brightly tomorrow.
- She is going to bake a cake for her friend’s birthday.
- We will have a picnic in the park on Saturday.
- He will get a gift for his little sister.
- I won’t be able to attend the party on Friday.
- The store won’t be open after 9 PM.
- She isn’t going to travel abroad this summer.
- They won’t have a class on Saturday.
- He won’t get his new bicycle until next month.
- Will you come to my birthday party next Saturday?
- Are they going to the zoo tomorrow?
- Will the movie start at 7 PM?
- Is she going to buy a new dress for the event?
- Will we have a test next week?
Spontaneous Decisions
Spontaneous decisions are choices made in the moment, without extensive planning or forethought, often based on immediate feelings or circumstances.
Examples:
- I think I’ll have pizza for dinner tonight.
- She suddenly decided to join the dance class.
- He spontaneously chose to go for a walk in the park.
- We’ve decided to watch a movie this evening.
- They just decided to visit the beach this weekend.
- I won’t eat cake, I’m not hungry.
- She changed her mind and won’t play outside.
- He decided he won’t watch TV tonight.
- We won’t go to the park, it’s too hot.
- They won’t buy ice cream, they’re on a diet.
- Are you going to play outside now?
- Did she decide to read a book instead?
- Will he eat his vegetables today?
- Are we having pasta for dinner?
- Did they choose to watch a movie?
Offers, Promises, and Requests
Offers, promises, and requests are forms of communication where individuals express willingness to help, commit to a certain action, or ask for assistance or a favor, respectively.
Examples:
- I can help you with your homework. (Offer)
- I promise to be there for your graduation ceremony. (Promise)
- Would you like some assistance carrying those bags? (Offer)
- I assure you, I will finish the project on time. (Promise)
- Could you please pass me the salt? (Request)
- I can’t help with that, I’m not feeling well. (Offer)
- I’m sorry, I can’t give you a ride, my car isn’t working. (Offer)
- She can’t lend you her book, she’s using it. (Offer)
- I won’t forget to return your pen tomorrow. (Promise)
- She can’t promise to attend the party, she might be busy. (Promise)
- They won’t guarantee delivery by Friday. (Promise)
- Could you please not make noise while I’m on the phone? (Request)
- Would you mind not touching my computer without asking? (Request)
- Can I help you with anything? (Offer)
- Would you like some tea or coffee? (Offer)
- Will you promise to return the book when you’re done? (Promise)
- Can you assure me that you’ll be there on time? (Promise)
- Could you please turn down the volume on the TV? (Request)
- Would you mind not leaving the lights on when you leave? (Request)
Scheduled Events
Scheduled events are planned activities set to happen at specific times and dates in the future. They are organized in advance and follow a predetermined timetable. Examples include meetings, appointments, classes, concerts, and flights.
Examples:
- The movie starts at 3 PM on Sunday.
- We have a family picnic next Saturday.
- The class ends at noon.
- Her birthday party is on Friday evening.
- The concert is tomorrow night.
- The meeting is not happening today.
- The play got canceled due to bad weather.
- Unfortunately, the event won’t take place.
- The lecture has been postponed to next week.
- The flight got delayed until further notice.
- What time does the game start on Sunday?
- Is the party still on for this weekend?
- Will the workshop be rescheduled for a later date?
- Are we meeting at the usual location for the hike?
- Can you confirm if the flight is delayed?
Facts or Certainties about the Future
Facts or certainties about the future refer to events or situations that are known or expected to happen with a high degree of confidence.
Examples:
- The sun will rise tomorrow morning.
- The company will release their new product next month.
- She will graduate in June.
- The train will depart at exactly 3 PM.
- They will arrive at the airport an hour before the flight.
- The store won’t be open after 9 PM.
- The concert won’t happen if it keeps raining.
- Unfortunately, the lecture has been canceled.
- The event was called off due to unforeseen circumstances.
- The class won’t take place if the instructor is absent.
- Will the meeting start at 2 PM as scheduled?
- Are we sure the package will arrive by Friday?
- Can we expect clear skies for the event?
- Is it certain that the train will arrive on time?
- Will the store be open on New Year’s Day?
Simple Future Tense Chart
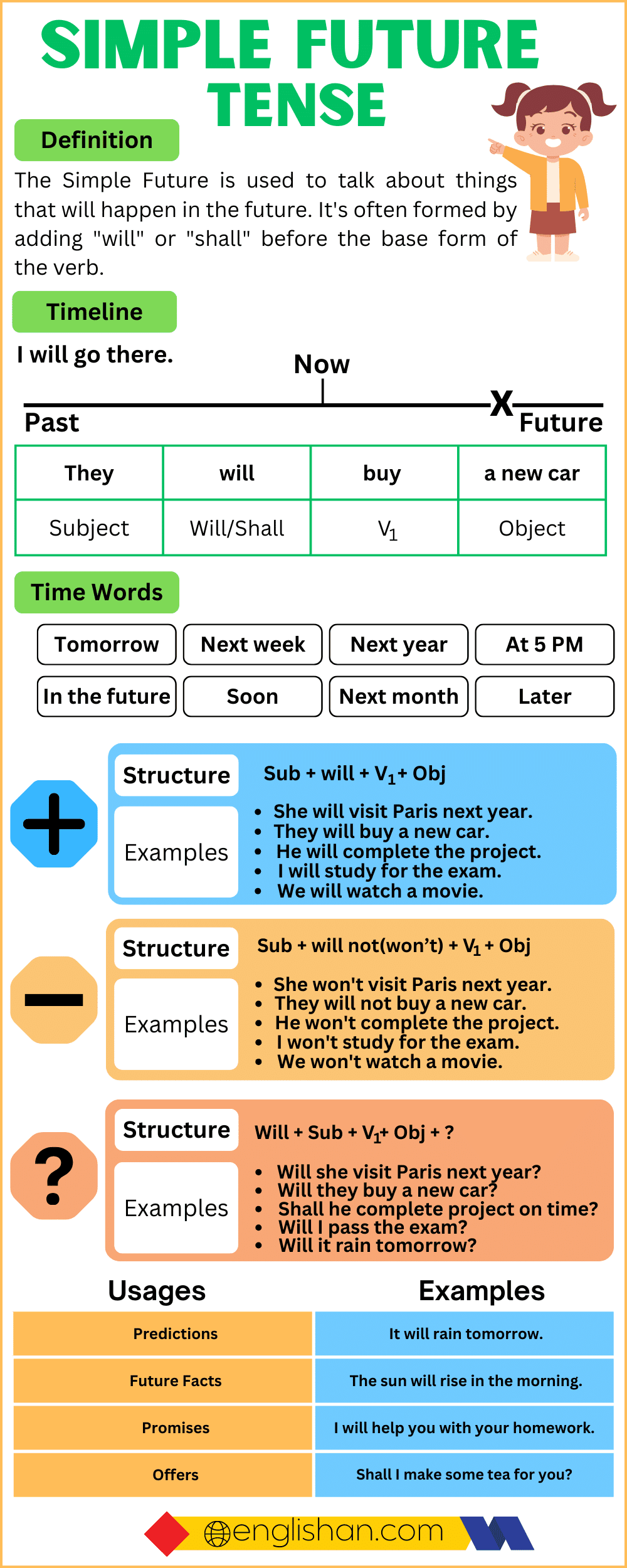
Time Expressions
Time expressions are words or phrases that tell us when an action happens. They provide information about the timing or duration of events. Examples include yesterday, next week, and at 3 PM. They help establish a timeline in communication.
Examples:
- She will call you tomorrow.
- They are leaving in an hour.
- I have an appointment at 3 PM.
- We’ll meet next week.
- He’ll arrive soon.
Be Going To vs. Simple Future
Used for intentions, plans, and predictions based on current evidence.
Examples:
- She is going to start a new job next month.
- She’s going to read a book tonight.
- They’re going to play in the park after lunch.
- He’s going to eat pizza for dinner.
- We’re going to visit Grandma tomorrow.
- I’m going to watch a movie this weekend.
Used for intentions, plans, and predictions based on current evidence.
Examples:
- I will call you later.
- She will complete her assignment before the deadline.
- They are going to visit the museum this Saturday.
- He will probably win the race; he’s been training hard.
- We are planning to have a picnic in the park next Sunday.
- The weather forecast suggests it will rain later today.
Forming the Simple Future Tense
Affirmative Sentences
Affirmative sentences are statements that express a fact, confirmation, or agreement. They convey a positive or true assertion.
- They will attend the concert on Saturday.
- He will play the guitar at the event.
- We will have lunch together tomorrow.
- She will help her friend with the project.
- They will take a vacation in the summer.
- He will learn to swim this year.
- We will meet at the coffee shop in the evening.
- She will visit the museum next week.
- They will celebrate their anniversary in style.
- He will fix the broken window.
- We will adopt a puppy from the shelter.
- She will bake cookies for the bake sale.
- They will organize a charity event.
- He will join a fitness class.
- We will explore a new hiking trail.
- She will volunteer at the local community center.
- They will learn a new language.
- He will start a blog about his travels.
- We will have a family picnic in the park.
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
| Subject | Will | Verb (1st Form) | Object | Complement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| They | will | attend | the concert | on Saturday. |
| He | will | play | the guitar | at the event. |
| We | will | have | lunch together | tomorrow. |
| She | will | help | her friend | with the project. |
| They | will | take | a vacation | in the summer. |
| He | will | learn | to swim | this year. |
| We | will | meet | at the coffee shop | in the evening. |
| She | will | visit | the museum | next week. |
| They | will | celebrate | their anniversary | in style. |
| He | will | fix | the broken window | . |
| We | will | adopt | a puppy | from the shelter. |
| She | will | bake | cookies | for the bake sale. |
| They | will | organize | a charity event | . |
| He | will | join | a fitness class | . |
| We | will | explore | a new hiking trail | . |
| She | will | volunteer | at the local community center | . |
| They | will | learn | a new language | . |
| He | will | start | a blog about his travels | . |
| We | will | have | a family picnic | in the park. |
Negative Sentences
Negative sentences in the Simple Future Tense are formed by adding will not (or the contraction won’t) before the base form of the verb. This indicates that an action will not happen in the future.
Subject + will/shall + not + verb (1st form) + object.
- I will not eat candy before dinner.
- She will not watch TV all day.
- They will not visit the zoo next weekend.
- He will not forget his friend’s birthday.
- We will not play video games after school.
- She will not go to the party on Friday night.
- They will not travel to Europe this summer.
- He will not buy a new phone this month.
- We will not have pizza for dinner tonight.
- She will not visit her grandparents next month.
- They will not attend the concert next week.
- He will not pass the test without studying.
- We will not forget to water the plants.
- She will not play soccer in the rain.
- They will not go swimming in the cold water.
- He will not eat vegetables for dinner.
- We will not go for a walk in the dark.
- She will not stay up late on a school night.
- They will not have a picnic in the rain.
- He will not get a puppy for his birthday.
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
| Subject | Will/Shall Not | Verb (1st Form) | Object. |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | will not | eat | candy before dinner. |
| She | will not | watch | TV all day. |
| They | will not | visit | the zoo next weekend. |
| He | will not | forget | his friend’s birthday. |
| We | will not | play | video games after school. |
| She | will not | go | the party on Friday night. |
| They | will not | travel | Europe this summer. |
| He | will not | buy | a new phone this month. |
| We | will not | have | pizza for dinner tonight. |
| She | will not | visit | her grandparents next month. |
| They | will not | attend | the concert next week. |
| He | will not | pass | the test without studying. |
| We | will not | forget | to water the plants. |
| She | will not | play | soccer in the rain. |
| They | will not | go | swimming in the cold water. |
| He | will not | eat | vegetables for dinner. |
| We | will not | go | for a walk in the dark. |
| She | will not | stay up | late on a school night. |
| They | will not | have | a picnic in the rain. |
| He | will not | get | a puppy for his birthday. |
Interrogative Sentences
Interrogative sentences in the simple future tense are sentences that ask questions about future actions or events. They typically start with an auxiliary verb (will or shall) followed by the subject, and then the base form of the main verb.
Shall/Will + subject + verb (1st form) + object?
- Will you attend the meeting tomorrow?
- Shall we go for a walk this evening?
- Will they arrive on time for the party?
- Shall I bring some snacks for the trip?
- Will he call you later?
- Will you join us for the movie?
- Shall we have a picnic in the park?
- Will they attend the conference next month?
- Shall I book the tickets for the concert?
- Will he start his new job next week?
- Shall we visit the zoo on Saturday?
- Will she try the new restaurant in town?
- Shall I bring some snacks for the road trip?
- Will they go hiking in the mountains?
- Will you participate in the charity event?
- Shall we organize a family game night?
- Will he take a vacation this summer?
- Shall we watch a movie at home?
- Will she learn to play a musical instrument?
- Will they celebrate their anniversary in style?
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
| Shall/Will | Subject | Verb (1st Form) | Object | Complement? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Will | you | attend | the meeting | tomorrow? |
| Shall | we | go | for a walk | this evening? |
| Will | they | arrive | on time | for the party? |
| Shall | I | bring | some snacks | for the trip? |
| Will | he | call | you | later? |
| Will | you | join | us | for the movie? |
| Shall | we | have | a picnic | in the park? |
| Will | they | attend | the conference | next month? |
| Shall | I | book | the tickets | for the concert? |
| Will | he | start | his new job | next week? |
| Shall | we | visit | the zoo | on Saturday? |
| Will | she | try | the new restaurant | in town? |
| Shall | I | bring | some snacks | for the road trip? |
| Will | they | go | hiking | in the mountains? |
| Will | you | participate | in the charity event | ? |
| Shall | we | organize | a family game night | ? |
| Will | he | take | a vacation | this summer? |
| Shall | we | watch | a movie | at home? |
| Will | she | learn | to play a musical instrument | ? |
| Will | they | celebrate | their anniversary | in style? |
Simple Future Tense Example Sentences
Positive Sentences
- I shall read this book.
- He will go to Lahore tomorrow.
- I shall stand by you.
- It will be Eid tomorrow.
- She will learn her lesson.
- You will pass her examination.
- She will play.
- Martin will paint.
- He will go.
- The mail will pluck the flowers.
- You will sing a song.
- I will visit my grandparents next weekend.
- She will cook a delicious meal for dinner.
- They will go for a walk in the park.
- He will start a new job in September.
- We will have a party for his birthday.
- She will read a book in the afternoon.
- They will watch a movie on Friday night.
- He will buy a new car next month.
- We will clean the house on Saturday morning.
- She will plant flowers in her garden.
- I will play Hockey.
- He will take tea.
- We shall visit the zoo.
- The sun will rise in the east.
Negative Sentences
- It will not rain.
- He will not come here.
- You will not oppose me.
- We shall not waste our time.
- They will not for us.
- We will not watch a scary movie before bed.
- You will not fly the kite.
- The teacher will not punish us.
- She will not bake cookies without flour.
- They will not go to the beach in the winter.
- He will not forget to set his alarm.
- We will not have ice cream for breakfast.
- She will not wear shorts in the snow.
- They will not go on a hike in the dark.
- He will not run in flip-flops.
- We will not forget to bring snacks.
- She will not forget to do her homework.
- They will not miss the bus tomorrow morning.
- He will not forget to bring his umbrella in case it rains.
Interrogative Sentences
- Will she make tea?
- Shall we play a match?
- Will you vote for me?
- When will you return my book?
- How will you pass a base coin?
- Shall we plan a beach day this weekend?
- Will he attend the workshop on Tuesday?
- Will you be available for a meeting tomorrow?
- Shall I call you when I arrive?
- Will it snow in December?
- Shall we go for a walk in the evening?
- Will they volunteer at the local shelter?
- Shall I pick up some groceries on the way?
- Will she join a dance class this year?
- Will they adopt a pet from the shelter?
- Shall we have a family dinner on Sunday?
- Will he start a new project at work?
- Shall I bring my camera for the trip?
- Will you try the new dessert at the cafe?
- Shall we explore a new hiking trail?
- Will you wait for me?
- Will you keep fasts?
- Will the watchman watch?
- What will you do after the school life?
- I will study for my exam.
Quiz:
- She (will visit, visits) her friend tomorrow.
- They (will go, goes) to the park on Sunday.
- He thinks he (will finish, finishes) the work by evening.
- By this time next year, we (will have traveled, travels) to five different countries.
- I (will call, calls) you when I reach home.
- They (will not attend, does not attend) the meeting if it gets too late.
- We (will start, starts) our vacation in July.
- She (will bake, bake) a cake for the party.
- I’m sure they (will win, wins) the competition.
- If you practice regularly, you (will improve, improve) your skills.
- The train (will leave, leaves) at 8:00 AM.
- She (will buy, buys) a new car next month.
- We (will meet, meets) our friends at the café later.
- He (will not forget, does not forget) your birthday this year.
- They believe they (will succeed, succeeds) in their new venture.
- The sun (will set, sets) at 7:30 PM.
- I (will send, sends) you an email with the details.
- We (will have, has) a great time at the party.
- She (will study, studies) hard for the exam.
- If it rains, we (will stay, stays) indoors.
Answers:
- will visit
- will go
- will finish
- will have traveled
- will call
- will not attend
- will start
- will bake
- will win
- will improve
- will leave
- will buy
- will meet
- will not forget
- will succeed
- will set
- will send
- will have
- will study
- will stay
FAQS:
- When do I use “will” and when do I use “shall” in the future tense?
- In modern English, “will” is generally used for all subjects. “Shall” is less common and is sometimes used in formal or literary contexts.
- Can I use the simple future tense to make predictions?
- Yes, the simple future tense can be used to make predictions or express future certainty based on present evidence or knowledge.
- Can I use time expressions with the simple future tense?
- Yes, time expressions like “tomorrow,” “next week,” “in a month,” and so on, are often used with the simple future tense to specify when an action will occur.
- Can I use adverbs of frequency with the simple future tense?
- No, adverbs of frequency (e.g., always, usually, sometimes) are typically used with present tenses to describe how often an action occurs.
- Can I use the simple future tense for plans and intentions?
- Yes, the simple future tense can be used to express plans, intentions, or decisions that have been made regarding future actions.
- Yes, the simple future tense can be used to express plans, intentions, or decisions that have been made regarding future actions.
You May Also Like
- Simple Present Tense With Examples
- Simple Past Tense With Examples
- Past Indefinite Tense Worksheets
- Worksheet Tenses
- English Worksheets
- Time Expressions in English for All Tenses