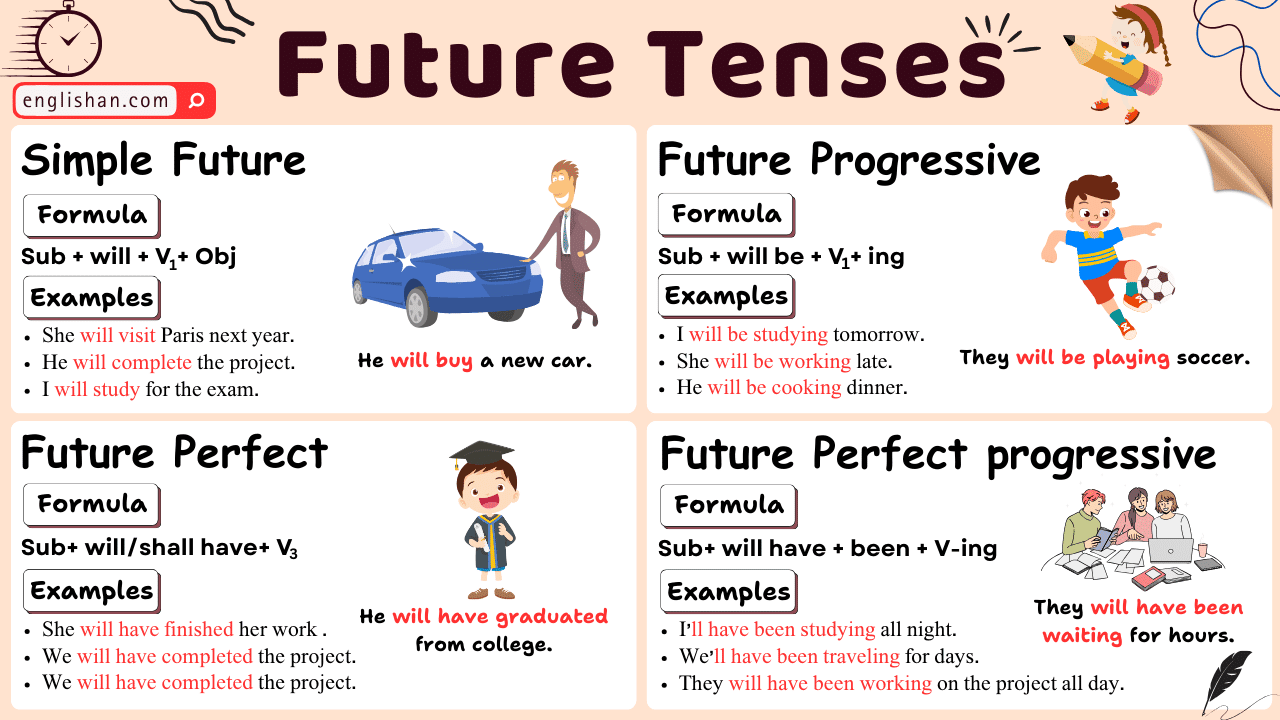
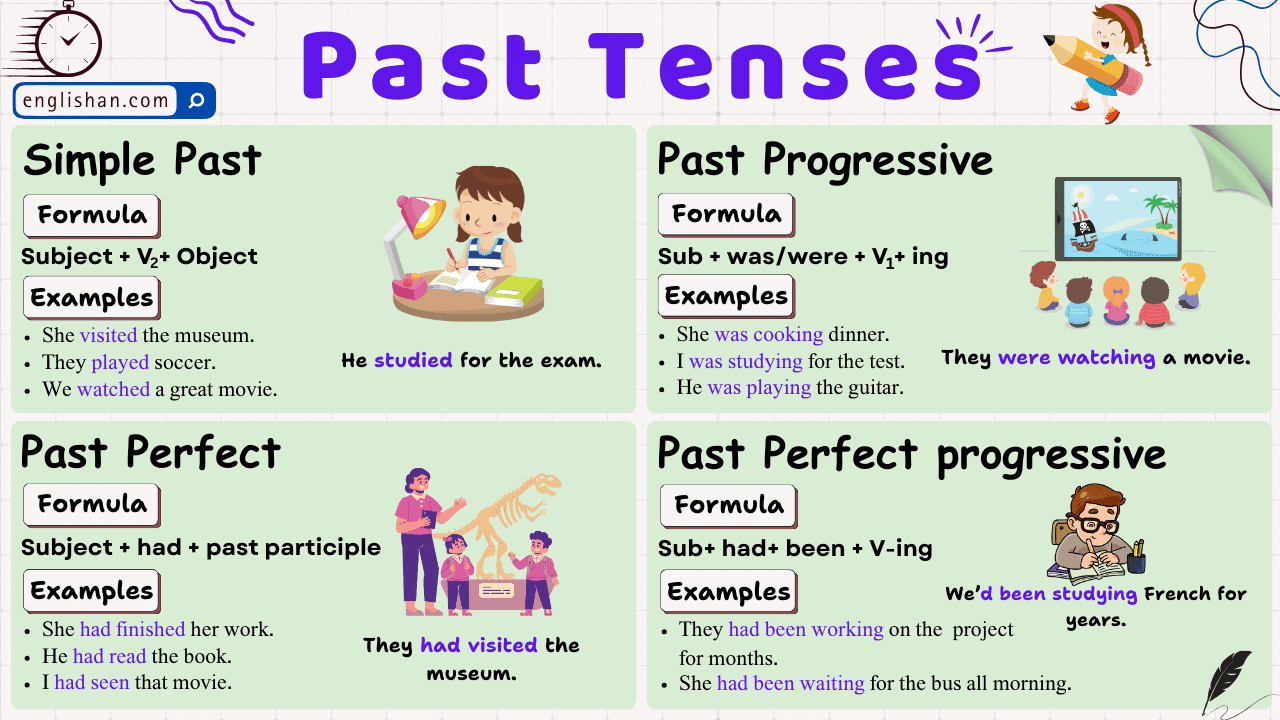
Contents
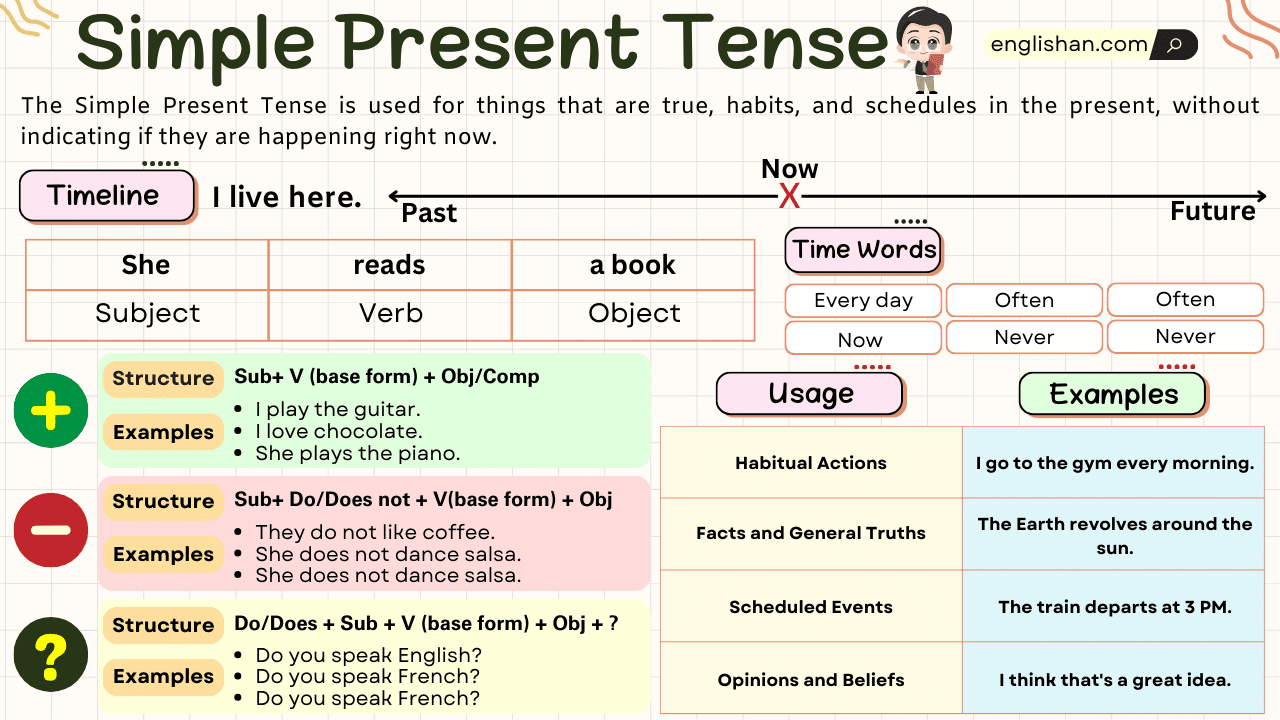
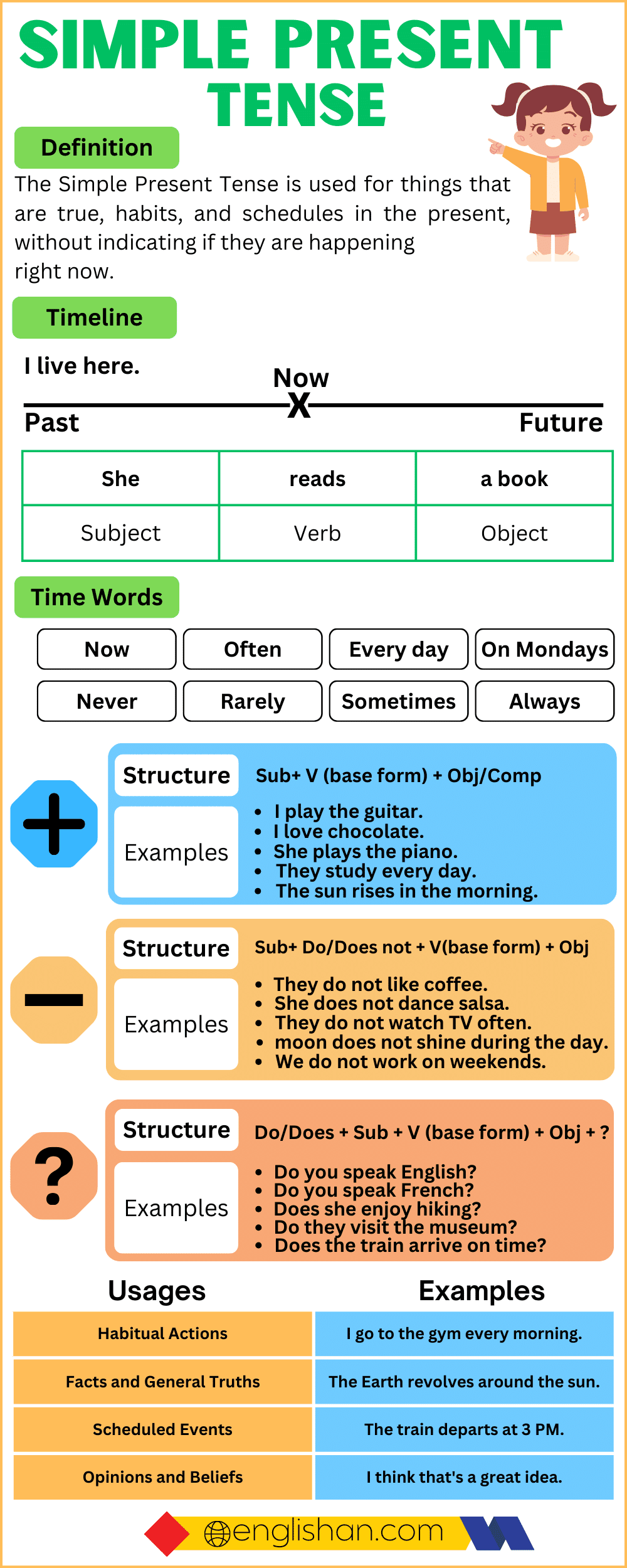
The Simple Present Tense is a grammatical tense used to describe actions, events, or situations that are general, habitual, or regular, and occur in the present time. It is used to convey facts, universal truths, habits, routines, and scheduled events.
Forming the Simple Present Tense
Affirmative Sentences
Affirmative sentences in the simple present tense express actions or states that occur regularly, habitually, or are generally true. The structure of affirmative sentences in the simple present tense often involves the base form of the verb (the verb without any additional endings or changes).
or
| Person | Example |
|---|---|
| First-person singular | I sing |
| Second person singular | You sing |
| Third person singular | He/She/It sings |
| First-person plural | We sing |
| Second person plural | You sing |
| Third person plural | They sing |
| Person | Example |
|---|---|
| First-person singular | I dance |
| Second person singular | You dance |
| Third person singular | He/She/It dances |
| First-person plural | We dance |
| Second person plural | You dance |
| Third person plural | They dance |
In other words, it only changes in the third person singular (he/she/it). It adds either s, es, or ies.
- I read in class 8.
- She goes to school in the morning.
- They play football on weekends.
- The sun rises in the east.
- It rains a lot in this region.
- The train departs at 7 AM.
- She speaks Spanish fluently.
- He always brushes his teeth before bed.
- The cat chases the mouse.
- The store opens at 9 AM.
- They go to school on foot.
- We take breakfast at 7 o’clock.
- I agree with you.
- You take a bath daily.
- She wears new clothes.
- He cleans his teeth.
- I hate smoking.
- The crow caws.
- I always speak the truth.
- She leads a simple life.
- He fixes the computer when it has issues.
- She washes her car every Saturday.
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
| Subject | Verb (1st form) | Object | Complement. |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | read | – | in class 8. |
| She | goes | school | in the morning. |
| They | play | football | on weekends. |
| The sun | rises | – | in the east. |
| It | rains | a lot | in this region. |
| The train | departs | – | at 7 AM. |
| She | speaks | Spanish | fluently. |
| He | brushes | his teeth | before bed. |
| The cat | chases | the mouse | . |
| The store | opens | – | at 9 AM. |
| They | go | school | on foot. |
| We | take | breakfast | at 7 o’clock. |
| I | agree | – | with you. |
| You | take | a bath | daily. |
| She | wears | new clothes | . |
| He | cleans | his teeth | . |
| I | hate | smoking | . |
| The crow | caws | – | . |
| I | always speak | the truth | . |
| She | leads | a simple life | . |
| He | fixes | the computer | when it has issues. |
| She | washes | her car | every Saturday. |
Negative Sentences
Negative sentences in the simple present tense express actions or states that do not happen regularly, habitually, or are not generally true. In negative sentences, we typically use the auxiliary verb do (in its base form do or does) along with not, and the base form of the main verb. To create a negative sentence, use do not + [base form of the verb]. (Use does not with third person singular (he/she/it).
Subject + do not/ does not + verb(1st form) + object.
- I do not like coffee.
- You do not speak Spanish.
- We do not play tennis on Sundays.
- They do not eat meat.
- He does not watch TV in the morning.
- She does not drive a car.
- It does not rain much in this area.
- The cat does not like water.
- We do not visit our grandparents often.
- You do not understand French.
- He does not play the guitar.
- She does not cook dinner on Fridays.
- It does not snow in our city.
- They do not study on weekends.
- I do not go to the gym every day.
- You do not work on Saturdays.
- We do not travel abroad frequently.
- He does not take sugar in his tea.
- She does not read novels regularly.
- The bus does not arrive on time.
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
| Subject | Do not/Does not | Verb (1st Form) | Object | Complementation. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | do not | like | coffee | . |
| You | do not | speak | Spanish | . |
| We | do not | play | tennis | on Sundays. |
| They | do not | eat | meat | . |
| He | does not | watch | TV | in the morning. |
| She | does not | drive | a car | . |
| It | does not | rain | much | in this area. |
| The cat | does not | like | water | . |
| We | do not | visit | our grandparents | often. |
| You | do not | understand | French | . |
| He | does not | play | the guitar | . |
| She | does not | cook | dinner | on Fridays. |
| It | does not | snow | – | in our city. |
| They | do not | study | – | on weekends. |
| I | do not | go | to the gym | every day. |
| You | do not | work | – | on Saturdays. |
| We | do not | travel | abroad | frequently. |
| He | does not | take | sugar | in his tea. |
| She | does not | read | novels | regularly. |
| The bus | does not | arrive | – | on time. |
Using “do not” (don’t):
- I don’t like spicy food.
- She doesn’t play video games.
- They don’t go to the gym on Saturday.
- He doesn’t watch horror movies.
- We don’t eat fast food very often.
Using “does not” (doesn’t):
- She doesn’t like coffee.
- He doesn’t play video games.
- The car doesn’t start in the cold weather.
- Mary doesn’t work on Mondays.
- It doesn’t rain much in the desert.
Interrogative Sentences
If you need to ask a question, you can use the following word order for a yes/no question:
- Does she read books every day?
- Do they play football on weekends?
- Does he speak French fluently?
- Does the sun rise in the west?
- Do we visit our grandparents often?
- Do you go to the gym every day?
- Do cats chase dogs?
- Does he like vanilla ice cream?
- Does the store open at 9 AM?
- Does the train depart at 7 AM?
- Do we live near the park?
- Do they enjoy swimming?
- Does she take the bus to work?
- Does he work as a chef?
- Does the cat meow loudly?
- Do you play the violin in the evenings?
- Do birds sing at night?
- Does she dance gracefully?
- Do we eat lunch at 2 PM?
- Does it rain a lot in this city?
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
| Do/Does | Subject | Verb (1st Form) | Object | Complement+? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Does | she | read | books | every day? |
| Do | they | play | football | on weekends? |
| Does | he | speak | French | fluently? |
| Does | the sun | rise | – | in the west? |
| Do | we | visit | our grandparents | often? |
| Do | you | go | the gym | every day? |
| Do | cats | chase | dogs | ? |
| Does | he | like | vanilla ice cream | ? |
| Does | the store | open | – | at 9 AM? |
| Does | the train | depart | – | at 7 AM? |
| Do | we | live | near the park | ? |
| Do | they | enjoy | swimming | ? |
| Does | she | take | the bus to work | ? |
| Does | he | work | as a chef | ? |
| Does | the cat | meow | – | loudly? |
| Do | you | play | the violin | in the evenings? |
| Do | birds | sing | – | at night? |
| Does | she | dance | – | gracefully? |
| Do | we | eat | lunch | at 2 PM? |
| Does | it | rain | a lot | in this city? |
The Spelling Rules
In simple present tense, we often add s or es to the verb when talking about he, she, or it (like a single person or thing). Here’s how it works:
- For most verbs, just add s: He walks, she runs, it rains.
- If a verb ends in ss, sh, ch, x, or o, add es: He passes, she washes, it matches, he fixes, it goes.
- If a verb ends in a consonant + y, change y to i and add es: He cries, she flies, it dries.
Formation of Verbs that end in sh, ch, s, ss,x /o +es:
| Base Form | Person Singular |
|---|---|
| Wash | washes |
| Wish | Wishes |
| Go | Goes |
| Finish | Finishes |
| Watch | Watches |
| Miss | Misses |
| Pass | Passes |
| Fix | Fixes |
| Go | Goes |
| Do | Does |
| Kiss | Kisses |
| Dress | Dresses |
| Mash | Mashes |
| Cross | Crosses |
| Guess | Guesses |
For verbs ending [consonant]-y, change the y to i and add es:
| Base Form | Third-Person Singular Form |
|---|---|
| Study | Studies |
| Fly | Flies |
| Try | Tries |
| Cry | Cries |
| Apply | Applies |
| Identify | Identifies |
| Reply | Replies |
| Multiply | Multiplies |
| Carry | Carries |
| Spy | Spies |
| Comply | Complies |
| Deny | Denies |
| Supply | Supplies |
| Defy | Defies |
| Apply | Applies |
Usage of Simple Present Tense
1. Habits and Routines
- It is used to describe actions that are habitual, repeated, or regular.
Examples:
-
- She reads a book every night before bed. (Habit)
- She wakes up at 6 AM every morning. (Routine)
- They have breakfast together before work. (Routine)
- He takes a walk in the park every evening. (Habit)
- We watch our favorite TV show every Monday night. (Routine)
- The children play soccer after school. (Habit)
2. General Truths and Facts
- The Simple Present Tense is used to state facts that are generally true and do not change over time.
Examples:
-
- The Earth revolves around the sun. (General Truth)
- Water is made of hydrogen and oxygen. (Facts)
- Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius (General Truth).
- Gravity pulls things towards the Earth. (Facts)
- The sky appears blue on clear days (General Truth).
- Our body has many bones. (Facts)
- The moon has gravitational effects on Earth’s tides. (General Truth)
- The human body requires oxygen to survive. (General Truth)
- Water’s chemical name is H2O. (Facts)
- The Nile River is very long. (General Truth)
3. Scheduled Events
- It can be used to express future events that are part of a schedule, especially in the context of timetables and plans.
Examples:
-
- The train departs at 3 PM.
- The train departs at 8:00 AM tomorrow.
- The conference starts on Monday at 9:00 AM.
- Our flight lands at 3:30 PM next week.
- The school assembly takes place every Friday morning.
- The concert begins at 7:30 PM this Saturday.
4. Universal Truths
- It is used to convey principles, scientific facts, and truths that apply universally.
Examples:
-
- Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.
- The Earth rotates on its axis.
- Water freezes at zero degrees Celsius.
- The Earth rotates on its axis.
- Birds fly in the sky.
- The sun rises in the east.
- Plants need sunlight to grow.
- Fish live in water.
5. Commentaries on Narratives
- When providing commentary on a book, movie, or story, the Simple Present Tense is often used to discuss events in the plot.
Examples:
-
- In the story, the protagonist lives in a small town.
- The brave knight draws his sword to face the dragon.
- The curious kitten climbs up the tree to explore.
- The wise old owl watches silently from its perch.
- The mischievous elves giggle as they plan their pranks.
- The gentle breeze rustles the leaves in the forest.
- The colorful flowers bloom in the springtime.
6. Instructions and Directions
- The Simple Present Tense is used for giving directions or instructions, especially in recipes or manuals.
Examples:
-
- First, you mix the ingredients together. (Instruction)
- Open the book to page 10. (Direction)
- Mix the ingredients in a bowl. (Instruction)
- Turn left at the next intersection. (Direction)
- Wait for the green light before crossing the street. (Direction)
- Write your name at the top of the paper. (Instruction)
- Read the instructions before assembling the toy. (Instruction)
7. Sports Commentaries
- In sports commentary, the Simple Present Tense is often used to describe ongoing events in real time.
Examples:
-
- The quarterback throws the ball to the wide receiver.
- The striker shoots and scores! What a fantastic goal!
- The pitcher throws a fastball, and it’s a strike!
- The sprinter runs down the track with incredible speed.
- The goalie blocks the shot, preventing a goal.
- The golfer tees off with precision and accuracy.
- The basketball player dribbles down the court, looking for an open teammate
Simple Present Tense Example Sentences
Positive Sentences
- She practices yoga every morning.
- They eat breakfast at 7 AM.
- The company produces high-quality goods.
- We take our dog for a walk in the evening.
- The bus arrives at the station on time.
- They eat lunch at 12:00.
- He works at a software company.
- The teacher explains the lesson clearly.
- Birds sing in the trees.
- He knows how to speak Spanish fluently.
- The bakery bakes fresh bread daily.
- We play tennis on weekends.
- She enjoys watching movies in her free time.
- The river flows gently through the valley.
- They visit their grandparents every summer.
- The sun sets in the west.
- We have a meeting on Mondays.
- He helps his neighbors with gardening.
- The cat chases after the mouse.
- I work from 9 AM to 5 PM.
Negative Sentences
- She does not read books every day.
- They do not play football on weekends.
- He does not speak Spanish fluently.
- The sun does not rise in the west.
- We do not visit our grandparents often.
- I do not go to the gym three times a week.
- Cats do not chase elephants.
- He does not hate chocolate ice cream.
- The store does not open at 10 AM.
- The train does not depart at 8 AM.
- We do not live in a small house.
- They do not enjoy watching horror movies.
- She does not take the train to work.
- He does not work on Sundays.
- The dog does not meow.
- I do not play the guitar in the evenings.
- Birds do not fly at night.
- She does not sing off-key.
- We do not have breakfast at 5 PM.
- It does not snow in this area.
Interrogative Sentences
- Does she read books every day?
- Do they play football on weekends?
- Does he speak French fluently?
- Does the sun rise in the west?
- Do we visit our grandparents often?
- Do you go to the gym every day?
- Do cats chase dogs?
- Does he like vanilla ice cream?
- Does the store open at 9 AM?
- Does the train depart at 7 AM?
- Do we live near the park?
- Do they enjoy swimming?
- Does she take the bus to work?
- Does he work as a chef?
- Does the cat meow loudly?
- Do you play the violin in the evenings?
- Do birds sing at night?
- Does she dance gracefully?
- Do we eat lunch at 2 PM?
- Does it rain a lot in this city?
Quiz:
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs:
- She __________ (read) a book every night.
- They __________ (play) football on weekends.
- He __________ (speak) English fluently.
- The sun __________ (rise) in the east.
- We __________ (visit) our grandparents often.
- You __________ (go) to school every day.
- Cats __________ (chase) mice.
- He __________ (like) chocolate ice cream.
- The store __________ (open) at 9 AM.
- The train __________ (depart) at 7 AM.
- We __________ (live) near the beach.
- They __________ (enjoy) swimming.
- She __________ (take) the bus to work.
- He __________ (work) as a teacher.
- The cat __________ (meow) loudly.
Answers:
- reads
- play
- speaks
- rises
- visit
- go
- chase
- likes
- opens
- departs
- live
- enjoy
- takes
- works
- meows
FAQS:
- What is the Simple Present Tense?
- The Simple Present Tense, also known as the simple present tense, is a verb form that describes actions or events that are regular, habitual, or factual in the present time. It is used to express general truths, routines, and facts.
- How is the Simple Present Tense formed?
- For most verbs, in the Simple Present Tense:
- For singular subjects (he, she, it, a singular noun or pronoun), we add ‘s’ or ‘es’ to the base form of the verb.
- For plural subjects (I, you, we, they, plural nouns or pronouns), the verb remains in its base form.
- For most verbs, in the Simple Present Tense:
- When do we use the Simple Present Tense?
- The Simple Present Tense is used for:
- Stating general facts or truths.
- Describing regular actions or routines.
- Expressing habits or customs.
- Making statements that are generally true.
- Narrating events in a book or story.
- The Simple Present Tense is used for:
- What are some signal words associated with the Simple Present Tense?
- Signal words that often indicate the use of Simple Present Tense include:
- Always, usually, often, sometimes, rarely, never
- Every day, every week, every month, etc.
- On Mondays, on weekends, in the mornings, etc.
- Facts, general truths, laws of nature, etc.
- Signal words that often indicate the use of Simple Present Tense include:
- Can the Simple Present Tense be used in negative and interrogative sentences?
- Yes, the Simple Present Tense can be used in negative and interrogative sentences by adding the auxiliary verbs “do” or “does”:
- Negative: I do not (don’t) like coffee. / She does not (doesn’t) play basketball.
- Yes, the Simple Present Tense can be used in negative and interrogative sentences by adding the auxiliary verbs “do” or “does”:
-
-
- Interrogative: Do you like pizza? / Does he speak Spanish?
-
Download a High-Quality Printable Worksheet on Simple Present Tense
You May Also Like