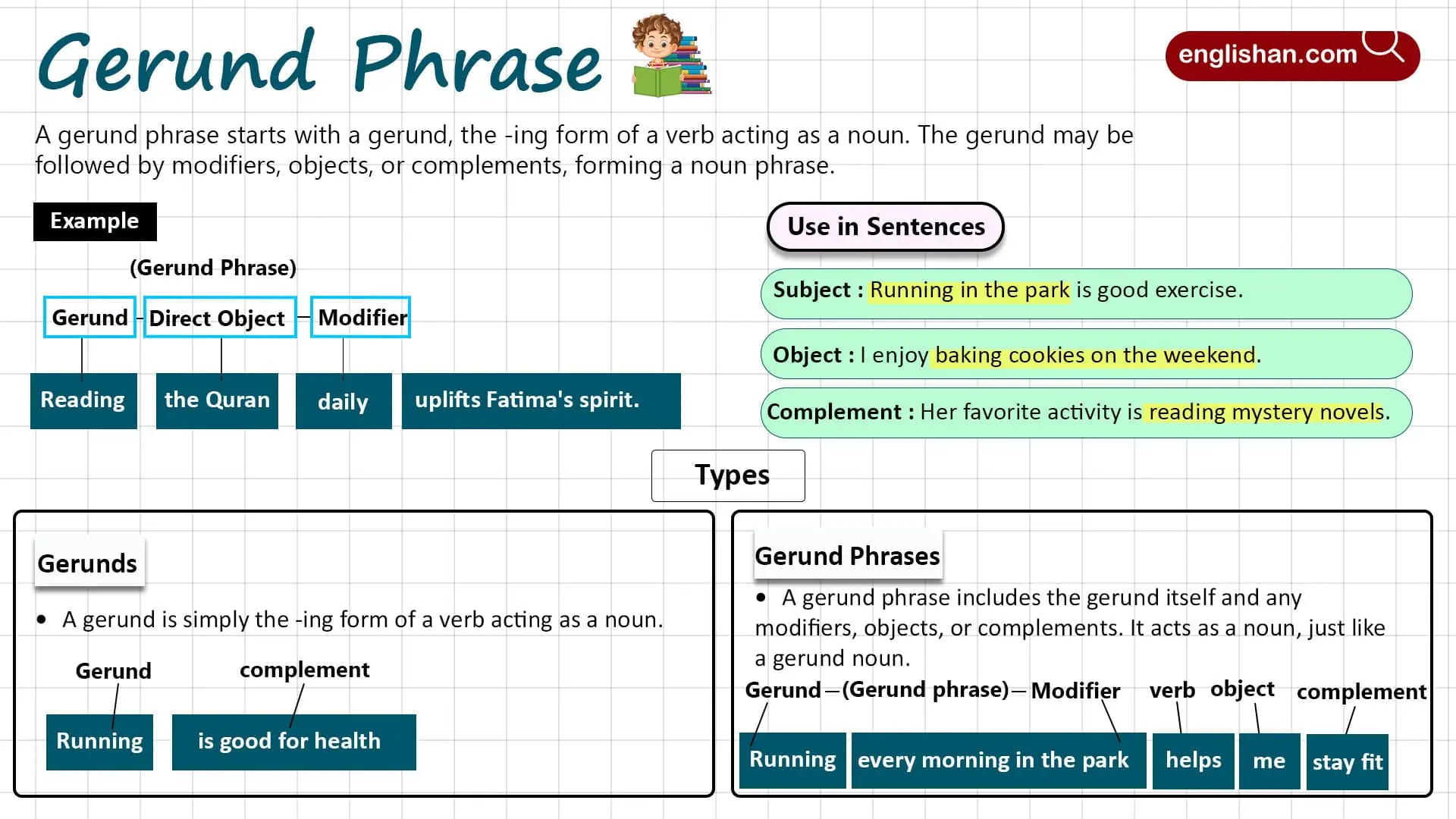
Transitive and intransitive verbs are two basic types of action verbs in English. A transitive verb needs a direct object to complete its meaning, while an intransitive verb does not. Understanding this difference helps you write clear and correct sentences. In this article, you’ll learn how to identify transitive and intransitive verbs in English, understand their usage, and avoid common mistakes through simple examples and sentence patterns.
What Are Transitive and Intransitive Verbs?
In English grammar, transitive verbs and intransitive verbs are two types of action verbs based on whether or not they require an object.
Transitive Verbs
A transitive verb needs a direct object to complete its meaning. The action passes from the subject to the object. If there is no object, the sentence feels incomplete.
Structure: Subject + Verb + Object
Example: He kicked the ball.
- Verb: kicked
- Object: the ball
The object answers the question “what?” or “whom?” after the verb.
More Examples:
- She bought a book.
- I opened the door.
- They watched a movie.

Ditransitive Verbs
Some transitive verbs take two objects — a direct object and an indirect object.
Example: He gave her a gift.
- Indirect object: her (to whom?)
- Direct object: a gift (what?)
Transitive verbs can be changed into passive voice.
Example:
- Active: She is reading a book.
- Passive: A book is being read by her.
Intransitive Verbs
An intransitive verb does not take a direct object. The action stays with the subject. These verbs often make complete sense on their own.
Structure: Subject + Verb
Example: He sleeps peacefully.
- No object follows the verb.
More Examples:
- They arrived late.
- She cries loudly.
- The baby smiled.
Intransitive verbs cannot be changed into passive voice.

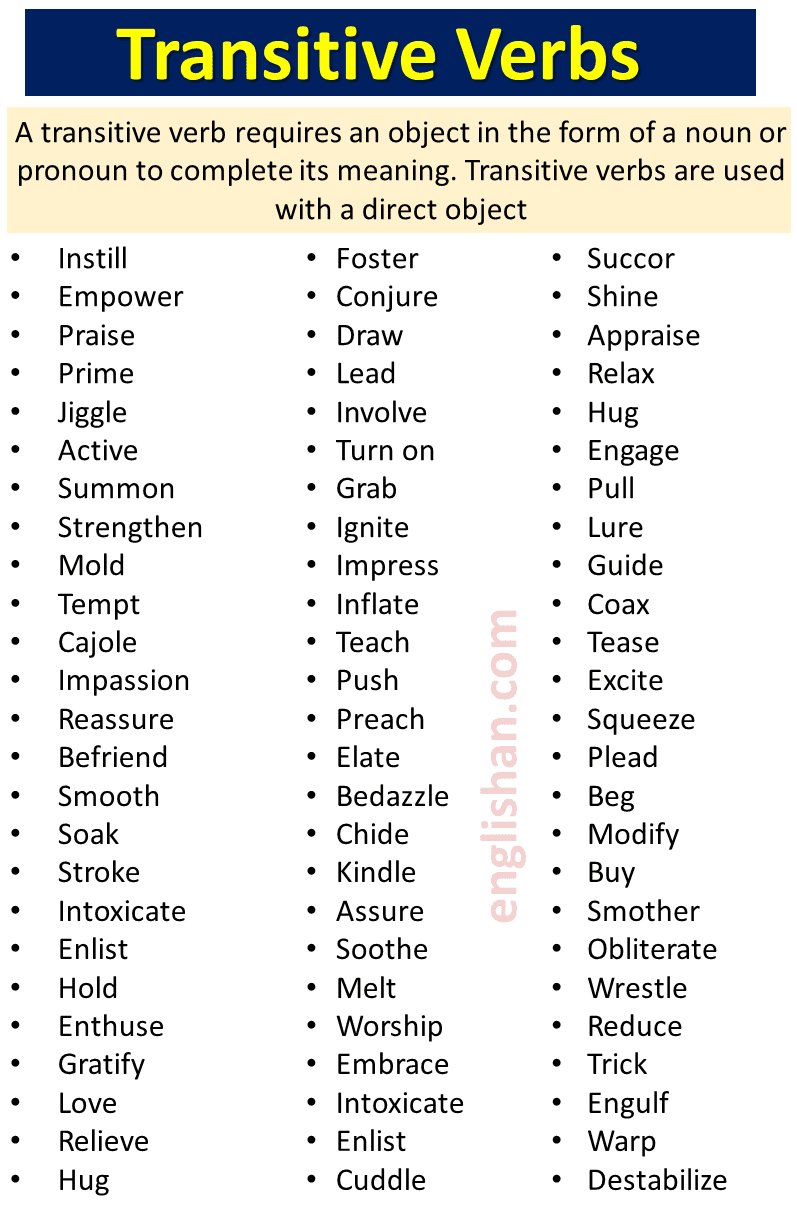
List of Transitive and Intransitive Verbs and Use in Sentences
Common Transitive Verbs
- bring: She brought her laptop to the meeting.
- build: They built a new house last year.
- buy: He bought a new phone.
- carry: She carried the baby carefully.
- catch: He caught the ball.
- close: Please close the window.
- cook: I cooked dinner for the family.
- cut: He cut the paper with scissors.
- deliver: They delivered the package on time.
- eat: She ate an apple.
- find: I found my keys.
- give: He gave me a pen.
- have: They have a new car.
- hold: She held the baby tightly.
- kick: He kicked the ball.
- know: I know the answer.
- like: She likes chocolate.
- make: He made a cake.
- open: Please open the door.
- play: They played the guitar.
- read: She read the book.
- see: I saw a movie.
- send: He sent a message.
- show: She showed me her drawings.
- take: I took a photo.
- tell: He told a story.
- use: She used a dictionary.
- watch: They watched a film.
- write: He wrote a letter.
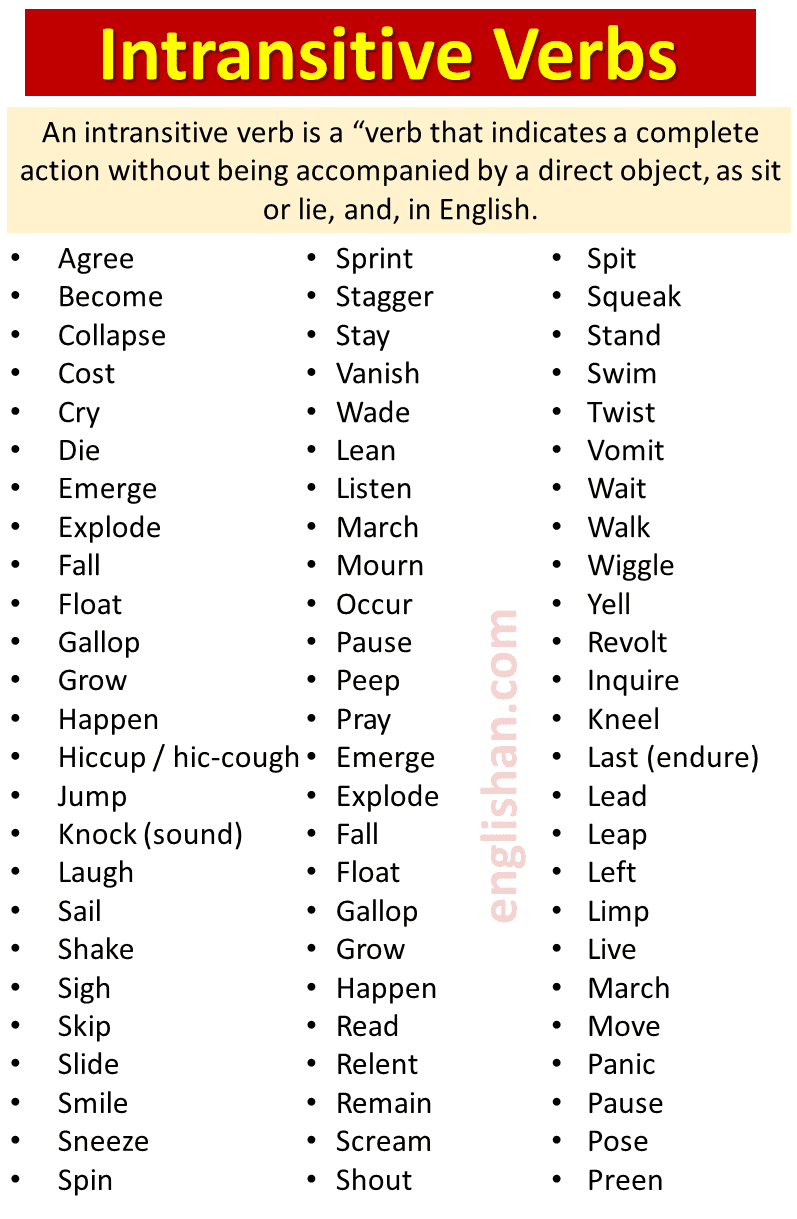
Common Intransitive Verbs
- arrive: They arrived late.
- come: She came home early.
- cry: The baby cried loudly.
- die: His grandfather died peacefully.
- disappear: The magician disappeared quickly.
- fall: Leaves fall in autumn.
- go: We go to the park every Sunday.
- grow: The tree grows fast.
- happen: What happened yesterday?
- jump: The dog jumped high.
- laugh: She laughed at the joke.
- leave: He left early.
- live: They live in Canada.
- occur: Accidents occur suddenly.
- rise: The sun rises at six.
- run: He runs every morning.
- shine: The stars shone brightly.
- sit: Please sit here.
- sleep: The child slept peacefully.
- smile: She smiled sweetly.
- sneeze: He sneezed loudly.
- stand: They stood in line.
- stay: We stayed home.
- swim: She swam in the pool.
- travel: He travels a lot.
- wait: Please wait a minute.
- walk: They walked to school.
- work: She works in an office.
- yawn: The student yawned during class.
Common Ditransitive Verbs
- bring: She brought me some flowers.
- buy: He bought her a necklace.
- deny: They denied him the chance.
- feed: She fed the dog some meat.
- give: He gave me a gift.
- grant: The teacher granted us permission.
- hand: She handed him a note.
- leave: I left her a message.
- lend: He lent me his book.
- offer: They offered us a discount.
- owe: I owe you an apology.
- pass: She passed him the salt.
- pay: He paid them the money.
- read: She read him a story.
- sell: They sold me a ticket.
- send: He sent her a card.
- show: I showed them the way.
- teach: She taught us grammar.
- tell: He told me a joke.
- throw: She threw him the ball.
- write: I wrote her a letter.
FAQs:
Transitive verbs need a direct object to complete their meaning.
1. Example: She reads a book.
(Here, “reads” needs the object “a book” to make sense.)
Intransitive verbs do not need an object. The action is complete on its own.
2. Example: He runs fast.
(Here, “runs” does not need an object; the action is complete by itself.)
So, transitive verbs need something to act on, but intransitive verbs do not.
Here are 12 examples of intransitive verbs:
1. Run
2. Sleep
3. Laugh
4. Arrive
5. Jump
6. Cry
7. Swim
8. Dance
9. Talk
10. Wait
11. Shout
12. Wander
These verbs do not need an object to complete their meaning.
The sentence “I am ten years old” uses the verb “am,” which is a linking verb.
A linking verb connects the subject (I) to more information about it (ten years old).
So, it’s neither transitive nor intransitive—it’s a linking verb.
Transitive phrasal verbs need an object to make sense.
Example: She turned off the light.
(Here, “turned off” needs the object “the light.”)
Intransitive phrasal verbs do not need an object.
Example: The car broke down.
(Here, “broke down” doesn’t need an object.)
In short:
Transitive = Needs an object.
Intransitive = Doesn’t need an object.
You May Also Like