In this blog post, we will help you learn the names of important internal body parts in English. Understanding these terms is essential for improving your vocabulary and talking about the human body clearly. Whether you’re studying for health classes or just want to expand your knowledge, these words will be useful for both everyday conversations and learning.
For more vocabulary on different topics, visit our Vocabulary Category.
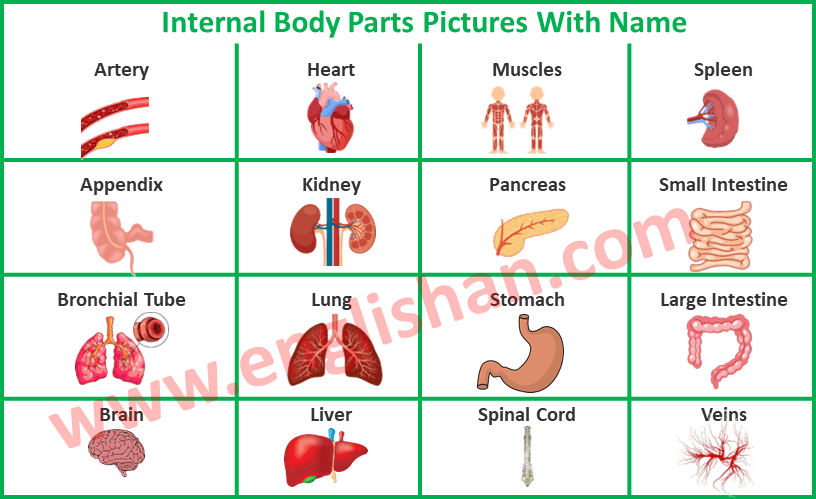
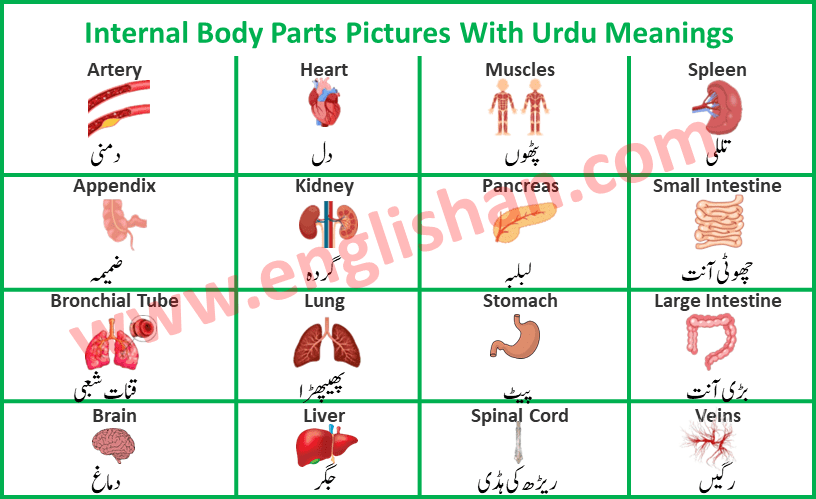
List of Internal Body Parts
- Artery: Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to different parts of the body.

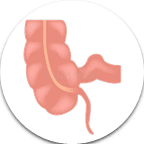
- Appendix: The appendix is a small pouch-like organ located in the lower right abdomen. Its exact function isn’t clear, but it may play a role in the immune system.

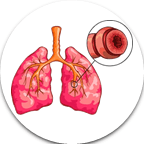
- Bronchial Tube: Bronchial tubes are air passages that connect the trachea (windpipe) to the lungs, allowing air to flow in and out.

- Brain: The brain is the control center of the body. It controls thoughts, emotions, movements, and many other functions.

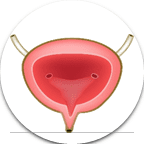
- Bladder: The bladder stores urine before it’s eliminated from the body.

- Bone Marrow: Bone marrow is a soft tissue inside bones where blood cells are produced.

- Capillaries: Capillaries are tiny blood vessels that connect arteries and veins, allowing for exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste between blood and tissues.

- Fatty Tissue: Fatty tissue stores energy and cushions organs.

- Gallbladder: The gallbladder stores bile produced by the liver and releases it to help digest fats.

- Gullet (Esophagus): The gullet, also known as the esophagus, is a tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach.

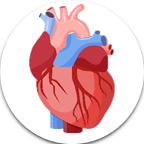
- Heart: The heart pumps blood throughout the body, supplying oxygen and nutrients to cells.

- Kidney: Kidneys filter waste and excess fluids from the blood, producing urine.

- Lung: Lungs help us breathe by taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide.

- Liver: The liver processes nutrients, detoxifies substances, and produces bile for digestion.

- Muscles: Muscles enable movement and provide structure to the body.

- Pancreas: The pancreas produces enzymes for digestion and regulates blood sugar levels.

- Stomach: The stomach digests food through the secretion of acids and enzymes.

- Spinal Cord: The spinal cord transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body, controlling movements and sensations.

- Spleen: The spleen filters blood and plays a role in the immune system.

- Small Intestine: The small intestine absorbs nutrients from digested food.

- Large Intestine (Colon): The large intestine absorbs water from digested food and forms feces for elimination.

- Veins: Veins return oxygen-depleted blood to the heart.

- Thyroid: The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism and growth.

FAQs
Here are some simple internal body parts:
1. Heart – Pumps blood.
2. Lungs – Help you breathe.
3. Stomach – Breaks down food.
4. Liver – Cleans the blood.
5. Kidneys – Remove waste from blood.
6. Intestines – Absorb food nutrients.
7. Brain – Controls everything in the body.
8. Bladder – Stores urine.
9. Pancreas – Helps digest food and control sugar.
10. Spleen – Helps fight infections.
These body parts work together to keep you healthy!
Here are 20 body parts names:
1. Head
2. Eyes
3. Ears
4. Nose
5. Mouth
6. Neck
7. Shoulders
8. Arms
9. Elbows
10. Hands
11. Fingers
12. Chest
13. Stomach
14. Back
15. Hips
16. Legs
17. Knees
18. Feet
19. Toes
20. Skin
These are common body parts you see and use every day!
Here are the 12 body systems made easy:
1. Heart System – Moves blood (heart, blood vessels).
2. Breathing System – Helps you breathe (lungs, windpipe).
3. Food System – Breaks down food (stomach, intestines).
4. Brain System – Controls the body (brain, nerves).
5. Muscle System – Helps you move (muscles).
6. Bone System – Gives your body shape (bones).
7. Pee System – Removes waste (kidneys, bladder).
8. Hormone System – Sends body messages (glands like thyroid).
9. Baby System – Makes babies (ovaries, testes).
10. Fight Germs System – Keeps you healthy (spleen, lymph nodes).
11. Skin System – Protects you (skin, hair).
12. Fluid System – Moves body fluids (lymph nodes, vessels).
These systems work together to keep your body working!
Here are 12 types of anatomy:
1. Big Parts – Looks at large body parts like bones and muscles.
2. Tiny Parts – Studies small things like cells.
3. Body Areas – Focuses on parts like the head or arms.
4. Organ Groups – Looks at organ systems like the heart and lungs.
5. Outside Body – Studies what you can see, like skin.
6. Body Growth – Studies how the body grows.
7. Before Birth – Looks at how a baby grows inside the mother.
8. Humans vs Animals – Compares human and animal bodies.
9. Sick Body – Studies how diseases affect the body.
10. Body Scans – Uses X-rays or scans to see inside the body.
11. Doctor Work – Focuses on anatomy for medical care.
12. How It Works – Studies how body parts work together.
Easy to understand and helpful!
You May Also Like