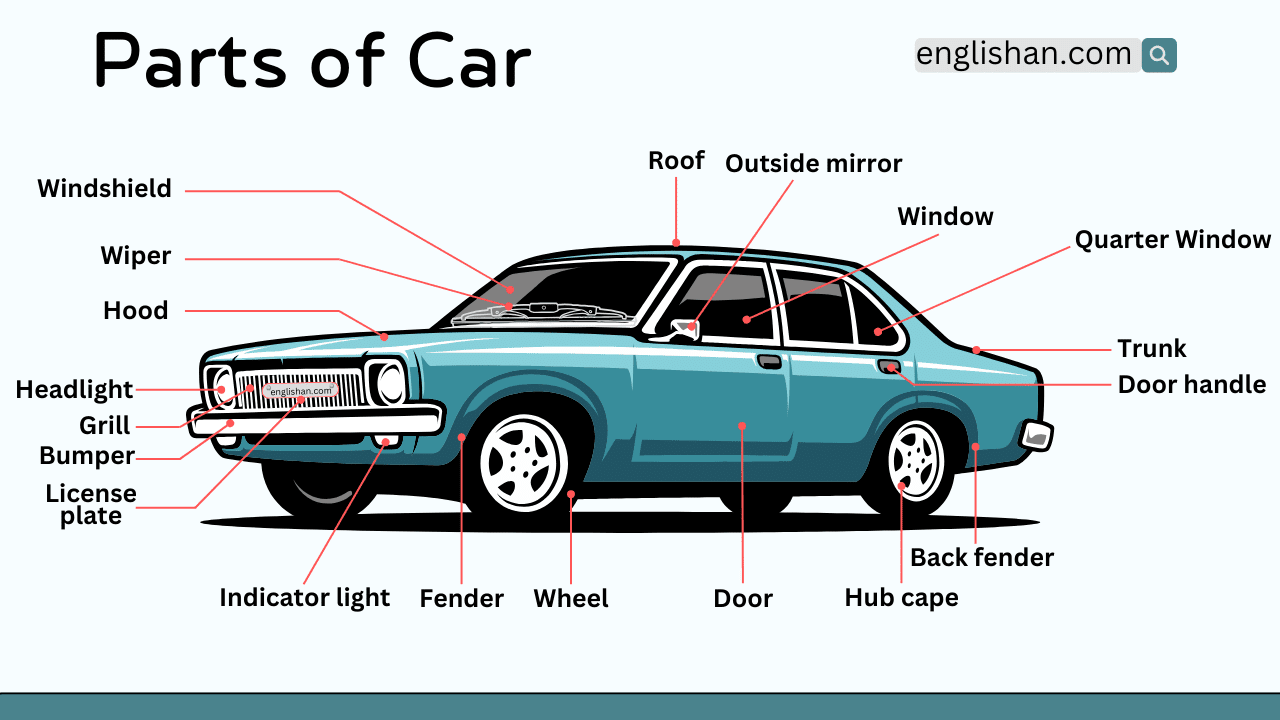
The cabin of a vehicle is more than a place to sit; it is where interior components and driver controls come together in daily operation. When you talk about adjusting climate settings, reading the instrument cluster, or using the center console, weak wording can blur the difference between trim pieces and functional hardware.
In this article, we break down the parts of a car interior using standard passenger vehicles as reference. The coverage includes the dashboard, steering wheel, instrument cluster, center console, gear selector, infotainment screen, air vents, seats, seat belts, headliner, and door panels, with notes where designs vary. The labeled diagram below helps connect each name to its exact position.
Car Interior Diagram With Names
A car interior is a controlled driving environment built around information delivery, vehicle operation, passenger comfort, and safety protection. Every component inside the cabin works as part of a coordinated system. Control inputs from the driver are processed through mechanical and electronic systems, while structural and safety components protect occupants during movement. When viewed carefully, the interior is not just a seating area but a structured arrangement of control interfaces, display systems, and restraint components working together.
Card Dashboard And Windscreen Parts
The dashboard area forms the primary driver interface. It houses vehicle information displays, climate systems, control modules, and structural supports that reinforce the front cabin area. Rather than functioning as simple trim, this section integrates electronics, safety systems, and airflow channels.
Dashboard
The dashboard acts as the central housing for multiple vehicle subsystems. It supports electrical wiring, air distribution ducts, display modules, and structural reinforcement elements. A well-designed dashboard contributes to:
- Organized control access
- Clear information visibility
- Structural rigidity across the front cabin
It extends across the cabin beneath the windscreen and anchors the instrument and infotainment systems.
Instrument Panel
The instrument panel provides real-time vehicle data and operational feedback. It combines mechanical gauges with digital displays to monitor speed, engine behavior, and system alerts. Its purpose includes:
- Displaying driving speed
- Showing engine revolutions
- Reporting warning signals
- Indicating fuel levels
It is aligned directly in front of the steering wheel for direct driver visibility.
Speedometer
The speedometer measures and displays vehicle speed. Accurate speed reading ensures controlled driving and compliance with road limits. It forms part of the instrument cluster.
Tachometer
The tachometer monitors engine revolutions per minute. It helps maintain proper gear shifts and engine efficiency.
Notification Indicators
Notification indicators display system warnings such as engine faults, low fuel, battery alerts, and safety reminders. These visual signals form part of the instrument cluster display.
Infotainment System
The infotainment system integrates media, navigation, and connectivity functions. It supports:
- Audio playback
- Touchscreen navigation
- Bluetooth connectivity
- Voice command control
It is embedded into the central dashboard section.
Windscreen
The windscreen provides forward visibility while contributing to structural strength and cabin sealing. It works with defrost and demister systems to maintain clarity. It forms the front glass barrier of the vehicle cabin.
Defrost Grill And Demister
The defrost grill directs airflow toward the windscreen to clear condensation. The demister system removes fog and frost by channeling warm air across the glass surface. These components operate through vents integrated into the upper dashboard.
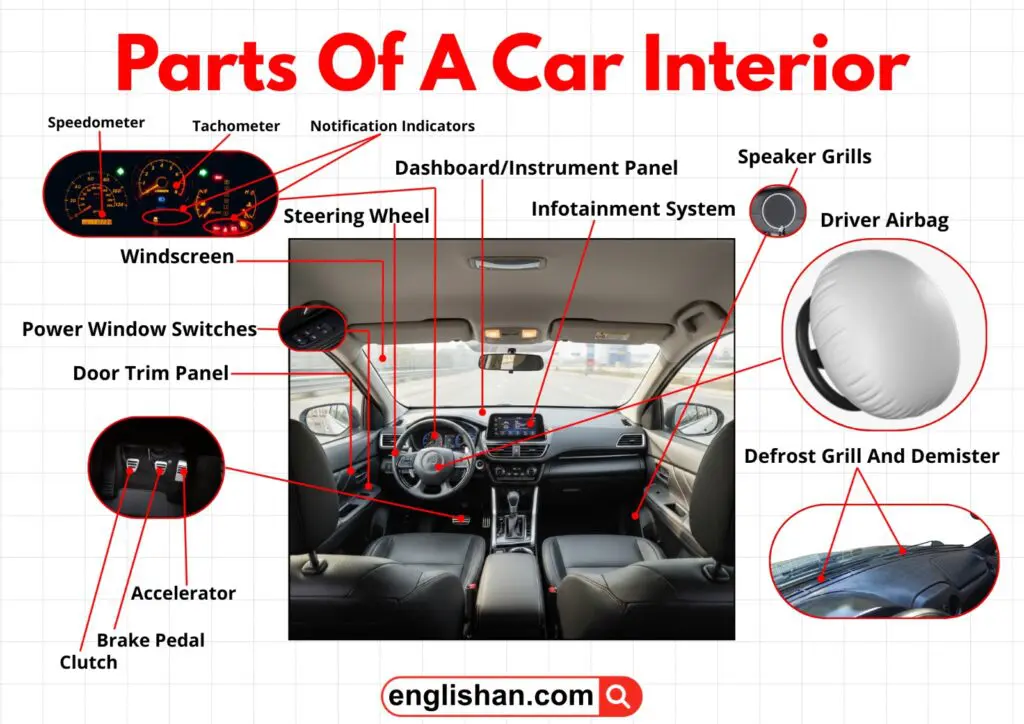
Steering Wheel And Control Interface
This section forms the primary driver command system. Steering input, signaling, and secondary controls are centralized here to maintain focus and reduce distraction.
Steering Wheel
The steering wheel transmits rotational input to the steering mechanism, converting hand motion into directional movement of the wheels. Modern steering wheels also integrate control switches to reduce hand movement during driving. These integrated controls may include:
- Audio adjustments
- Call management
- Cruise control functions
The steering wheel is mounted on the steering column directly in front of the driver.
Driver Airbag
The driver airbag is a critical impact protection device. During a frontal collision, it deploys rapidly to cushion the driver and reduce injury. It is concealed within the central hub of the steering wheel.
Combination Switch And Stalks
The combination switch controls multiple vehicle systems through lever-based inputs. These include:
- Turn indicators
- Headlight activation
- Wiper speed selection
These stalks extend from either side of the steering column.
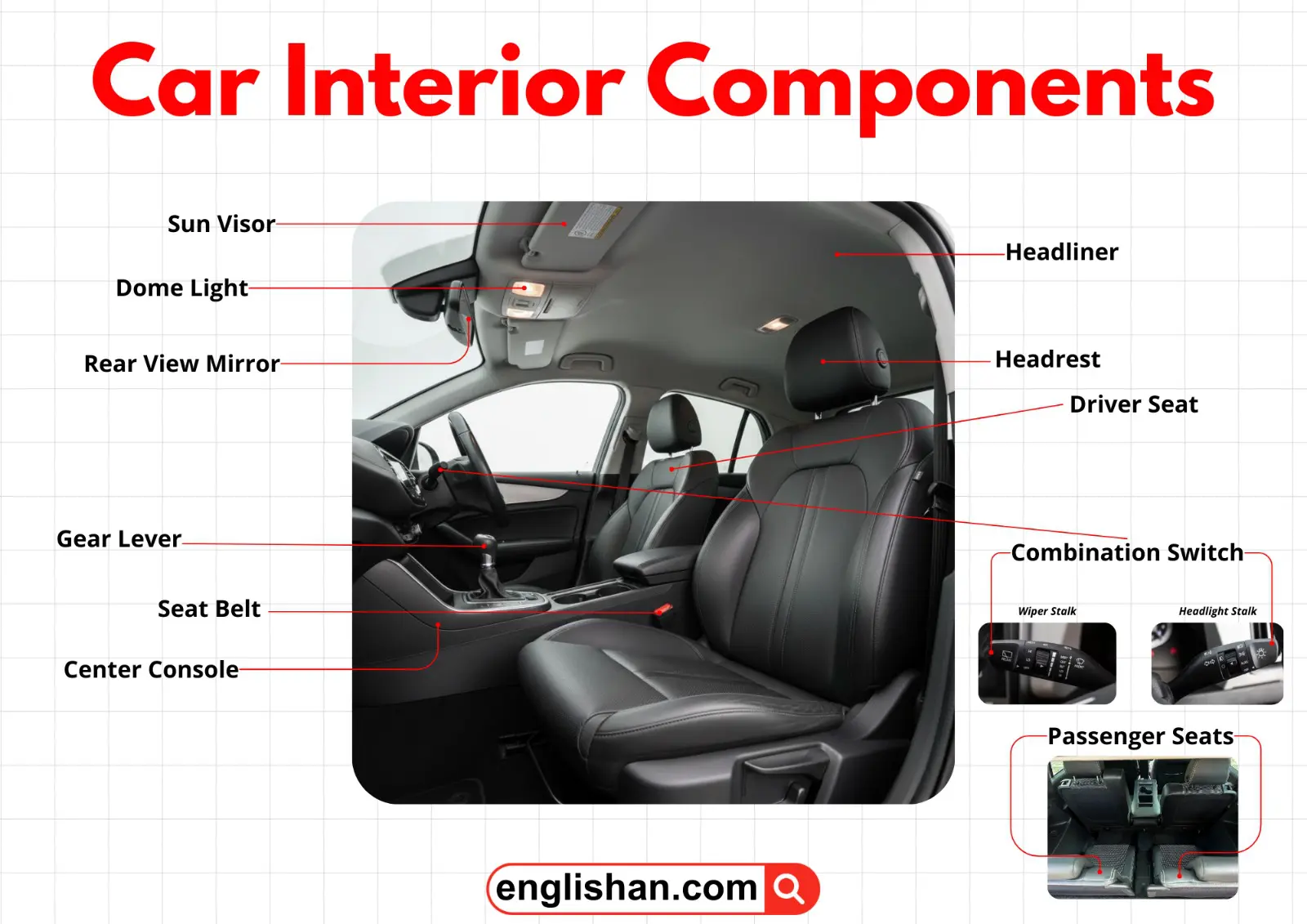
Seats And Cabin Structure
The seating system is more than padding. It is engineered for posture alignment, occupant restraint, and impact absorption. Seat frames are anchored to the vehicle floor structure to ensure stability during movement and collision.
Driver Seat
The driver seat supports posture and reach alignment for safe vehicle operation. Adjustment mechanisms allow:
- Forward and backward sliding
- Seat height variation
- Backrest angle control
It is mounted on floor rails directly behind the steering assembly.
Passenger Seats
Passenger seats provide support and safety across multiple rows. Rear seats may fold to expand storage space. These seats are secured to the cabin floor structure.
Headrest
The headrest protects against neck injury during sudden rear impact. It reduces excessive backward head motion. It is attached to the upper portion of each seat.
Seat Belt
The seat belt functions as a primary restraint system. It locks during sudden deceleration to prevent forward movement. It connects from the vehicle pillar to the seat frame across the occupant’s torso.
Door And Window Control Parts
Interior door panels contain control switches, structural padding, and integrated safety components. They combine trim design with electrical routing and mechanical linkages.
Door Trim Panel
The door trim panel covers internal metal structures and wiring harnesses. It provides insulation and aesthetic finish while supporting switch assemblies. It forms the inner surface of the vehicle door.
Power Window Switches
Power window switches control glass movement using electric motors. These switches regulate:
- Upward movement
- Downward movement
- Automatic closing functions
They are embedded within the door panel near the armrest.
Inner Release Lever
The inner release lever disengages the door latch mechanism, allowing the door to open from inside.
Speaker Grills
Speaker grills protect embedded audio speakers while allowing sound projection. They are integrated into the lower section of the door panel.
Gear Lever And Pedal Controls
This section translates driver input into mechanical or electronic vehicle movement.
Gear Lever
The gear lever selects transmission modes. It determines:
- Drive engagement
- Reverse operation
- Neutral position
It is positioned within the center console between the front seats.
Accelerator
The accelerator pedal regulates engine power output by controlling throttle input.
Brake Pedal
The brake pedal activates the braking system, reducing wheel rotation and slowing the vehicle.
Clutch
The clutch disconnects engine power from the transmission during gear shifts in manual vehicles.
Roof And Overhead Components
The roof interior houses lighting, structural padding, and visibility aids.
Headliner
The headliner covers the interior roof structure and provides insulation and noise reduction.
Sun Visor
The sun visor reduces glare and improves forward visibility during bright conditions.
Rear View Mirror
The rear view mirror provides rearward visibility and supports safe lane changes.
Dome Light
The dome light illuminates the cabin during entry and low-light conditions.
Car Interior Key Takeaways
A car interior operates as a coordinated cabin system where the dashboard delivers information, steering components manage direction, seating systems provide restraint and support, and door assemblies integrate controls and protection. Driver inputs transfer through pedals and transmission controls to produce movement, while airbags and structural supports enhance safety. Though design varies across vehicle models, all interior parts work together to maintain control, visibility, comfort, and occupant protection.
You May Also Like