Have you ever struggled to describe a skin concern because you could not recall the right word? Mastering the vocabulary of the face is essential for clear communication, whether you are at a doctor’s appointment or following a makeup tutorial. Using precise terms ensures you get the right help without confusion.
We cover all major features here, from the forehead and temples down to the chin and jawline. While parts like eyelids and nostrils are universal, their shapes vary uniquely from person to person. The labeled diagram below helps you match each name to its location instantly.
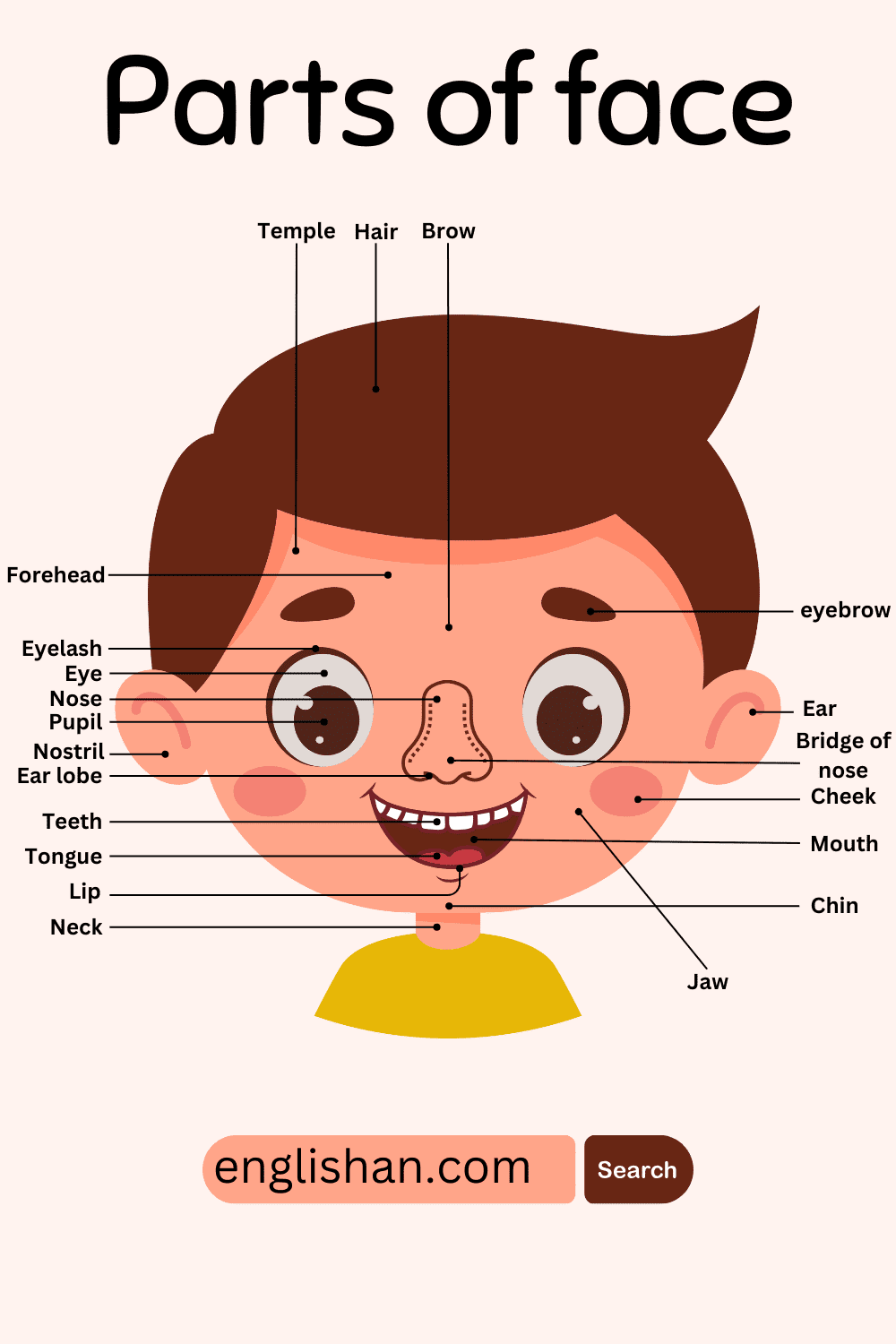
Face Parts Names In English
The face is a complex area of the head that comprises various features and structures. Here are the main parts of the face:
Forehead
Above the brows, this area often carries the most visible expression lines from repeated movement. It is also a common place for sweat and oil buildup, so texture can shift through the day. Skin tone here can look different from nearby areas because exposure and care vary.
Eyes
Vision depends on a coordinated set of parts that protect, focus, and react to light. Eyelids and lashes shield the surface, while the eye itself manages sight and movement. Redness, dryness, and strain often show here first.
Nose
Breathing and smell both rely on this structure, so it is doing more than shaping a profile. Inside, airflow and scent detection work together, and outside, skin can be more oily or more sensitive. Its surface details, like pores, can be more noticeable than on other areas.
Cheeks
Soft tissue here shapes the face at rest and during expression. Changes in hydration, sleep, and diet can show as puffiness or hollowness. Color shifts such as flushing or uneven tone often appear on the cheeks.
Mouth
Speech and eating depend on coordinated movement and control in this opening. Moisture balance matters because dryness can change comfort and appearance fast. Many small changes, like cracks or irritation, become noticeable here quickly.
Lips
Unlike most facial skin, this tissue is thinner and loses moisture faster. That is why dryness, peeling, and fine lines can develop with weather or habits. Natural color varies widely and can also shift with irritation.
Chin
The skin and underlying shape here affect how the lower face reads in profile and expression. Breakouts often cluster in this area due to oil production and irritation. Texture can swing between smooth and rough depending on shaving or friction.
Jaw
A strong hinge and muscle system supports chewing and sustained speech. Tension can build from clenching, which may change comfort and facial shape over time. Skin along this area also reacts easily to shaving, hair growth, and rubbing.
Ears
Hearing depends on structures that channel sound and maintain balance cues. Skin here can be sensitive and may react to pressure from glasses, masks, or headphones. Piercings and inflammation can also change texture and comfort.
Facial Hair
Growth patterns vary by age, hormones, and genetics, which changes density and texture. Shaving, trimming, and grooming can affect skin sensitivity and visible irritation. Eyebrows also shape expression through thickness and arch.
Skin
This outer layer sets tone, texture, and overall facial appearance. Oil level, hydration, and barrier strength influence shine, dryness, and irritation. Marks such as freckles, moles, pimples, and scars often sit on top of these baseline traits.
Front Parts Of The Face
Frontal parts of face refer to the structures and features located at the front portion of the head. Here are the key frontal parts of the face:
- Forehead: The upper part of the face, extending from the eyebrows to the hairline.
- Eyes: The organs of sight, positioned in the eye sockets or orbits.
- Eyebrows: The hair-covered arches above the eyes.
- Eyelids: The movable covers that protect and control the exposure of the eyes.
- Eyelashes: Short hairs that grow along the edges of the eyelids.
- Nose: The central part of the face that protrudes, involved in breathing and smelling.
- Cheeks: The fleshy areas on the sides of the face below the eyes.
- Mouth: The opening used for speaking, eating, and breathing.
- Lips: The soft, movable parts surrounding the mouth.
- Chin: The bottom and front part of the face, below the mouth.
These frontal parts collectively contribute to the facial expression, communication, and sensory functions of the face. They also play a significant role in conveying emotions and expressions through movements and features in this area.
Side And Lower Parts Of The Face
Side and lower parts of the face contribute to the overall structure and expression of an individual. Here are the key components:
- Cheeks: The fleshy areas on the sides of the face, below the eyes. Cheeks contribute to facial fullness and expressions.
- Jawline: The area along the lower edge of the jaw, defining the contour of the lower face.
- Jaw: The lower part of the face, including the jawbone. It plays a role in chewing and facial symmetry.
- Chin: The bottom and front part of the face, below the mouth. The chin contributes to the overall facial profile.
- Neck: The portion connecting the head to the body. The neck is essential for head movement and supports the weight of the head.
- Ears: Organs of hearing, located on each side of the head. Ears contribute to the overall facial symmetry.
These side and lower face parts, along with the frontal parts, work together to create a person’s unique appearance. The combination of features in these areas influences facial expressions, communication, and individual characteristics.
Auxiliary Features
While these facial features might not immediately catch your attention, they significantly contribute to the overall facial landscape. Acquainting yourself with these elements will enhance your vocabulary toolkit for describing facial characteristics.
Wrinkle
Skin can form lines and folds when elasticity declines or when movement repeats in the same pattern. Depth can range from faint creases to deeper grooves, depending on age, skin type, and sun exposure. Texture changes usually become more noticeable over time.
Freckle
Clusters of pigment can create small, flat spots with a tan to brown tone. Sun exposure often makes them darker, while reduced exposure can fade them. Some people get just a few, while others have many.
Mole
A pigmented spot forms when melanocytes group together in one area. It may stay flat or become raised, and color can range from light brown to near black. Many remain unchanged for years, although some shift gradually.
Pimple
When a pore clogs, trapped oil and bacteria can trigger an inflamed bump. It can look red, swollen, or filled, depending on the type. After it settles, discoloration or a mark may remain for a while.
Scar
After skin damage, new tissue can leave a lasting mark with a different texture. Some scars rise above the surface, while others sink or feel tight. Color often changes as healing progresses and the tissue matures.
These additional features, alongside the main facial parts, contribute to the unique character of your face.
Miscellaneous Terms for Parts of Face
Here are some miscellaneous terms for various parts and features of the face:
- Temples: The sides of the head, above and to the sides of the eyes.
- Eyelashes: Short hairs growing along the edges of the eyelids.
- Nasolabial Fold: The crease or line that runs from the sides of the nose to the corners of the mouth.
- Philtrum: The vertical groove between the base of the nose and the upper lip.
- Dimples: Small indentations, often on the cheeks, that appear when a person smiles.
- Adam’s Apple: The protrusion in the throat, more prominent in males, created by the thyroid cartilage.
- Pupils: The dark, circular openings in the center of the eyes.
- Tear Ducts: The small openings near the inner corners of the eyes that allow tears to drain.
- Cleft Chin: A dimple or indentation in the chin.
- Jawline: The outline or contour of the lower jaw.
- Laugh Lines: Lines or wrinkles around the eyes and mouth, often associated with smiling and laughing.
- Cupid’s Bow: The double curve of the upper lip, resembling the bow of Cupid.
- Crow’s Feet: Wrinkles that form around the outer corners of the eyes, typically due to aging.
- Adams’ Apple: The prominent bulge in the throat, more noticeable in males.
- Nostrils: The openings of the nose.
Key Takeaways on Parts of Face
The face works as one system, where surface features and underlying structures act together rather than as isolated pieces. For parts of face, the core purpose is sensing, since eyes, nose, mouth, and skin all register input from the surroundings. Shape affects expression because muscle form changes how movement appears. Skin texture and bone structure vary by genetics and age, which sets natural limits and patterns. We frame accurate naming as precision, so each term reflects exact meaning in writing and speech.
FAQs
The main parts of the face include the forehead, eyes, nose, cheeks, mouth, lips, chin, jaw, ears, and neck.
The forehead is a prominent facial feature and plays a role in overall facial aesthetics. It also contributes to expressions and can be a site for wrinkles.
Eyelashes help protect the eyes from debris and play a role in preventing irritants from entering the eyes.
The nose is not only crucial for breathing but also contributes to the sense of smell, and its shape can impact facial aesthetics.
Facial muscles and features like the eyes and mouth work together to express a wide range of emotions, from joy to sadness and surprise.
The jawline contributes to facial definition and contour. It is often associated with attractiveness and symmetry.
Ears are included in facial anatomy as they contribute to the overall symmetry and appearance of the face.
Lips are essential for verbal communication and expressing emotions through smiling, frowning, and other facial movements.
You May Also Like