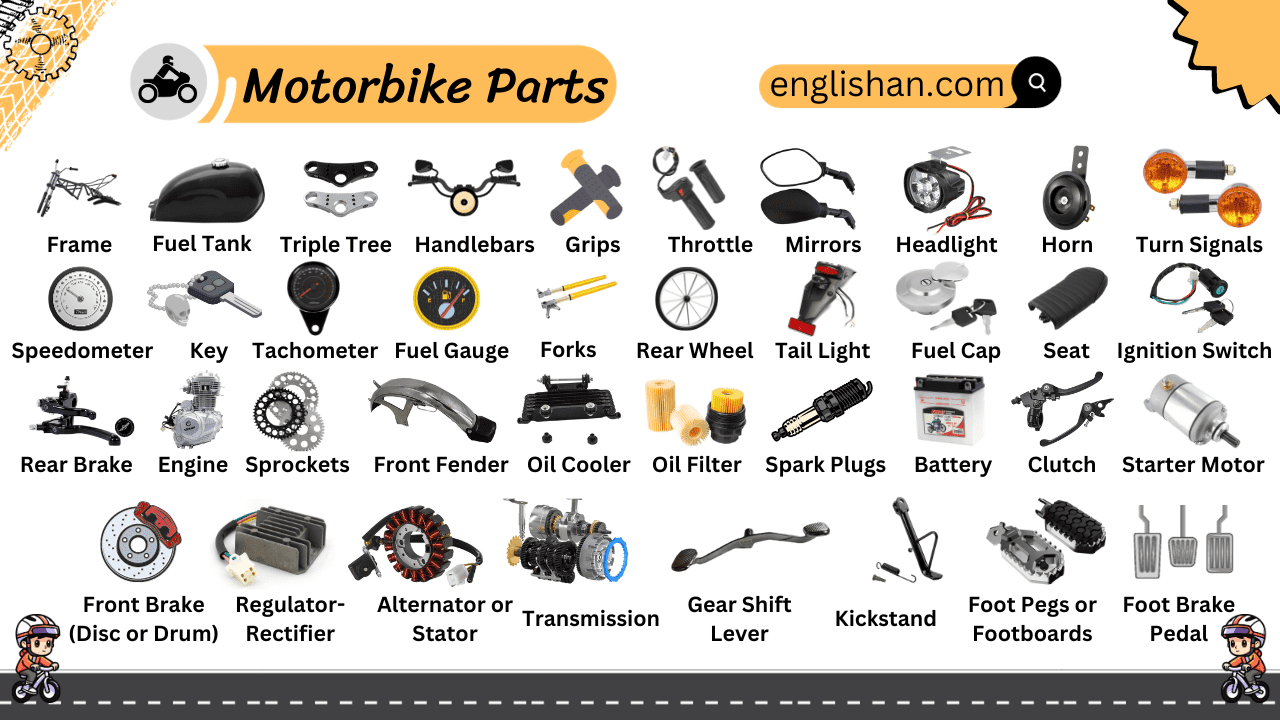
A motorcycle is a combination of various parts that come together to make riding both thrilling and safe. These parts ensure the bike moves smoothly and is easy to handle. Whether you’re riding for fun or daily use, understanding the different parts of a motorcycle can make your rides more enjoyable and help with basic maintenance.
Parts of Motorcycle with Pictures
In this post, we’ll learn the names of parts of motorcycles, and the specific parts can vary depending on the make and model of the motorcycle.
Electrical Parts of Motorcycle

Battery
The energy source for the motorbike. It not only helps start the engine but also powers all the bike’s electrical components.
Headlight
A front-facing light that illuminates the way ahead, essential for nighttime or foggy rides.

Horn
An auditory alert system. A quick press sounds a warning to other road users or pedestrians.

Turn Signals
Blinking indicators located on either side of the bike. They signal the rider’s intention to turn or change lanes.

Tail Light
A rear-facing light that indicates the bike’s presence to vehicles behind, especially important in the dark or fog.

Ignition Switch
A switch that starts or stops the engine. The bike’s key is inserted here to bring the engine to life.

Spark Plugs
Small devices essential for the engine’s operation. They ignite the fuel, enabling the engine to run.

Starter Motor
An electrical component that jumpstarts the engine. It’s activated by pressing the bike’s start button.

Tachometer
An instrument that indicates the rotation speed of the engine’s crankshaft. It helps riders maintain an optimal engine speed.

Fuel Gauge
Displays the amount of fuel left in the tank. It’s crucial for riders to ensure they don’t run out of fuel during their journey.

Stator
Part of the bike’s electrical system. It generates power for the battery, ensuring the bike’s electrical components remain functional.
Control Components of Motorcycle

Clutch
A vital component that allows the rider to control the bike’s speed. It works by engaging or disengaging power to the wheels, helping in changing gears.
Starter Paddle
A manual way to start the bike. By giving it a firm push, the engine is kick-started into action.

Throttle
The bike’s accelerator. A twist here regulates the engine’s speed, dictating how fast or slow the bike moves.

Brake Cable
A cable that connects the brake lever to the braking system. It’s essential for stopping the bike when needed.

Handlebars
Bars that the rider holds onto, known as handlebars, are crucial for directing the bike. They play an essential role in steering and control, making them one of the important parts of a motorcycle. Proper handling ensures the rider can maneuver the bike smoothly and safely.

Speedometer
An instrument that shows the bike’s speed. It helps riders monitor their speed and stay within legal limits.
Grips
Located at the ends of the handlebars, these are what the rider holds onto. They ensure a firm grip, which is vital for safe handling and control.

Rear Brake
The braking system for the back wheel. Activating it slows down or stops the bike, depending on the pressure applied.
Front Brake
The braking system for the front wheel. Vital for halting the bike, especially at higher speeds.

Gear Shift Lever
A pedal used by riders to change gears. Shifting gears is crucial for managing the bike’s speed and torque.

Brake Rod
A connecting rod that translates the action of pressing the brake into the braking mechanism, assisting in halting the bike.

Toolkit
A collection of essential tools useful for repairing and maintaining the motorbike. It’s like a first-aid kit for the bike’s mechanical needs.
Structural Components of Bike
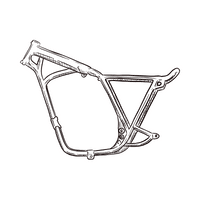
Frame
The main structural component of the bike. It holds everything together and ensures the bike’s stability.

Triple Tree
The component that connects the handlebars and the forks to the motorcycle frame. It plays a central role in steering and maneuvering the bike.
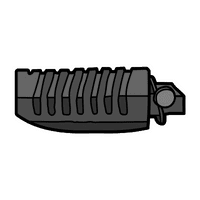
Foot Pegs
Resting places for the rider’s feet while riding. They ensure comfort and better control during a journey.

Safety Bar
A protective feature on some bikes. It’s designed to safeguard both the rider and the bike during falls or mishaps.

Kickstand
A metal stand that allows the bike to stay upright when parked.

Forks
Long structures at the front of the bike that support the front wheel. They also play a role in shock absorption, ensuring a smooth ride.
Engine and Power Components
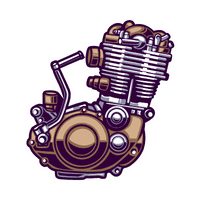
Engine
The heart of the bike. It burns fuel to produce power, propelling the motorcycle forward.

Sprockets
Toothed wheels that work with the chain to transfer power from the engine to the rear wheel.
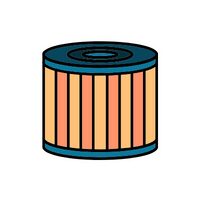
Oil Filter
A component that cleans the engine oil. It traps impurities, ensuring only clean oil circulates within the engine.

Muffler
Functions as the bike’s noise reducer. It minimizes the sound produced by exhaust gases from the engine.

Oil Cooler
A device that cools the engine oil, ensuring it remains at an optimal temperature. This helps in the smoother functioning of the engine.
Other Components
Rim
The outer circular edge of a wheel, known as the rim, is vital for holding the tire securely in its proper position. Among the essential parts of a motorcycle, the rim ensures stability and proper alignment, allowing for smooth and safe rides.
Fuel Cap
A lid located on the fuel tank, the fuel cap is opened when refueling and ensures the fuel remains securely contained. As one of the important parts of a motorcycle, it plays a vital role in preventing fuel leaks and maintaining safety while riding.
Seat
The cushioned area where the rider sits. Designed for maximum comfort during rides.

Tube
Located inside the tire and filled with air, the inner tube plays a crucial role in ensuring the tire remains inflated for a smooth and comfortable ride. As one of the essential parts of a motorcycle, it helps maintain proper air pressure, ensuring the tire performs effectively and provides a stable riding experience.

Fuel Tank
A storage unit for the bike’s fuel. It’s filled with petrol or diesel, depending on the bike’s model.

Key
A small device used to start the bike. Inserting and turning it in the ignition switch sets the engine in motion.

Front Fender
A protective component located above the front wheel. It shields the rider from water, mud, and debris thrown up by the wheel.
All Parts of Motorcyle in one Picture
FAQs
Motorcycles have many parts that work together to make them run. Some key parts include:
1. Engine – The heart of the motorcycle, it powers the bike.
2. Wheels – Used for movement and stability.
3. Brakes – For stopping the bike.
4. Handlebars – Used to steer the motorcycle.
5. Fuel Tank – Stores the fuel.
6. Seat – Where the rider sits.
7. Headlights – For visibility in the dark.
8. Suspension – Helps absorb bumps on the road.
The price of a 70cc motorcycle in Pakistan typically ranges from PKR 90,000 to PKR 110,000, depending on the brand and model. For instance, the Ravi Humsafar 70 costs around PKR 90,000, while the United 70 is priced at about PKR 109,500【40†source】【42†source】. Prices may vary by location and dealer.
Here’s a simpler explanation of the three main types of motorcycles:
1. Cruiser Motorcycles
These are comfortable bikes for long rides, with low seats and wide tires. They are great for relaxed, easy riding. Example: Harley-Davidson.
2. Sport Motorcycles
These bikes are fast, lightweight, and built for speed and handling. They are ideal for riders who enjoy speed and agility. Example: Yamaha YZF-R1.
3. Touring Motorcycles
Designed for long trips, touring bikes have large fuel tanks, comfortable seats, and lots of storage space. Example: Honda Gold Wing.
You May Also Like