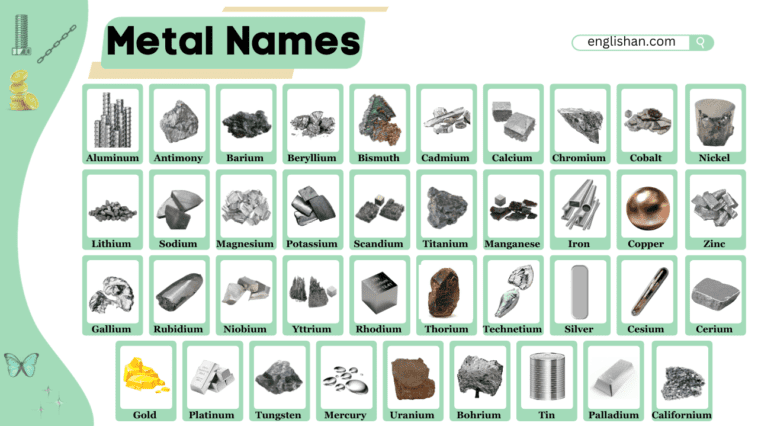
Let’s talk about metal names – the words we use for different metals. These names are like a secret code, telling us about the metals. Some are easy, like gold and silver, while others sound like they come from a magical language.
There are strong metals, like iron and copper, and special ones, like platinum and palladium. Some metals, such as cesium and rubidium, have names that sound a bit unusual, adding a fun twist to the mix.
In this journey of metal words, we discover a special language that paints a picture of each metal’s character. So, join the adventure as we unravel the mystery behind the names of metals and find out what makes each one special.
Names of some common metals in English
Iron (Fe): A strong and abundant metal used in construction and manufacturing.
Copper (Cu): Known for its excellent conductivity, used in electrical wiring and plumbing.
Aluminum (Al): Lightweight metal used in aerospace, packaging, and construction.
Gold (Au): Precious metal valued for its rarity and use in jewelry and electronics.
Silver (Ag): Precious metal with antimicrobial properties, used in jewelry and photography.
Platinum (Pt): Precious metal with high corrosion resistance, used in jewelry and catalytic converters.
Lead (Pb): Dense and malleable metal, historically used in pipes and batteries.
Zinc (Zn): Corrosion-resistant metal used in galvanization and as an essential nutrient.
Nickel (Ni): Alloyed with other metals to improve strength, corrosion resistance, and conductivity.
Tin (Sn): Malleable metal used in solder and as a coating for other metals.
Mercury (Hg): Liquid metal at room temperature, historically used in thermometers.
Titanium (Ti): Lightweight and strong metal used in aerospace, medical implants, and sports equipment.
Brass: Alloy of copper and zinc, known for its gold-like appearance and corrosion resistance.
Bronze: Alloy of copper and tin, historically used for tools, weapons, and art.
Steel: Alloy of iron and carbon, known for its strength and versatility.
Chromium (Cr): Hard and corrosion-resistant metal used in stainless steel and plating.
Cobalt (Co): Used in alloys, magnets, and as a component in rechargeable batteries.
Manganese (Mn): Used in steel production and as a component in batteries.
Tungsten (W): Very high melting point metal used in high-temperature applications.
Vanadium (V): Used in alloys for strength and corrosion resistance.
Magnesium (Mg): Lightweight metal used in aerospace and automotive industries.
Rhodium (Rh): Precious metal often used as a catalyst in chemical reactions.
Palladium (Pd): Precious metal used in catalytic converters and electronics.
Lithium (Li): Lightweight metal used in batteries and certain medications.
Gallium (Ga): Low melting point metal used in electronics.
Indium (In): Used in electronics and as an alloy to improve other metals.
Bismuth (Bi): Brittle metal is often used in alloys and pharmaceuticals.
Antimony (Sb): Used in flame retardants and as an alloy with lead.
Tellurium (Te): Used in alloys and electronics.
Ruthenium (Ru): Rare metal used in electronics and catalysis.
Iridium (Ir): Dense and corrosion-resistant metal used in spark plugs and electronics.
Osmium (Os): Densest naturally occurring element, used in alloys.
Scandium (Sc): Lightweight metal used in aerospace alloys.
Yttrium (Y): Used in alloys and electronics.
Niobium (Nb): Used in alloys, superconductors, and medical implants.
Tantalum (Ta): Resistant to corrosion and used in electronics and medical implants.
Hafnium (Hf): Used in alloys with titanium and in nuclear reactors.
Rhenium (Re): High melting point metal used in high-temperature applications.
Cadmium (Cd): Used in batteries, pigments, and as a corrosion-resistant coating.
Cesium (Cs): Alkali metal used in atomic clocks and in drilling fluids.
Strontium (Sr): Used in fireworks, flares, and certain alloys.
Barium (Ba): Used in drilling fluids, fireworks, and medical imaging.
Thallium (Tl): Used in electronics, optics, and as a contrast agent in medical imaging.
Lanthanum (La): Rare earth element used in alloys and catalysts.
Cerium (Ce): Rare earth element used in catalysts, glass manufacturing, and as a polishing agent.
Praseodymium (Pr): Rare earth element used in magnets and alloys.
Neodymium (Nd): Rare earth element used in magnets and lasers.
Promethium (Pm): Radioactive element used in nuclear batteries.
Samarium (Sm): Rare earth element used in magnets and nuclear reactors.
Europium (Eu): Rare earth element used in phosphors for color displays.
Gadolinium (Gd): Used in medical imaging and neutron capture therapy.
Terbium (Tb): Rare earth element used in phosphors for color displays.
Dysprosium (Dy): Rare earth element used in magnets and nuclear reactors.
Holmium (Ho): Used in certain lasers and nuclear reactors.
Erbium (Er): Used in lasers, amplifiers, and as a pink coloring agent in glass.
Thulium (Tm): Used in lasers and medical imaging.
Ytterbium (Yb): Used in lasers, nuclear reactors, and certain alloys.
Lutetium (Lu): Rare earth element used in certain medical applications.
Actinium (Ac): Radioactive element used in neutron sources.
Thorium (Th): Radioactive element with potential applications in nuclear energy.
Protactinium (Pa): Radioactive element with limited practical applications.
Uranium (U): Radioactive element used in nuclear reactors and weapons.
Neptunium (Np): Artificially produced radioactive element.
Plutonium (Pu): Artificially produced radioactive element used in nuclear weapons and reactors.
Americium (Am): Artificially produced radioactive element used in smoke detectors.
Curium (Cm): Artificially produced radioactive element with research applications.
Berkelium (Bk): Artificially produced radioactive element with research applications.
Californium (Cf): Artificially produced radioactive element with research applications.
Einsteinium (Es): Artificially produced radioactive element with research applications.
Fermium (Fm): Artificially produced radioactive element with research applications.
List of Metals Name with Symbols on the periodic table:
| Sr. No | Metal Elements | Symbol | Atomic Number |
| 1. | Aluminium | Al | 13 |
| 2. | Scandium | Sc | 21 |
| 3. | Zinc | Zn | 30 |
| 4. | Gallium | Ga | 31 |
| 5. | Rubidium | Rb | 37 |
| 6. | Strontium | Sr | 38 |
| 7. | Potassium | K | 19 |
| 8. | Calcium | Ca | 20 |
| 9. | Gadolinium | Gd | 64 |
| 10. | Terbium | Tb | 65 |
| 11. | Dysprosium | Dy | 66 |
| 12. | Lanthanum | La | 57 |
| 13. | Cerium | Ce | 58 |
| 14. | Praseodymium | Pr | 59 |
| 15. | Lithium | Li | 3 |
| 16. | Beryllium | Be | 4 |
| 17. | Sodium | Na | 11 |
| 18. | Magnesium | Mg | 12 |
| 19. | Molybdenum | Mo | 42 |
| 20. | Technetium | Tc | 43 |
| 21. | Ruthenium | Ru | 44 |
| 22. | Gold | Au | 79 |
| 23. | Mercury | Hg | 80 |
| 24. | Thallium | Tl | 81 |
| 25. | Lead | Pb | 82 |
| 26. | Yttrium | Y | 39 |
| 27. | Zirconium | Zr | 40 |
| 28. | Niobium | Nb | 41 |
| 29. | Flerovium | Fl | 114 |
| 30. | Moscovium | Mc | 115 |
| 31. | Livermorium | Lv | 116 |
| 32. | Silver | Ag | 47 |
| 33. | Cadmium | Cd | 48 |
| 34. | Indium | In | 49 |
| 35. | Osmium | Os | 76 |
| 36. | Iridium | Ir | 77 |
| 37. | Platinum | Pt | 78 |
| 38. | Neodymium | Nd | 60 |
| 39. | Promethium | Pm | 61 |
| 40. | Samarium | Sm | 62 |
| 41. | Berkelium | Bk | 97 |
| 42. | Californium | Cf | 98 |
| 43. | Einsteinium | Es | 99 |
| 44. | Fermium | Fm | 100 |
| 45. | Europium | Eu | 63 |
| 46. | Holmium | Ho | 67 |
| 47. | Erbium | Er | 68 |
| 48. | Thulium | Tm | 69 |
| 49. | Ytterbium | Yb | 70 |
| 50. | Uranium | U | 92 |
| 51. | Neptunium | Np | 93 |
| 52. | Plutonium | Pu | 94 |
| 53. | Americium | Am | 95 |
| 54. | Curium | Cm | 96 |
| 55. | Lutetium | Lu | 71 |
| 56. | Hafnium | Hf | 72 |
| 57. | Tantalum | Ta | 73 |
| 58. | Tungsten | W | 74 |
| 59. | Rhenium | Re | 75 |
| 60. | Darmstadtium | Ds | 110 |
| 61. | Roentgenium | Rg | 111 |
| 62. | Copernicium | Cn | 112 |
| 63. | Nihonium | Nh | 113 |
| 64. | Bismuth | Bi | 83 |
| 65. | Polonium | Po | 84 |
| 66. | Francium | Fr | 87 |
| 67. | Radium | Ra | 88 |
| 68. | Seaborgium | Sg | 106 |
| 69. | Bohrium | Bh | 107 |
| 70. | Hassium | Hs | 108 |
| 71. | Meitnerium | Mt | 109 |
| 72. | Actinium | Ac | 89 |
| 73. | Thorium | Th | 90 |
| 74. | Protactinium | Pa | 91 |
| 75. | Mendelevium | Md | 101 |
| 76. | Nobelium | No | 102 |
| 77. | Lawrencium | Lr | 103 |
| 78. | Rutherfordium | Rf | 104 |
| 79. | Dubnium | Db | 105 |
| 80. | Titanium | Ti | 22 |
| 81. | Vanadium | V | 23 |
| 82. | Chromium | Cr | 24 |
| 83. | Manganese | Mn | 25 |
| 84. | Tin | Sn | 50 |
| 85. | Cesium | Cs | 55 |
| 86. | Barium | Ba | 56 |
| 87. | Iron | Fe | 26 |
| 88. | Cobalt | Co | 27 |
| 89. | Nickel | Ni | 28 |
| 90. | Copper | Cu | 29 |
You May Also Like
- Musical Instruments Names
- Parts of Computer
- Natural Vocabulary on Earth
- Types of Adverb
- Tools Name
- Symbols of Maths
- Medical Equipment