A sentence is the largest independent grammatical unit of every language. In our daily life, we use some group of words arranged in a certain way to communicate with others or to express ourselves, In English grammar, these groups of words are called sentences and there are different Types of Sentences in English grammar.
What is a sentence?
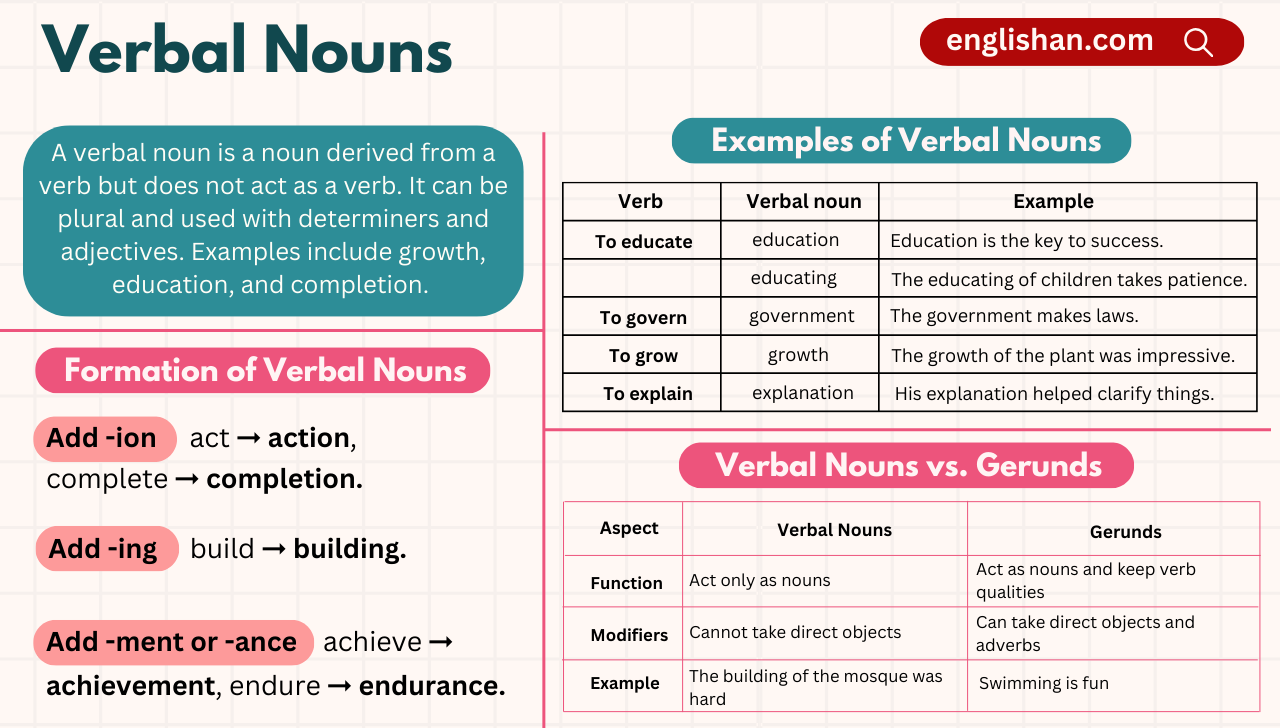
Any combination or group of related words that express a complete thought is called a sentence. There can be one or more than one clauses or phrases in a sentence. A sentence must have a complete idea that stands alone (independent clause).
A sentence must contain at least one subject and predicate. And it always starts with a capital letter and ends with a punctuation mark (full stop, question mark, or exclamation mark) according to the function of a sentence.
A sentence follows this pattern;
Subject + verb + object
The basic parts of a sentence are the subject, predicate, object, indirect object, and complement.
For example,
- He is watching a movie. (Subject)
- I am reading a newspaper. (predicate)
- She goes to school. (Object)
- The man builds his family a house. (indirect object)
- This man seems kind. (complement)
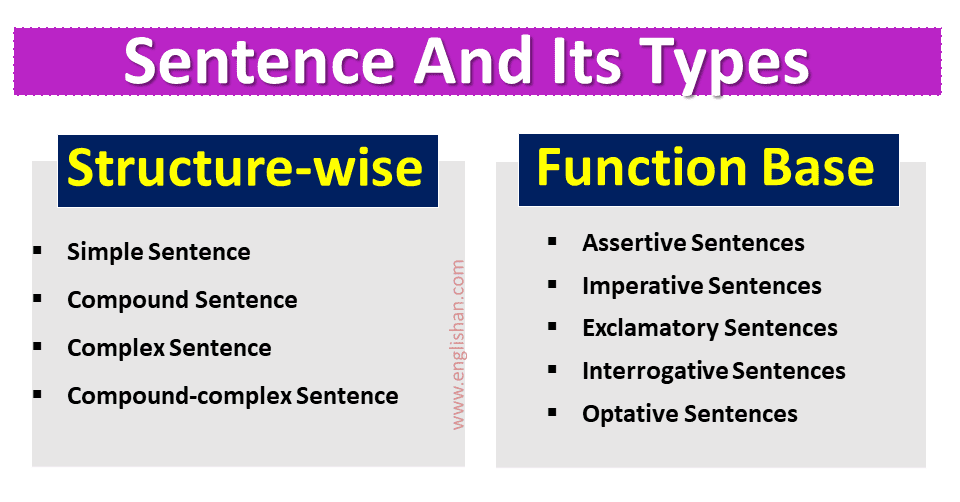
There are different types of sentences, based on structure\formation and function\meaning.
Types of Sentences by Structure
Based on structure or formation, sentences are divided into four types:
- Simple sentence
- Compound sentence
- Complex sentence
- Compound-complex sentence
Simple sentence
A simple sentence contains only one independent clause (an independent clause consists of a subject, and a predicate and expresses a complete thought).
Examples of Compound Simple Sentences
- They are playing football.
- The children are making noise.
Compound sentence
A compound sentence contains two or more independent clauses. We can join two or more independent clauses to create a compound sentence with a semicolon, or with a comma and coordinating conjunction (FANBOYS; for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so).
Examples of Compound Sentences
- He is poor but he is honest.
- I’m studying hard so I can get a good job.
Complex sentence
When we combine an independent clause with at least one dependent clause, we get a complex sentence. A complex sentence always has a relative pronoun or subordinator (as, because, since, although, if, which who, etc.)
Examples of Complex Sentences
- Although it is raining, It is quite hot today.
- She went to see a doctor because she was sick.
Compound-Complex Sentence
A compound-complex sentence contains two independent clauses and at least one dependent clause.
Examples of Compound Complex Sentences
- After I graduated, I wanted to travel but I had to work hard immediately.
- Usually, I take a walk every day while the sun sets, but it was raining today.

Types of Sentences by Function
Based on function or meaning sentences are divided into five types;
- Declarative or assertive sentences
- Imperative sentences
- Exclamatory sentences
- Interrogative sentences
- Optative sentences
Declarative or assertive sentences (statement)
Declarative or assertive sentences make statements or tell us that some action or incident has taken place and normally ends with a full stop. These sentences can be affirmative or negative.
For example,
- I’m going to Lahore.
- He didn’t write a letter.
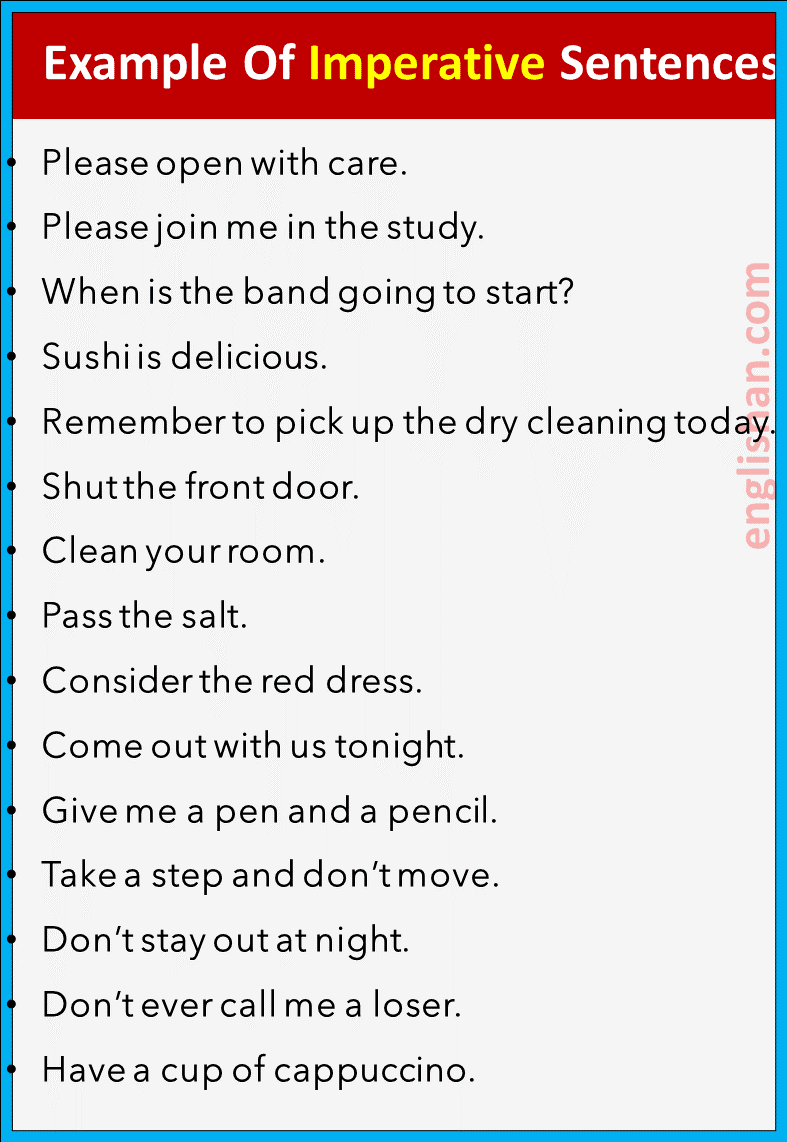
Imperative sentences (command)
A sentence that expresses a command, request, demand, or suggestion and usually ends with a full stop is called an imperative sentence.
For example,
- Be seated, please!
- Stop whispering.
Exclamatory sentences ( exclamation)
A sentence that expresses some strong feelings or sentiments (sadness, happiness, surprise) and ends with an exclamation mark is called an exclamatory sentence.
For example,
- How beautiful the mountains are!
- Oh no! he is not coming to the party!
Interrogative sentences (question)
A sentence that asks a question or inquired about something and ends with a question mark is called an Interrogative sentence.
For example,
- How many topics do you have to study?
- Where are you going?
Optative sentences (pray)
A sentence that expresses a wish, hope, desire, or curse is called an optative sentence.
For example,
- May Allah bless you!
- I wish I could see him tomorrow.

FAQs
The 4 types of sentences are:
Declarative: Makes a statement. (e.g., “I like pizza.”)
Interrogative: Asks a question. (e.g., “Do you like pizza?”)
Imperative: Gives a command. (e.g., “Eat your pizza.”)
Exclamatory: Shows strong emotion. (e.g., “What a delicious pizza!”)
The forms of sentences are:
Simple Sentence: One independent clause.
Example: “She runs fast.”
Compound Sentence: Two independent clauses joined by a conjunction.
Example: “I like pizza, and she likes pasta.”
Complex Sentence: One independent clause and one dependent clause.
Example: “I went to bed after I finished my homework.”
Compound-Complex Sentence: Two independent clauses and one or more dependent clauses.
Example: “I went to the store because we needed milk, and I bought bread.”
A simple sentence has only one independent clause, which means it expresses a complete thought with a subject and a verb.
Example:
“She sings.”
“The cat is sleeping.”
It doesn’t have any additional clauses or phrases, making it short and straightforward.
You May Also Like