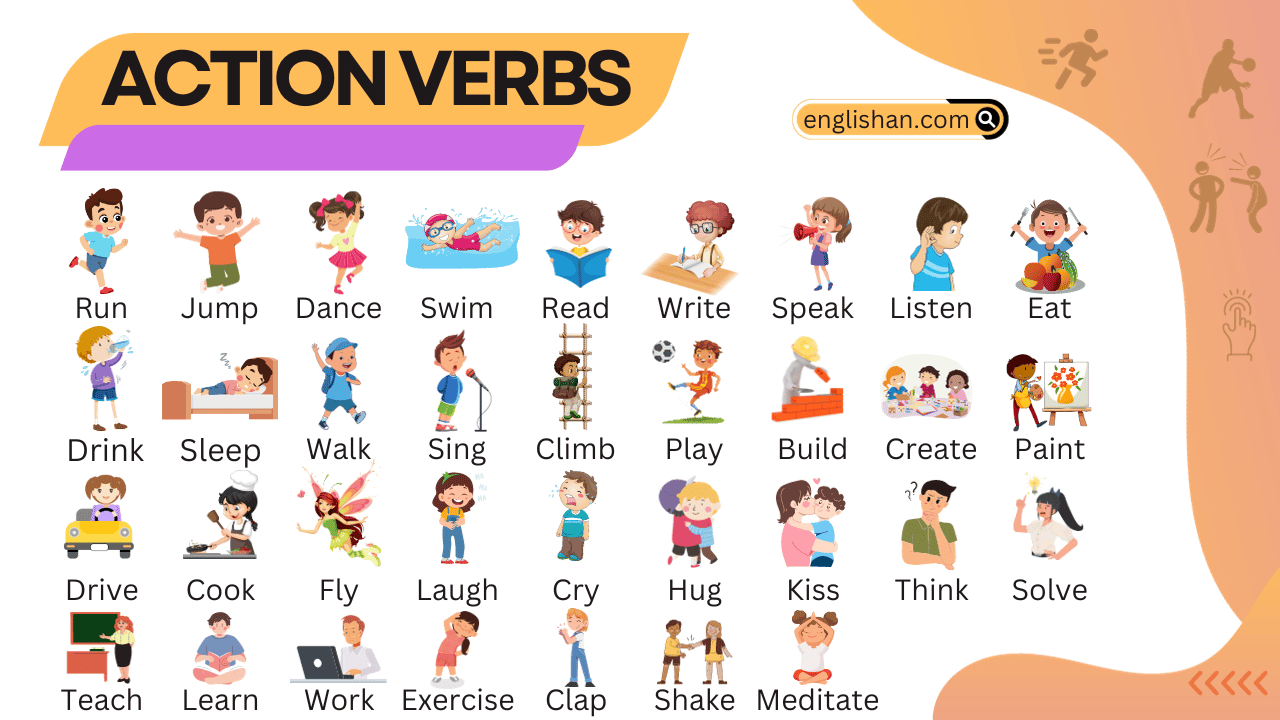
Contents
Learning about the types of soil is essential for understanding how different soils support plant growth, agriculture, and construction. In this blog post, you will learn about various soil types with pictures to enhance your vocabulary. Whether it’s sandy soil, clay soil, or loamy soil, knowing these names will help improve your English.
Improve your vocabulary by exploring more Picture Vocabulary.
Types of Soil
Coarse-Grained Soils
These soils have large particles and drain quickly, making them ideal for specific types of agriculture and landscaping.
Sandy Soil
A soil with large, coarse particles that drains water quickly and lacks nutrients.
Chalky Soil
A type of alkaline soil rich in calcium carbonate, often found in dry regions.
Desert Soil
A dry, sandy soil found in arid regions, low in organic matter and water retention.
Fine-Grained Soils
These soils have smaller particles and retain water well, making them ideal for crops and gardening.
Clay Soil
A dense soil with fine particles that holds water but is prone to becoming hard when dry.
Silt Soil
A smooth soil with fine particles that retains water better than sandy soil but drains slower.
Loamy Soil
A balanced mix of sand, silt, and clay, considered ideal for farming due to its good drainage and nutrient retention.
Organic and Special Soils
These soils contain high organic matter or unique properties that influence their use.
Peaty Soil
A dark, moisture-rich soil high in organic content, often found in wetlands.
Saline Soil
A soil with high salt content, commonly found in coastal or dry regions, which affects plant growth.
Marshy Soil
A waterlogged soil found in swamps and wetlands, rich in decomposed organic material.
Agricultural and Geologically Important Soils
These soils are significant for farming and geological processes.
Laterite Soil
A reddish soil rich in iron and aluminum, commonly found in tropical regions.
Black Soil
A nutrient-rich soil ideal for growing cotton, known for its moisture retention.
Red Soil
A soil with high iron content, giving it a red color, commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions.
Alluvial Soil
A fertile soil deposited by rivers, found in floodplains and ideal for agriculture.
Volcanic Soil
A highly fertile soil formed from volcanic ash, rich in minerals that support plant growth.
Alkaline Soil
A soil with a high pH, often requiring treatment to support plant growth.

Interesting Facts About Soil
Soil plays a vital role in the Earth’s ecosystem, supporting plant growth and filtering water. Here are some fascinating facts:
- Soil formation takes hundreds to thousands of years.
- Black soil is ideal for cotton farming due to its moisture retention.
- Volcanic soil is one of the most fertile soils due to mineral-rich ash deposits.
- Alluvial soil supports large-scale agriculture, especially in river valleys.
- Sandy soil drains quickly but requires fertilizers to support crops.
FAQs
1. What is the most fertile type of soil?
Loamy soil is considered the most fertile because it has a balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay, providing good drainage and nutrient retention.
2. What is the difference between clay soil and sandy soil?
Clay soil holds water well but becomes hard when dry, while sandy soil drains quickly and is loose in texture, making it less fertile.
3. Why is black soil important for farming?
Black soil retains moisture well and is rich in minerals, making it ideal for growing crops like cotton and cereals.
You May Also Like