Contents
Discover the different types of phrases that are used to make meaningful sentences. Read on our blog post to learn more!
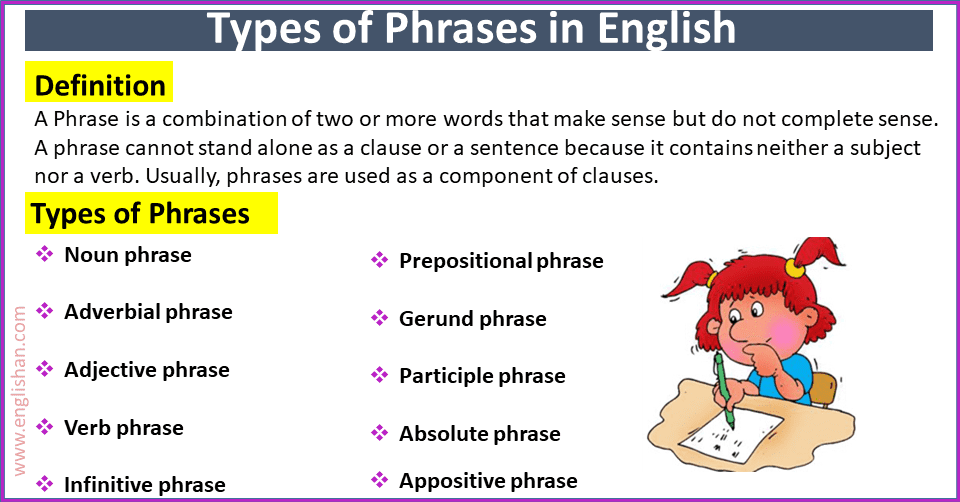
A Phrase is a combination of two or more words that make sense but do not complete sense. A phrase cannot stand alone as a clause or a sentence because it contains neither a subject nor a verb. Usually, phrases are used as a component of clauses. A phrase by itself cannot convey a complete thought but it strengthens a sentence to become meaningful. There can be more than one phrase in a sentence and phrase. And when a smaller phrase appears inside a larger one it is called a Nesting phrase. For example,
- He told me a sad story.
- I like writing short stories.
- After a few minutes, I’ll meet you in the cafeteria.
Phrases functions as a noun, adjective, verb, preposition, or an adverb in a sentence. According to their functions, phrases are divided into different types of phrases for instance,
Types of phrases
- Noun phrase
- Adverbial phrase
- Adjective phrase
- Verb phrase
- Infinitive phrase
- Prepositional phrase
- Gerund phrase
- Participle phrase
- Absolute phrase
- Appositive phrase
Noun phrase
A group of related words that functions as a noun in a sentence. It contains a noun and other associated words (modifiers and determiners) that give us more information about a noun. And it acts as a subject an object or a complement in a sentence.
For example,
- We enjoy playing cricket.
- He wants to pass the exam.
- The teacher is coming to the classroom.

Adverbial phrase
A group of words that function as an adverb in a sentence to modify a verb, adjective, or another adverb. An adverbial phrase gives us more information about the verb or a sentence by answering questions like how, when, why, and where an action takes place.
For example,
- I will do it in a minute. (when)
- He answered in a very rude manner. (how)
- The cat is hiding under the table.

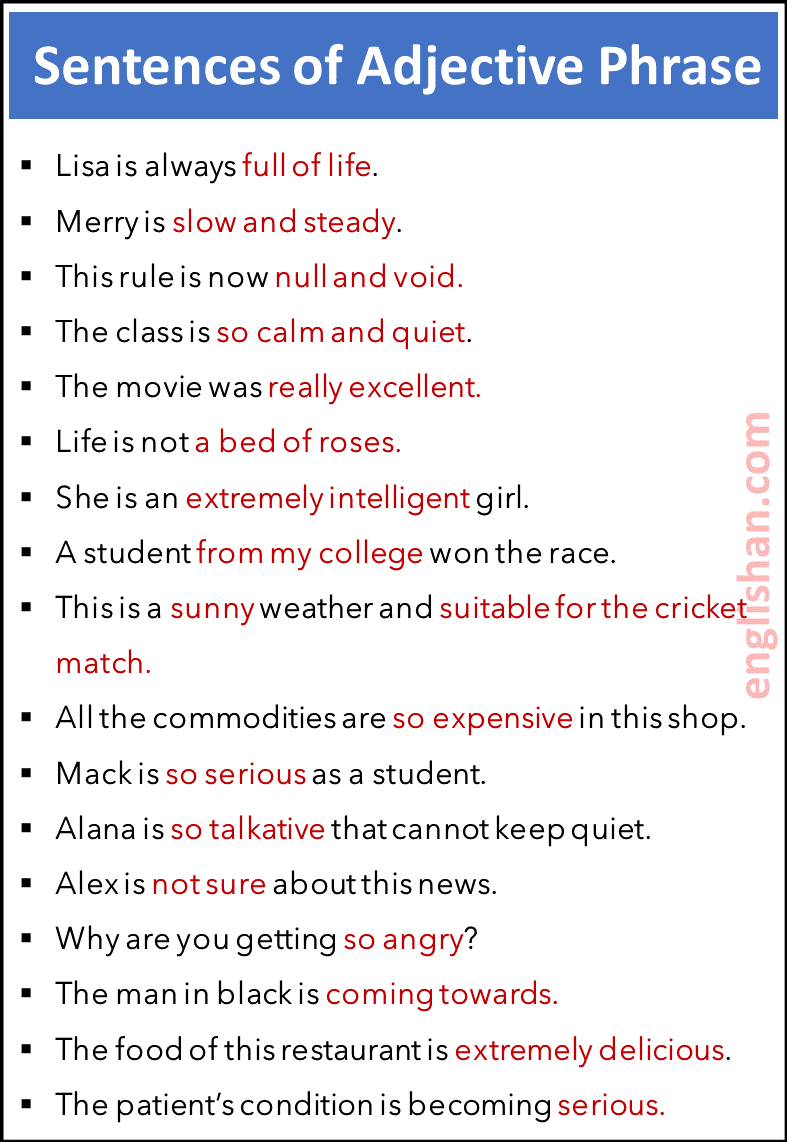
Adjective phrase
A group of words that functions as an adjective in a sentence. It gives us more information about a noun or a pronoun. An adjective phrase consists of adjectives, modifiers, and other words modifying a noun or a pronoun.
For example,
Life is not a bed of roses.
She is an extremely intelligent girl.
A student from my college won the race.
Verb phrase
A verb phrase consists of a model or helping verb plus the main verb. A verb phrase plays the role of a verb in a sentence.
For example,
- Beautiful flowers are blooming.
- She will go to the party.
- The students must reach on time for the class.

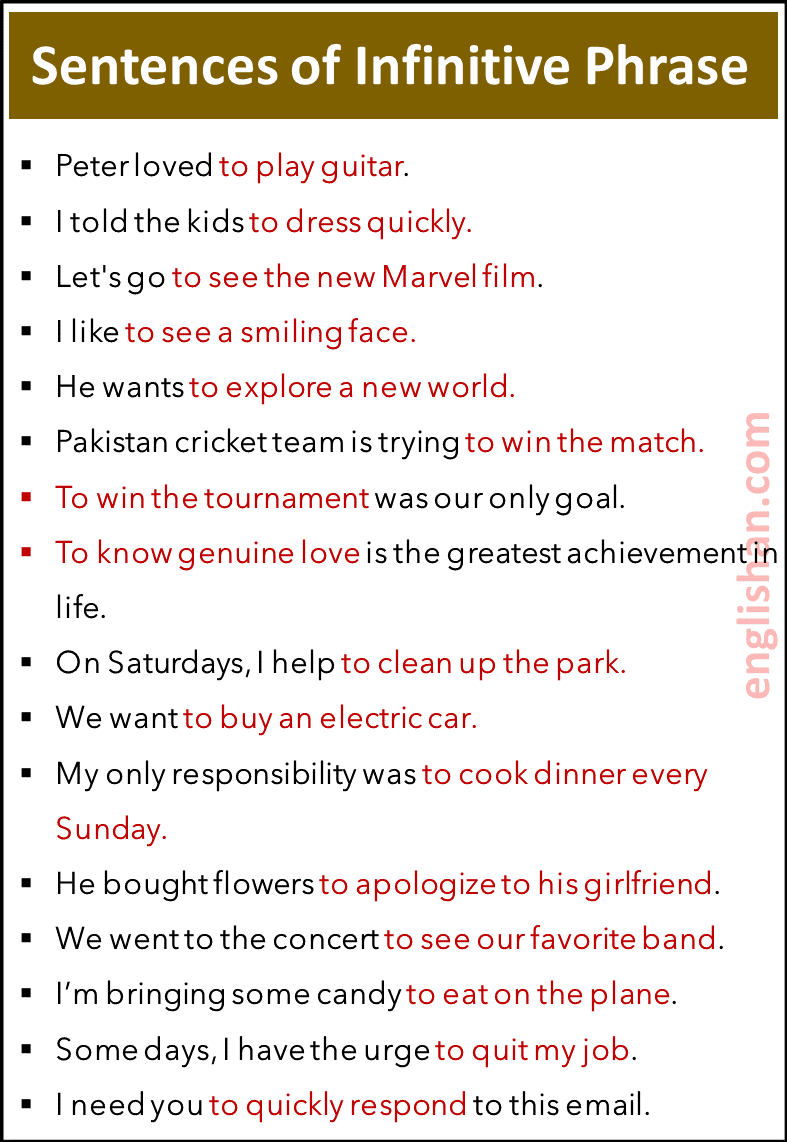
Infinitive phrase
An infinitive phrase begins with the infinitive form of the verb (to + first form of a verb) Plus modifiers or other related words. It functions either as a noun or adjective or adverb in a sentence.
For example,
- I like to see a smiling face.
- He wants to explore a new world.
- Pakistan cricket team is trying to win the match.
Prepositional phrase
A prepositional phrase is a group of words that begins with a proposition and includes the object of the preposition ( noun, pronoun, or other modifiers). The prepositional phrase functions either as an adjective or adverb in a sentence.
For example,
- The earth rotates on its axis.
- He lives in a small village.
- She is sleeping on the couch.

Gerund phrase
An Ing form of the verb that functions as a noun in a sentence is called a gerund. A gerund phrase consists of a gerund (verb + Ing), its object, and modifiers. It functions as a noun and is used as a subject or object in a sentence.
For example,
- I love writing comic books.
- He was accused of smuggling.
- They are thinking of emigrating.

Participle phrase
A participle phrase consists of a present participle (verb + ing) or a past participle (2nd form of the verb) and often includes an object or modifier to complete the thought. It functions as an adjective and is separated by commas. For example,
- The table, made of steel, is very pricey.
- The girl, standing next to the bus is my sister.
- I received a mail, mentioning my exam.

Absolute phrase
An absolute phrase is also called a nominative phrase consisting of a noun, a pronoun, a participle, and another related modifier. It refers to the interdependent group of words that has separate subjects. An absolute phrase is similar to a clause but unlike a clause, it hasn’t any finite verb. It gives us more information about the entire sentence and is separated by a comma.
For example,
- He, having an injury in his leg, won the race.
- Their eyes follow, the hook of the ball.
- Weather permitting, the meeting will be held tomorrow.

Appositive phrase
When we combine two sentences with the help of defining clause, it becomes a phrase in apposition. And these phrases are mostly used in the middle or at the end of a sentence.
For example,
- Karachi, the first capital of Pakistan, is the most populated city in Pakistan.
- Ali, my best friend, is very hardworking.
- The magistrate, the agha khan, was a kind man.
FAQs:
Here are the 5 types of phrases:
1. Noun Phrase – A group of words acting like a noun.
Example: The big dog.
2. Verb Phrase – A group of words acting like a verb.
Example: Has been working.
3. Adjective Phrase – A group of words that describe a noun.
Example: The book on the table.
4. Adverb Phrase – A group of words that describe a verb, adjective, or adverb.
Example: She sings very loudly.
5. Prepositional Phrase – A group of words starting with a preposition.
Example: The cat is under the bed.
Here are the 7 types of phrases:
1. Noun Phrase – Acts like a noun. The tall tree swayed.
2. Verb Phrase – Acts like a verb. She has been reading.
3. Adjective Phrase – Describes a noun. The dog with the red collar.
4. Adverb Phrase – Describes a verb, adjective, or adverb. He ran very quickly.
5. Prepositional Phrase – Starts with a preposition. The book is on the table.
6. Infinitive Phrase – Starts with “to” + verb. I want to eat pizza.
7. Gerund Phrase – A verb + ing acting as a noun. Running in the morning is fun.
Here are 12 simple examples of phrases:
1. Noun Phrase – The red apple fell.
2. Verb Phrase – She is running fast.
3. Adjective Phrase – The house with the blue door is nice.
4. Adverb Phrase – He works very hard.
5. Prepositional Phrase – The cat is under the table.
6. Infinitive Phrase – I want to play soccer.
7. Gerund Phrase – Swimming in the pool is fun.
8. Participial Phrase – Running fast, he caught the ball.
9. Absolute Phrase – Her hands shaking, she opened the letter.
10. Appositive Phrase – My friend, a great artist, painted the picture.
11. Verb + Object Phrase – She ate the pizza.
12. Adjective + Noun Phrase – A big dog barked loudly.
Here are 12 examples of phrases:
1. The tall tree
2. Is running fast
3. With the blue door
4. Very clearly
5. Under the table
6. To play soccer
7. Swimming in the pool
8. Running fast
9. A talented musician
10. Ate the pizza
11. On the shelf
12. With great speed
The difference between idioms and phrases:
Idioms are expressions where the meaning is not literal.
Example: “Piece of cake” means something is easy.
Phrases are groups of words with a literal meaning.
Example: “On the table” means something is physically on top of the table.
You May Also Like