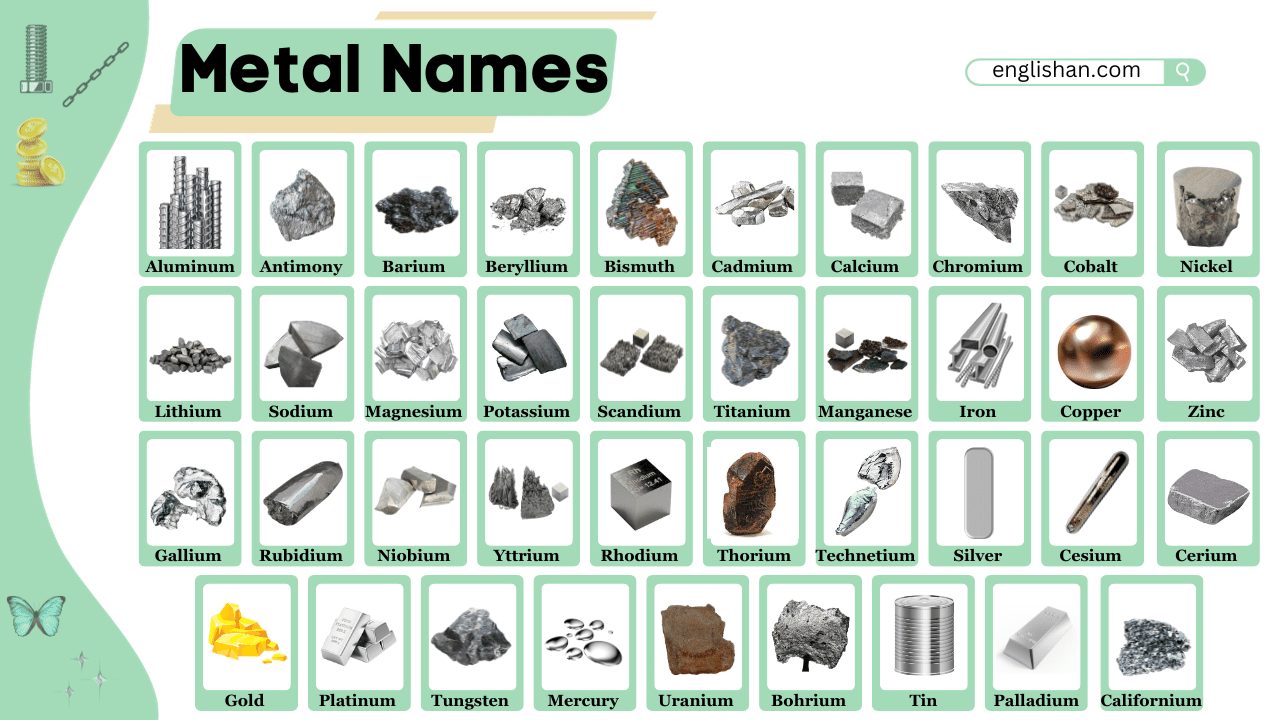
Learning metal names in English helps kids and beginners recognize different types of metals used in words and visuals. Whether you’re reading science books or ESL material, knowing these metal words will make vocabulary easier and more fun. From common metals like iron to precious ones like gold, this list will help you learn them by name and image. Let’s explore the most useful metal names in English for students and vocabulary learners.
Common Metal Names List
These metals are widely used in everyday life, from household items to batteries and structural components. Dividing them into practical categories helps learners group and recall them better.
Light Metals
- Aluminum: This silvery metal is rust-resistant and lightweight. It’s used in cans, airplanes, and window frames.
- Magnesium: Very light and flammable. Used in fireworks, flares, and strong car parts.
- Calcium: Needed for bones. As a metal, used in some refining and chemical reactions.
- Beryllium: Lightweight and strong. Common in aerospace tools and electrical parts.
- Potassium: Soft and important in medicine. Helps with nerves and heart signals.
- Sodium: Very soft and reactive. Used in labs and special lamps.
- Rubidium: Soft and reactive. Used in research and electronics.
- Cesium: Very soft and reactive. Used in atomic clocks and lab tools.
- Gallium: Melts in your hand. Found in solar panels and LEDs.
- Scandium: Strengthens aluminum. Used in planes and sports gear.
Conductive and Electrical Metals
- Copper: A reddish metal that carries electricity well. Used in wires, motors, and home devices.
- Silver: Shiny and conducts electricity. Used in jewelry, coins, and tech screens.
- Gold: Rare and valuable. Used in electronics and high-end connectors.
- Aluminum: Also conducts electricity and is used in power cables.
- Ruthenium: A rare metal used in electronics. It helps chips last longer and conduct electricity better.
Heavy Duty Metals
- Steel: A mix of iron and carbon. Strong and found in buildings, machines, and cookware.
- Iron: Common in tools and construction. Adds strength and stability.
- Lead: A heavy metal used in batteries. It also blocks harmful radiation.
- Zirconium: Resists heat and corrosion. Used in reactors and surgical tools.
- Niobium: Resists corrosion. Strengthens steel and helps make superconductors.
- Tungsten: Has a very high melting point. Used in lightbulbs and hard tools.
- Titanium: Lightweight but strong. Found in airplanes and implants.
- Chromium: Adds shine and resists rust. Used in plating, steel, and colored glass.
- Manganese: Added to steel to make it stronger. Found in machines and tools.
- Vanadium: Used in tough alloys. Improves strength and flexibility of metal parts.
Battery and Energy-Related Metals
- Lithium: It’s a light metal used in batteries. Found in phones, laptops, and electric cars for storing energy.
- Cobalt: Found in batteries and magnets. It helps store power and supports electric technologies.
- Nickel: Used in many rechargeable batteries and also in stainless steel.
- Cadmium: Soft and toxic. Used in pigments and batteries.
Rare and Colorful Metals
- Bismuth: Colorful and safe. Used in cosmetics and fire alarms.
- Osmium: Densest known metal. Used in pens, circuits, and scientific gear.
- Iridium: Very hard and shiny. Found in pens, spark plugs, and lasting tools.
- Rhodium: Shiny and corrosion-resistant. Used in mirrors, jewelry, and cars.
- Yttrium: Found in LEDs and lasers. Used in cancer treatment too.
- Cerium: Makes sparks in lighters. Also used for polishing glass.
- Antimony: Hard and brittle. Found in fireproofing and some old batteries.
- Barium: Glows green in fireworks. Used in X-ray contrast liquids.
Ferrous and Non-Ferrous Metals Names
Metals are often sorted by whether they contain iron. Ferrous metals are magnetic and strong. Non-ferrous ones are lighter and resist corrosion better.
Iron-Based (Ferrous) Metal Names
- Iron
- Steel
- Cast Iron
- Carbon Steel
- Wrought Iron
Non-Ferrous Metals Without Iron
- Copper
- Aluminum
- Zinc
- Nickel
- Tin
- Lead
- Brass
- Bronze
Precious and Rare Metals
These metals are valuable because of their rarity, durability, or shine. They’re often used in jewelry, coins, electronics, and even in medical tools.
Metals Used in Jewelry and Trade
- Gold
- Silver
- Platinum
- Rhodium
High-Value Rare Metals
- Palladium
- Iridium
- Osmium
- Ruthenium
- Rhodium
- Scandium
- Yttrium
Industrial and Structural Metals
These metals help support buildings, bridges, vehicles, and machines. They are chosen for being strong, workable, and resistant to damage.
Metals Used in Construction and Engineering
- Steel
- Iron
- Copper
- Aluminum
- Manganese
Machine and Heavy Use Metals
- Titanium
- Tungsten
- Chromium
- Nickel
- Vanadium
- Zirconium
- Niobium
Names of Alkali and Transition Metals
Some metals are highly reactive, others are more stable and colorful. This section includes soft alkali metals and versatile transition metals.
Group 1 Soft Reactive Metals
- Lithium
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Rubidium
- Cesium
- Francium
Widely Used Transition Metals
- Iron
- Copper
- Nickel
- Zinc
- Chromium
- Titanium
- Manganese
- Cobalt
- Vanadium
Metal Alloys List
Alloys are made by mixing two or more metals. This gives them special properties, such as increased strength or resistance to rust.
Alloys and Their Base Elements
- Steel: Iron + Carbon
- Stainless Steel: Iron + Chromium + Nickel
- Bronze: Copper + Tin
- Brass: Copper + Zinc
- Solder: Tin + Lead
- Pewter: Tin + Copper + Antimony
- Nichrome: Nickel + Chromium
- Inconel: Nickel + Chromium + Iron
- Duralumin: Aluminum + Copper
- Titanium Alloy: Titanium + Aluminum or Vanadium
Metals Names and Symbols in Periodic Table
| Metal Elements | Symbol | Atomic Number |
| Aluminium | Al | 13 |
| Scandium | Sc | 21 |
| Zinc | Zn | 30 |
| Gallium | Ga | 31 |
| Rubidium | Rb | 37 |
| Strontium | Sr | 38 |
| Potassium | K | 19 |
| Calcium | Ca | 20 |
| Gadolinium | Gd | 64 |
| Terbium | Tb | 65 |
| Dysprosium | Dy | 66 |
| Lanthanum | La | 57 |
| Cerium | Ce | 58 |
| Praseodymium | Pr | 59 |
| Lithium | Li | 3 |
| Beryllium | Be | 4 |
| Sodium | Na | 11 |
| Magnesium | Mg | 12 |
| Molybdenum | Mo | 42 |
| Technetium | Tc | 43 |
| Ruthenium | Ru | 44 |
| Gold | Au | 79 |
| Mercury | Hg | 80 |
| Thallium | Tl | 81 |
| Lead | Pb | 82 |
| Yttrium | Y | 39 |
| Zirconium | Zr | 40 |
| Niobium | Nb | 41 |
| Flerovium | Fl | 114 |
| Moscovium | Mc | 115 |
| Livermorium | Lv | 116 |
| Silver | Ag | 47 |
| Cadmium | Cd | 48 |
| Indium | In | 49 |
| Osmium | Os | 76 |
| Iridium | Ir | 77 |
| Platinum | Pt | 78 |
| Neodymium | Nd | 60 |
| Promethium | Pm | 61 |
| Samarium | Sm | 62 |
| Berkelium | Bk | 97 |
| Californium | Cf | 98 |
| Einsteinium | Es | 99 |
| Fermium | Fm | 100 |
| Europium | Eu | 63 |
| Holmium | Ho | 67 |
| Erbium | Er | 68 |
| Thulium | Tm | 69 |
| Ytterbium | Yb | 70 |
| Uranium | U | 92 |
| Neptunium | Np | 93 |
| Plutonium | Pu | 94 |
| Americium | Am | 95 |
| Curium | Cm | 96 |
| Lutetium | Lu | 71 |
| Hafnium | Hf | 72 |
| Tantalum | Ta | 73 |
| Tungsten | W | 74 |
| Rhenium | Re | 75 |
| Darmstadtium | Ds | 110 |
| Roentgenium | Rg | 111 |
| Copernicium | Cn | 112 |
| Nihonium | Nh | 113 |
| Bismuth | Bi | 83 |
| Polonium | Po | 84 |
| Francium | Fr | 87 |
| Radium | Ra | 88 |
| Seaborgium | Sg | 106 |
| Bohrium | Bh | 107 |
| Hassium | Hs | 108 |
| Meitnerium | Mt | 109 |
| Actinium | Ac | 89 |
| Thorium | Th | 90 |
| Protactinium | Pa | 91 |
| Mendelevium | Md | 101 |
| Nobelium | No | 102 |
| Lawrencium | Lr | 103 |
| Rutherfordium | Rf | 104 |
| Dubnium | Db | 105 |
| Titanium | Ti | 22 |
| Vanadium | V | 23 |
| Chromium | Cr | 24 |
| Manganese | Mn | 25 |
| Tin | Sn | 50 |
| Cesium | Cs | 55 |
| Barium | Ba | 56 |
| Iron | Fe | 26 |
| Cobalt | Co | 27 |
| Nickel | Ni | 28 |
| Copper | Cu | 29 |
FAQs on Metals and Their Types
Here is a list of some common metals and their symbols:
Iron – Fe
Gold – Au
Silver – Ag
Copper – Cu
Aluminum – Al
Zinc – Zn
Lead – Pb
Magnesium – Mg
Titanium – Ti
Nickel – Ni
These are just a few examples of metals and their symbols. Let me know if you need more!
Here are some examples of elements and their symbols from the periodic table:
Hydrogen – H
Oxygen – O
Carbon – C
Nitrogen – N
Iron – Fe
Gold – Au
Silver – Ag
Copper – Cu
Aluminum – Al
Helium – He
These are just a few elements and their symbols. There are many more in the periodic table! Would you like more examples or a specific group of elements?
Read More