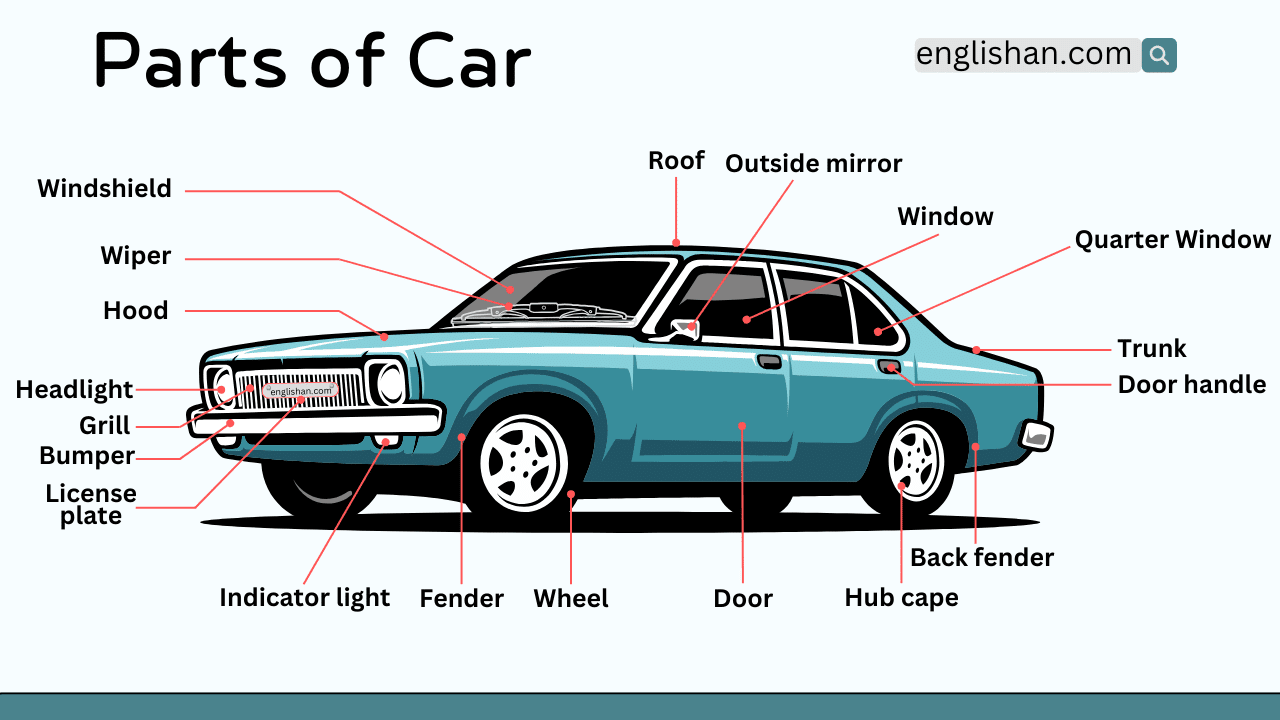
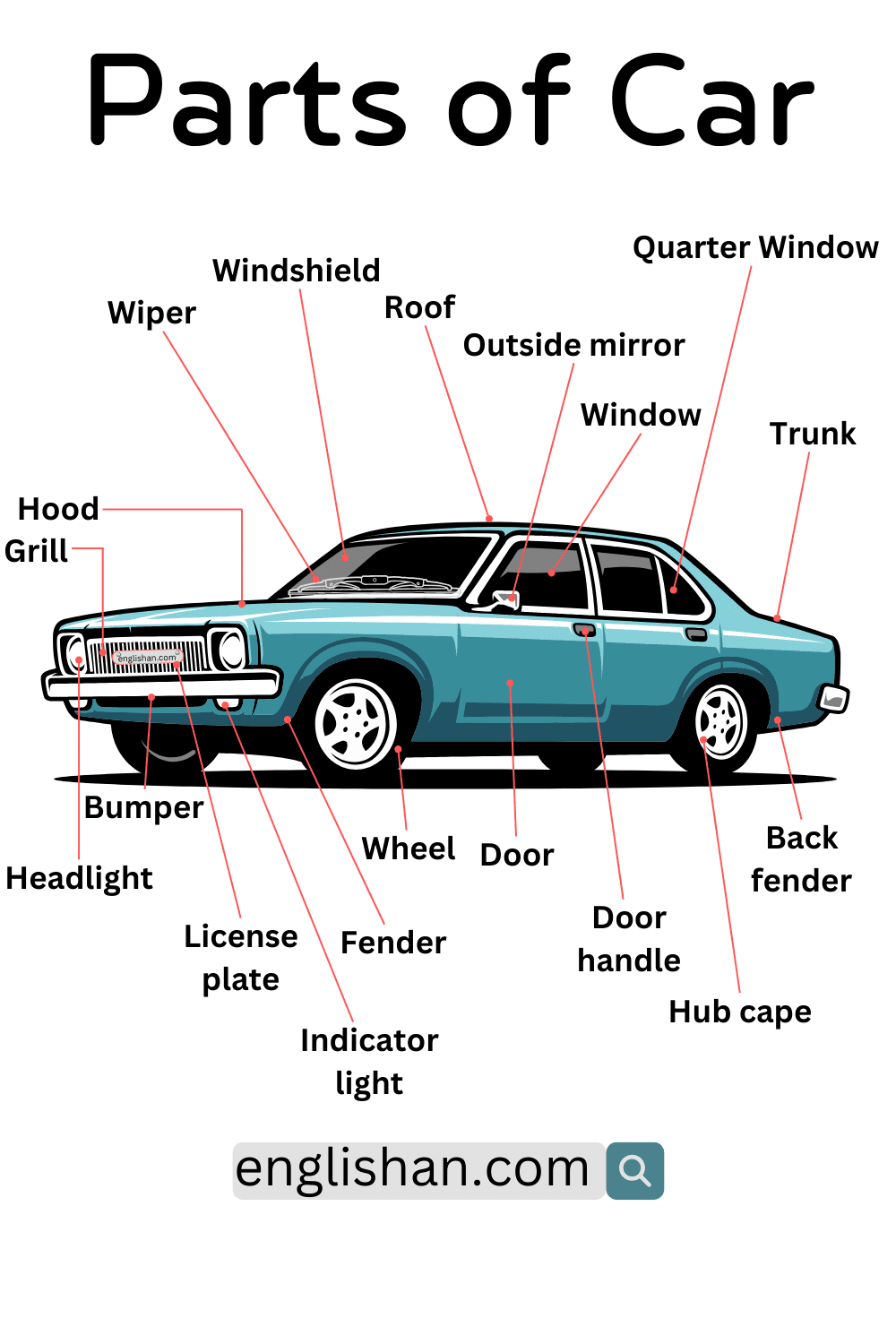
A car is made up of many automotive parts that work together, even though most stay hidden under panels and covers. If you are learning vehicle basics, talking with a mechanic, or studying how motion, control, and safety connect, missing the correct names can quickly cause confusion and weak explanations.
In this article, we break down the parts of a car with focus on standard passenger vehicles. The coverage includes the engine, transmission, radiator, suspension, brakes, battery, exhaust, and fuel system, using common layouts as reference. The labeled diagram below helps match each name to its position with confidence.
List of Car Parts Names
- Roof
- Sunroof
- Windshield
- Windshield Wiper
- Windshield Washer Nozzle
- Outside Rearview Mirror
- Rearview Mirror
- Side Window
- Quarter Window
- Front Vent Window
- Window Frame
- A Pillar
- B Pillar
- C Pillar
- Roof Post
- Door Post
- Door
- Door Handle
- Door Lock
- Trunk
- Trunk Lid
- Hood
- Fender
- Front Fender
- Back Fender
- Bumper
- Front Bumper
- Rear Bumper
- Grille
- Headlight
- Tail Light
- Turn Signal
- Fog Light
- License Plate
- License Plate Light
- Wheel
- Tire
- Rim
- Hub Cap
- Spare Wheel
- Body Side Moulding
- Underbody Shield
- Steering Wheel
- Steering Column
- Seat
- Seat Belt
- Dashboard
- Instrument Cluster
- Center Console
- Gear Lever
- Pedal
- Accelerator Pedal
- Brake Pedal
- Clutch Pedal
- Battery
- Alternator
- Starter Motor
- Radiator
- Cooling Fan
- Engine
- Air Filter
- Oil Filter
- Fuel Tank
- Fuel Pump
- Transmission
- Drive Shaft
- Axle
- Differential
- Muffler
- Exhaust Pipe
- Windshield Washer Reservoir
- Brake Disc
- Brake Caliper
- Brake Pad
- Brake Hose
Exterior Body And Glass Parts
These parts form the visible outer structure and glass areas of the car.
Roof
The roof is the top body panel covering the cabin. It:
- Protects occupants from weather
- Adds strength to the body shell
Sunroof
The sunroof is a movable glass panel set into the roof. It allows:
- Light into the cabin
- Airflow when opened
Windshield
The windshield is the large front glass panel. It:
- Shields occupants from wind and debris
- Provides forward visibility
Windshield Wiper
Windshield wipers are mounted at the lower edge of the windshield. They:
- Clear rain and dust
- Keep the glass visible while driving
Windows
Windows are glass panels fitted into doors and body frames. They allow:
- Side visibility
- Ventilation
Quarter Window
The quarter window is a small fixed glass section near the rear side area.
Front Vent Window
The front vent window is a small glass panel near the front door edge, used for airflow.
Window Frame
The window frame surrounds the edges of the glass. It:
- Holds the window in position
- Supports weather seals
Mirrors
Mirrors support rear and side visibility.
Outside Rearview Mirror
This mirror is mounted on the outer side of the door. It shows traffic beside and behind the car.
Rearview Mirror
The rearview mirror is mounted inside near the windshield. It reflects the view through the rear window.
Body Panels, Doors, And Structural Posts
These parts shape the car body and support doors and roof strength.
Pillars And Posts
Structural posts connect the roof to the body.
A Pillar
The A pillar is the front roof support beside the windshield.
B Pillar
The B pillar sits between the front and rear doors and adds side strength.
C Pillar
The C pillar is the rear roof support near the back window.
Roof Post
Roof posts are vertical supports between the roof and body.
Door Post
Door posts form the edges of the door opening and support hinges and latches.
Door
Doors are hinged side panels that:
- Allow entry and exit
- Seal the cabin when closed
Door Handle
Door handles are fitted on the door surface and operate the latch.
Trunk
The trunk is the rear storage compartment used for luggage and tools.
Fender
Fenders are curved body panels over the wheels. They:
- Block road spray
- Protect body panels
Front Fender
The front fender covers the front wheel area.
Back Fender
The back fender covers the rear wheel area.
Bumper
Bumpers are mounted at the front and rear ends. They:
- Absorb minor impacts
- Protect body panels
Grille
The grille is located at the front of the car. It allows air to enter the engine bay.
Lights And Plates
These parts support visibility and signaling.
Headlight
Headlights are mounted at the front corners. They illuminate the road ahead.
Tail Light
Tail lights are mounted at the rear. They show position and braking.
Turn Signal
Turn signals are placed at front and rear corners to indicate turning.
License Plate
License plates are mounted at the front and rear to display vehicle identification.
Wheels And Exterior Accessories
These parts support movement and exterior protection.
Wheel
Wheels are mounted at each corner under the body. They:
- Support vehicle weight
- Enable movement
Hub Cap
Hub caps cover the center of the wheel and protect wheel nuts.
Spare Wheel
The spare wheel is stored in the trunk or under the car and replaces a damaged tire.
Body Side Moulding
Body side mouldings run along the side panels and reduce scratch damage.
Shield
Shields are protective panels under or around the body that guard parts from debris.
Interior Control And Seating Parts
These parts are located inside the cabin and support driving and seating.
Steering Wheel
The steering wheel is positioned in front of the driver. It:
- Controls vehicle direction
Seat
Seats are mounted on the cabin floor and support occupants while driving.
Engine, Power, And Support Parts
These parts generate power and support engine operation.
Battery
The battery is placed in the engine bay. It:
- Stores electrical power
- Starts the engine
Alternator
The alternator is driven by the engine. It generates electricity and charges the battery.
Radiator
The radiator is positioned at the front of the engine bay. It:
- Cools engine fluid
Distributor
The distributor directs spark to engine cylinders in older ignition systems.
Air Filter
The air filter is housed near the engine intake. It cleans incoming air.
Oil Filter
The oil filter is attached to the engine block and removes dirt from engine oil.
Transmission
The transmission sits between the engine and wheels. It:
- Transfers power
- Adjusts speed
Line Shaft
The line shaft runs from the transmission toward the wheels and carries rotating force.
Muffler
The muffler is mounted under the car near the rear. It reduces exhaust noise.
Windshield Washer
The windshield washer sprays cleaning fluid onto the windshield to remove dirt.
Brake Parts
Brake parts control slowing and stopping.
Disk Brake
Disk brakes are mounted inside the wheel area. They:
- Slow wheel rotation
- Stop the vehicle
Key Takeaways
A car operates as a road system where exterior body parts form structure, interior parts provide control and seating, engine parts generate power, and brake parts manage stopping. Glass supports visibility, wheels carry load, and lights signal movement. Power flows from the engine through the transmission to the wheels, while brakes reduce motion when needed. Some variation exists in design, and the parts of a car work together to support controlled road travel.
FAQs
It generates electrical power for its electrical systems and charges the battery.
The suspension system.
The radiator helps in cooling the engine by dissipating heat.
Engine oil lubricates the engine parts, reducing friction and heat, and helps in maintaining engine performance.
Brake pads create friction against the brake rotors, causing the car to slow down or stop.
The bumper.
Anti-lock Braking System.
The transmission transfers power from the engine to the wheels, allowing the car to change speeds.
Proper tire pressure ensures safety, improves fuel efficiency, and extends tire life.
The air filter cleans the air entering the engine, improving fuel efficiency and protecting engine components.
You May Also Like
- Parts Of A Car Interior
- Parts of a Car Door
- Parts of a Car Wheel
- Parts of Motorcycle
- Bicycle Parts Names
- Parts of a Train