You pick up a leaf and wonder how it feeds the whole plant. The answer is in its parts: the blade that catches sunlight, the veins that carry water, and the petiole that holds it to the stem.
I have put together a simple guide to leaf parts with a clear diagram and plain explanations for each piece. You will see where they sit and how they work together to keep the plant alive.
By the end, you will know the name of each leaf part and be able to explain what it does, whether you are studying for a test, teaching a child, or just curious about how nature works.
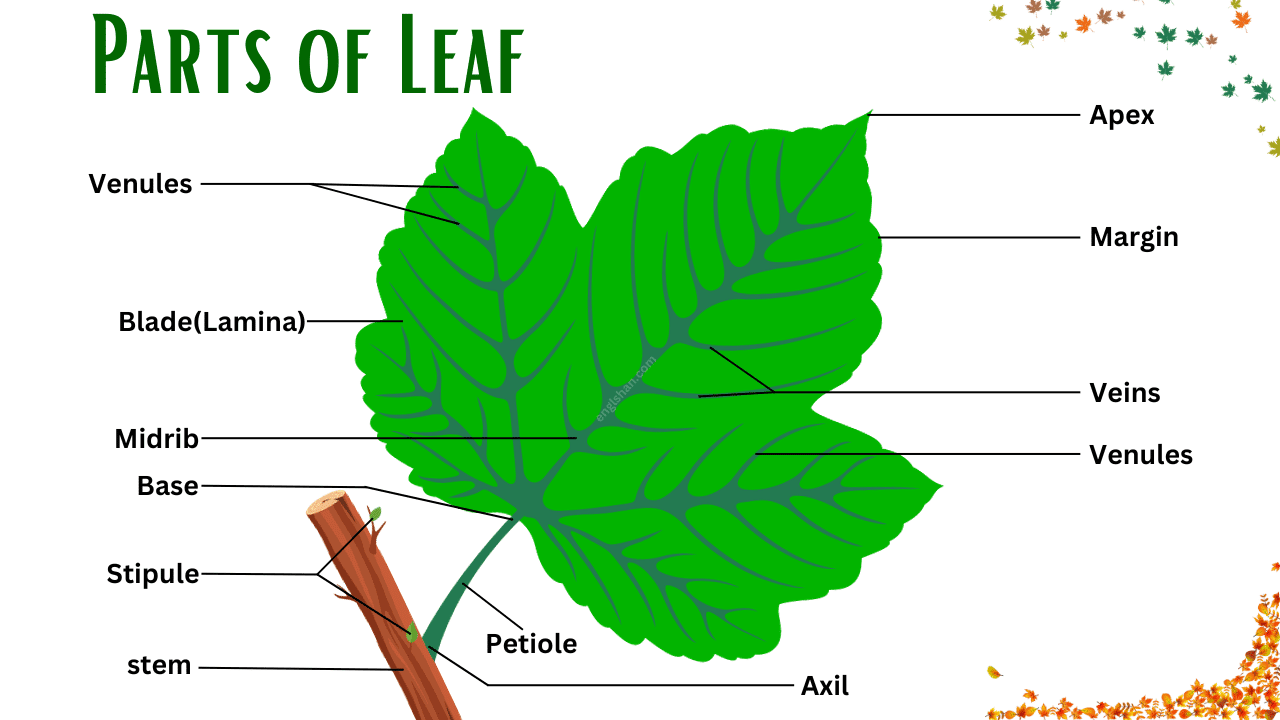
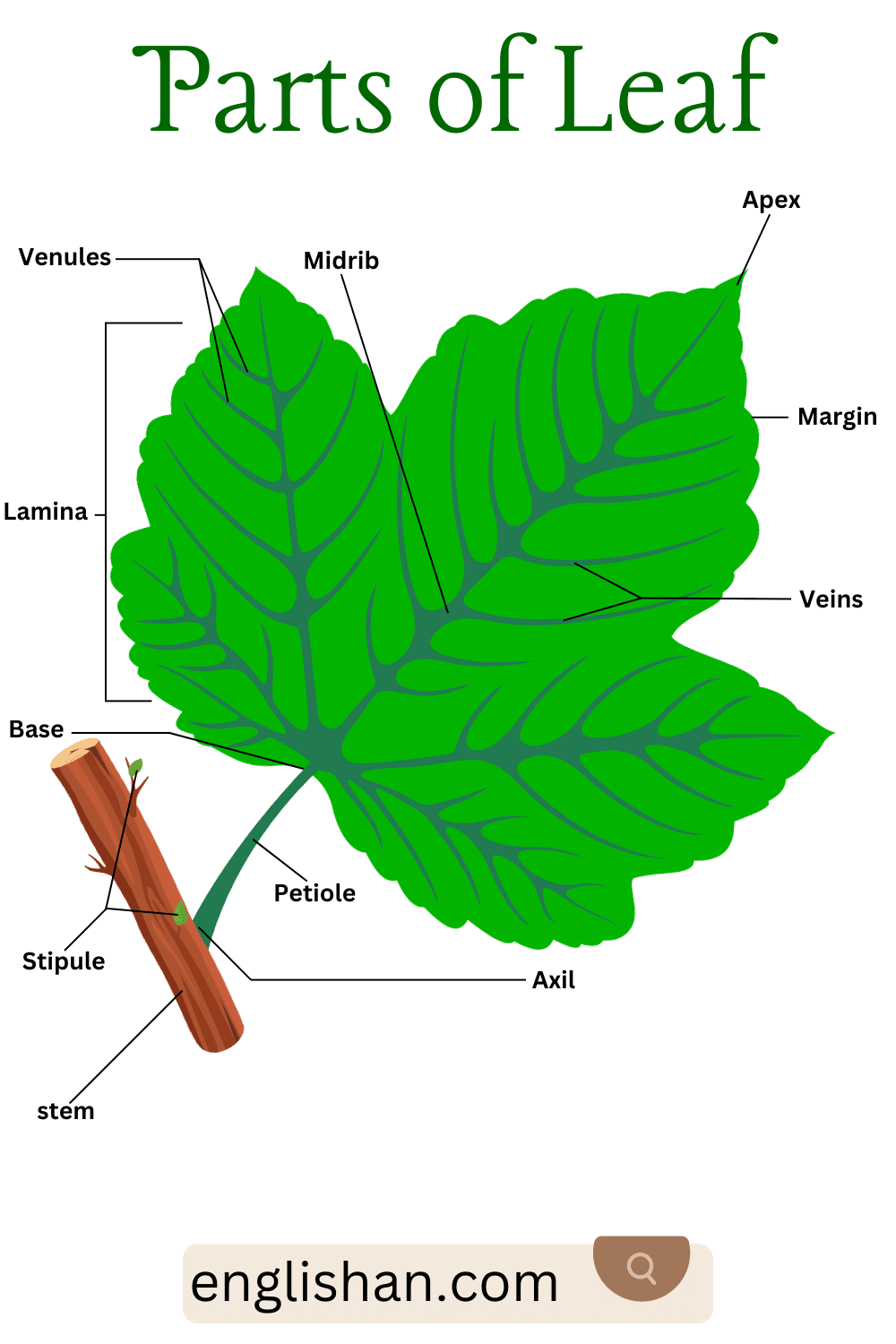
Parts of Leaf
Blade (Lamina)
The blade, or lamina, is the big, flat part of the leaf that is usually green. It’s where the plant makes its food using sunlight.
Midrib
The midrib is the thick line that runs down the middle of the leaf. It helps to hold the leaf up and carry water and food back and forth.
Base
The base is the part of the leaf that is closest to the stem or branch. It’s the spot where the leaf starts to spread out.
Stipule
Stipules are small, leaf-like parts that can be found at the base where the leaf joins the stem. Not all plants have them, but they can protect the leaf when it’s still growing.
Petiole
The petiole is like a little stick that connects the leaf blade to the plant’s stem. It helps the leaf to move and get more sunlight.
Stem
The stem is the main part that holds up the leaf and the rest of the plant. It acts like a tube for water and food to move through the plant.
Apex
The apex is the tip of the leaf, the part that points out the farthest from the stem. It’s the end of the leaf blade.
Margin
The margin is the edge of the leaf. It can be smooth, jagged, or have different patterns.
Veins
Veins are the lines you can see on the leaf blade. They are like little pipes that carry water and nutrients all through the leaf.
Venules
Venules are smaller lines that come off the veins. They help to spread the water and nutrients to all parts of the leaf.
Axil
The axil is the angle between the upper side of the stem and the leaf or branch that is growing out of it. It’s like a little pocket where you can sometimes find new flowers or leaves growing.
Functions
- Making Food: Leaves use sunlight to make food for the plant through a process called photosynthesis.
- Breathing: Leaves take in carbon dioxide from the air and release oxygen for us to breathe.
- Water Release: Leaves release extra water from the plant into the air, a process known as transpiration.
- Growth: Leaves can grow towards the light to help the plant get more of the sunlight it needs.
- Protection: Some leaves have sharp edges or substances that help protect the plant from animals and insects.
Types of Leaves
- Simple Leaves: These have one single blade on each stem. Examples include mango leaves and cherry leaves.
- Compound Leaves: These have many small leaflets joined to a single stem. Examples are the leaves of a rose or clover.
- Needle-like Leaves: Thin and pointy leaves that are good in cold places because they don’t lose much water. Pine trees have these kinds of leaves.
- Scale-like Leaves: These are small and look like scales, helping to reduce water loss. Juniper and cypress trees have these leaves.
- Spade-shaped Leaves: Wide and shaped like a spade, these are common in houseplants like the Chinese evergreen.
- Oval Leaves: Rounded or egg-shaped leaves that are very common, like the leaves on apple trees.
- Heart-shaped Leaves: These are shaped like a heart and can be found on plants like the redbud tree.
- Lobed Leaves: These have deep indentations but are still one piece, like oak leaves or maple leaves.
FAQs:
The 5 main parts of a leaf are:
1. Blade – The flat part of the leaf.
2. Petiole – The stem that connects the leaf to the plant.
3. Midrib – The central vein in the middle of the leaf.
4. eins – The lines that carry water and food.
5. Margin – The edge of the leaf.
These parts help the leaf make food for the plant!
The different parts of a leaf are:
1. Blade – The flat part of the leaf.
2. Petiole – The stem that holds the leaf.
3. Veins – Lines that carry water and food.
4. Midrib – The main vein in the center.
5. Margin – The edge of the leaf.
6. Apex – The tip of the leaf.
7. Base – The bottom part of the leaf.
These parts help the leaf do its job!
In Grade 4, a leaf is the part of a plant that helps make food.
Here’s what you learn:
1. Parts of a leaf: Blade, petiole, veins, and edges.
2. Function: Leaves use sunlight to make food for the plant.
3. Photosynthesis: The process that helps leaves make food using sunlight.
You also learn to identify different types of leaves!
The structures of simple leaves include:
1. Blade – The wide, flat part of the leaf.
2. Petiole – The stalk that connects the leaf to the stem.
3. Midrib – The main vein running down the center of the leaf.
4. Veins – Smaller lines that branch out from the midrib to carry water and nutrients.
5. Margin – The edge of the leaf, which can be smooth or jagged.
These parts work together to help the leaf carry out its job of making food for the plant!
You May Also Like
- Plants Names
- Plants Parts Names
- Types of Trees
- Gardening Tools
- Parts of Mushroom
- Green Leafy Vegetables