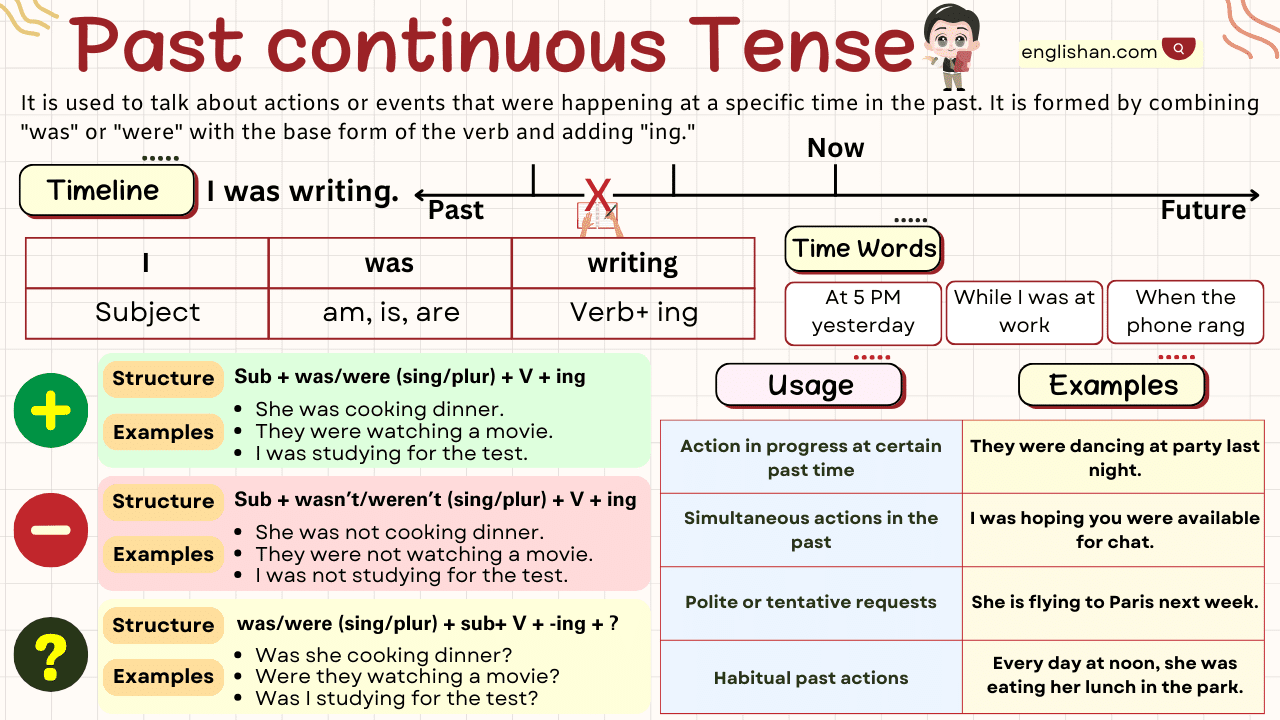
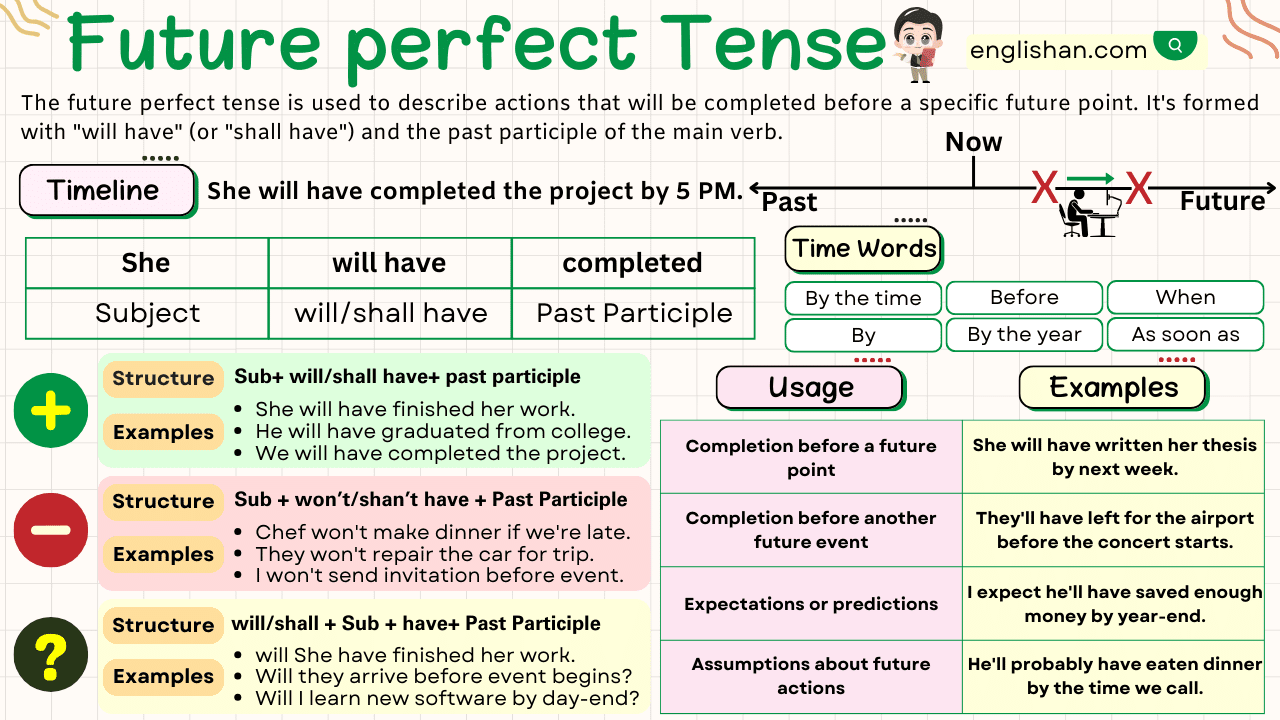
The Past Continuous Tense is used to describe actions that were ongoing at a specific time in the past. This tense is essential for setting a scene, describing simultaneous actions, or highlighting interruptions.
Examples:
- Ahmed was reading a book when the phone rang.
- They were playing football at 5 p.m. yesterday.
In these examples, the actions were in progress at a particular past moment.
Structures of the Past Continuous Tense
The Past Continuous Tense is constructed using the auxiliary verb was/were followed by the present participle (verb+ing) of the main verb. Let’s explore the different sentence structures:
Affirmative Sentences
Structure: Subject + was/were + present participle + object
Examples:
- Fatima was studying for her exam.
- The children were watching cartoons.
In these examples, the actions were ongoing in the past.
Negative Sentences
Structure: Subject + was/were not + present participle + object
Examples:
- He was not working on the project.
- We were not playing in the park.
Here, the sentences indicate that the actions were not happening at the specified past times.
Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Was/Were + subject + present participle + object?
Examples:
- Was Ahmed writing a letter?
- Were they preparing for the trip?
These questions ask if the actions were in progress during a specific time in the past.
Double Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Wh-question + was/were + subject + present participle + object?
Examples:
- What were they doing yesterday?
- Why was Sara crying during the movie?
These questions specify details about the actions occurring in the past.
Past Continuous Tense Chart
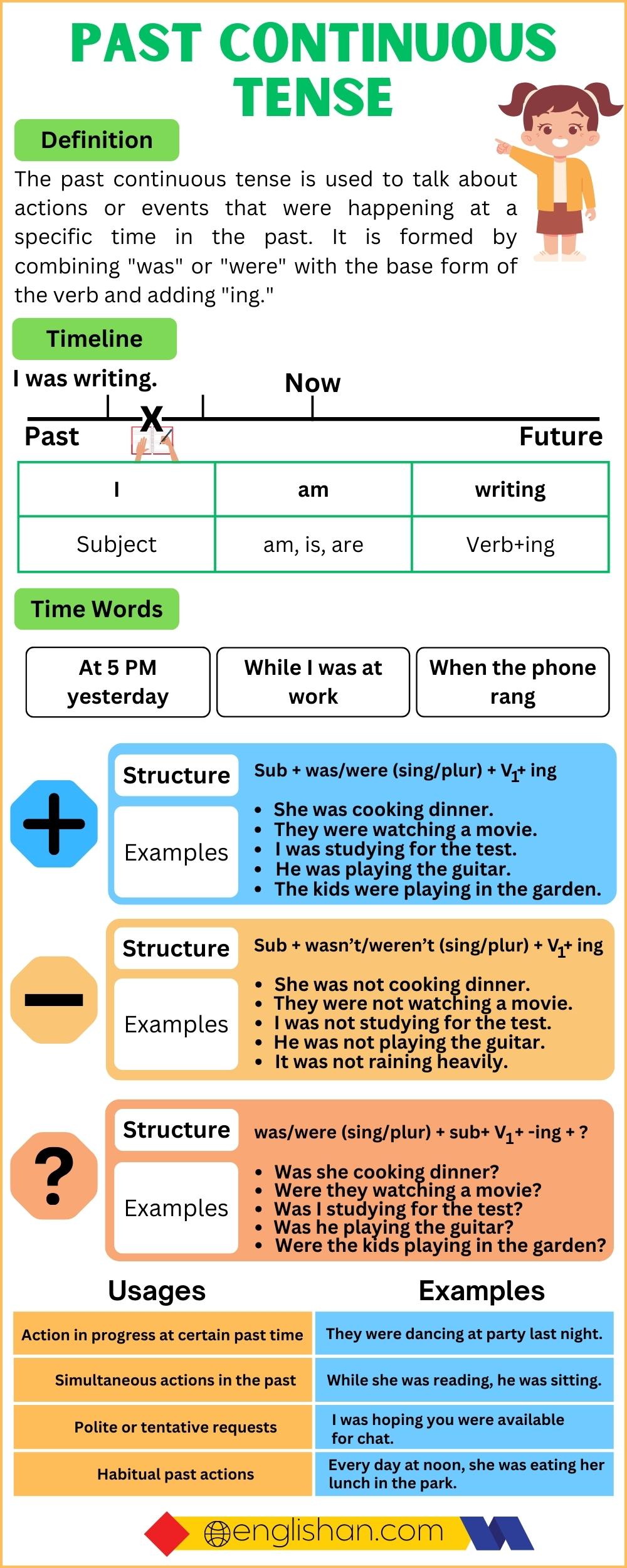
Subject-Verb Agreement
Subject-verb agreement in the Past Continuous Tense ensures that the correct form of “was” or “were” is used based on the subject. Understanding this agreement is crucial for forming grammatically correct sentences.
Here’s a quick guide:
| Subject | Helping Verb | Example |
| I/He/She/It | was | He was running. |
| We/You/They | were | They were studying. |
| Singular Noun | was | The teacher was teaching. |
| Plural Noun | were | The students were writing. |
Time Expressions
Certain time expressions are commonly used with the Past Continuous Tense to indicate the duration or specific moments of actions:
- While: While Ahmed was working, his friends were chatting.
- At that time: She was watching TV at that time.
- Yesterday: They were playing football yesterday afternoon.
- When: The phone rang when we were having dinner.
- All day: He was studying all day.
Adverb Placement
Adverbs are typically placed between “was/were” and the present participle or at the end of the sentence.
Examples:
- Ahmed was always helping his classmates.
- They were constantly arguing over small issues.
- She was working diligently on her project.
Uses of the Past Continuous Tense
The Past Continuous Tense serves several key purposes. Let’s explore them:
- Describing Ongoing Actions in the Past:
It is used to highlight actions that were in progress at a particular moment in the past.
Examples:
- She was reading a book at 8 p.m. last night.
- They were playing cricket during the match.
- Setting the Scene in the Past:
This use helps describe the background or atmosphere in a story.
Examples:
- The birds were singing, and the wind was blowing gently.
- Ahmed was writing while the children were playing outside.
- Describing Simultaneous Actions:
It is used to indicate two or more actions happening at the same time in the past.
Examples:
- While Sara was cooking, Ali was setting the table.
- They were dancing while the band was playing music.
- Highlighting Interruptions:
This tense is used in conjunction with the Simple Past to describe an action that was interrupted by another.
Examples:
- She was studying when her phone rang.
- They were walking home when it started raining.
Short Answers
In Past Continuous Tense, short answers are formed using was/were or wasn’t/weren’t.
Examples:
- Question: Was Ahmed working on the project?
- Yes, he was.
- No, he wasn’t.
- Question: Were they playing outside?
- Yes, they were.
- No, they weren’t.
Question Tags
Adding a question tag ensures confirmation in Past Continuous sentences. Use “was” or “were” in the tag.
Examples:
- She was working late, wasn’t she?
- They were arguing, weren’t they?
- Ahmed was studying, wasn’t he?
Examples of the Past Continuous Tense in Use
Affirmative:
- Ahmed was cleaning his room.
- They were eating dinner.
- She was studying for her exams.
Negative:
- She was not going to the market.
- They were not listening to the teacher.
- He was not helping his friends.
Interrogative:
- Was she working on the assignment?
- Were they practicing for the event?
- Was he traveling to Lahore?
Common Mistakes with the Past Continuous Tense
Here are some frequent errors and their corrections:
- ❌ She was go to the park.
- ✅ She was going to the park.
- ❌ They were sang during the event.
- ✅ They were singing during the event.
- ❌ Was he write a letter?
- ✅ Was he writing a letter?
FAQs
The past continuous tense is formed using the past tense of the auxiliary verb “to be” (was/were) and the base form of the main verb with “-ing” (e.g., was/were + verb + ing).
We use the past continuous tense to describe actions or events that were in progress at a specific time in the past or to emphasize the duration of an action.
Common time expressions include “while,” “when,” “at this time yesterday,” “at 6 PM last night,” and others that specify a particular time in the past.
Yes, the past continuous tense can be used to describe actions that were in progress when they were interrupted by another event in the past.
Look for was/were followed by a present participle (e.g., running, playing). Example: They were walking in the park.
Free Grammar and Vocabulary Worksheets Resources
You May Also Like