Contents
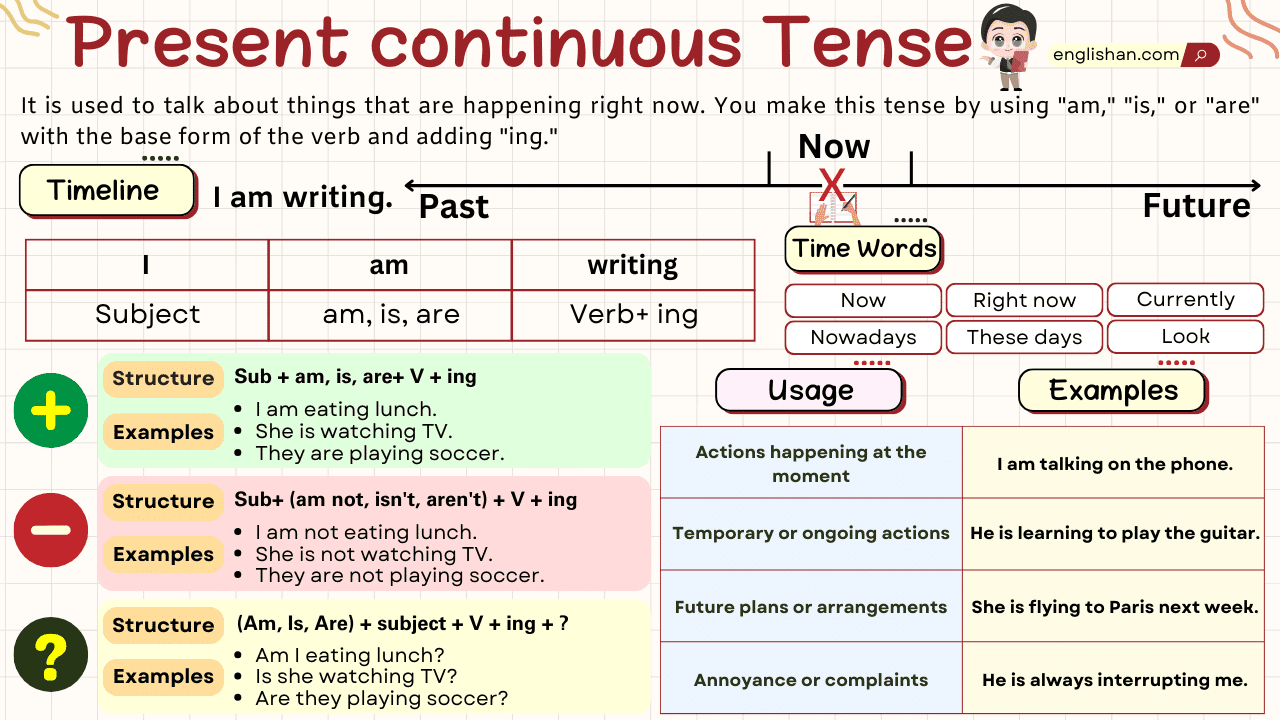
The Present Continuous Tense describes actions happening at the current moment or ongoing events in the present. It’s formed with a form of “to be” (am, is, are) plus the base verb with -ing (e.g., “I am running”).
Examples:
- She is reading a book.
- She is not reading a book.
- Is she reading a book?
Usages of the Present Continuous Tense
The Present Continuous Tense is used in several situations:
Actions Happening Now
- It is used to describe actions or events that are occurring at the current moment.
Examples:
- She is dancing at the party.
- They are playing a board game.
- I am writing a letter to my friend.
- The chef is preparing a delicious meal.
- The birds are singing in the garden.
- She is not sleeping at the moment.
- They are not watching TV right now.
- I am not eating chocolate.
- The cat is not chasing the mouse.
- The workers are not resting during their shift.
- Is she reading a book currently?
- Are they studying for their exams?
- Am I bothering you right now?
- Is the baby crying in the other room?
- Are the students presenting their projects today?
Temporary Situations
- It can be used to describe temporary or ongoing situations that may not be permanent.
Examples:
- She is living with her aunt for a few weeks.
- They are staying at a beach resort for their vacation.
- I am volunteering at the local shelter until I find a job.
- The company is renting a temporary office space while their main office is under renovation.
- We are using a borrowed car until ours gets fixed.
- She is not currently working at the office.
- They are not renting the apartment for the entire year.
- I am not attending the seminar next month.
- The project is not being implemented at this moment.
- He is not staying at the hotel for the entire week.
- Is she currently staying at her cousin’s place?
- Are they using a temporary office space during the renovations?
- Am I bothering you right now?
- Is the team working on the project until the deadline?
- Are you using a borrowed laptop until you get yours fixed?
Future Plans and Arrangements
- It can be used to talk about future plans and arrangements that have been already made.
Examples:
- They are flying to Paris next week.
- I am going to the beach next Saturday.
- They are watching a movie tonight.
- She is meeting her friend after school.
- We are visiting Grandma on Sunday.
- He is playing soccer with his friends tomorrow.
- I am not traveling abroad next month.
- They are not having a party this weekend.
- She is not attending the concert on Friday.
- We are not going shopping after work.
- He is not taking a vacation this year.
- Are you going to the beach next Saturday?
- Are they watching a movie tonight?
- Is she meeting her friend after school?
- Are we visiting Grandma on Sunday?
- Is he playing soccer with his friends tomorrow?
Annoyance or Irritation
- It can be used to express irritation or annoyance at repeated or ongoing actions.
Examples:
- He is always leaving the door open when he goes out.
- She is constantly talking on her phone during meetings.
- They are frequently forgetting to clean up after themselves.
- The TV is constantly blaring in the living room.
- My brother is incessantly playing loud music.
- He is not usually taking his turn in doing the dishes.
- She is not always arriving on time for our meetings.
- They are not frequently helping with household chores.
- The children are not normally listening to their parents.
- My neighbor is not consistently keeping their dog on a leash.
- Is he always leaving the lights on in his room?
- Is she frequently interrupting your work?
- Are they constantly making noise in the apartment?
- Is the TV always on in the living room?
- Is your brother regularly playing loud music?
Time Expressions
Time expressions help provide context about when an action is taking place. They can be used to indicate a specific time or a more general time frame.
Common Time Expressions
These are phrases or words that generally indicate when an action is happening. They are not tied to a specific point in time.
Examples of common time expressions:
- Now
- At the moment
- Currently
- Right now
- Today
- This week/month/year
- She is cooking dinner right now.
- They are playing in the park now.
- I am studying now.
- He is watching TV at the moment.
- She is talking on the phone at the moment.
- They are laughing at the moment.
- I am currently working on a project.
- She is currently reading a book.
- They are currently shopping for groceries.
- He is playing video games right now.
- She is cleaning her room right now.
- We are having dinner right now.
- They are going to the zoo today.
- She is meeting her friend for coffee today.
- We are visiting the museum today.
Specific Time Expressions
These expressions refer to a particular point in time or a specific time frame.
Examples:
- At 3 o’clock
- At noon
- In the evening
- On Monday
- Tomorrow
- Next month
- He is having lunch at noon.
- She is taking a break at noon.
- They are meeting at the park at noon.
- We are going for a walk in the evening.
- She is watching a movie in the evening.
- They are having a family dinner in the evening.
- He is attending a seminar on Monday.
- She is starting her new job on Monday.
- They are going for a hike on Monday.
- They are going to the beach tomorrow.
- She is visiting her grandparents tomorrow.
- I am meeting a client tomorrow.
Present Continuous Tense Chart
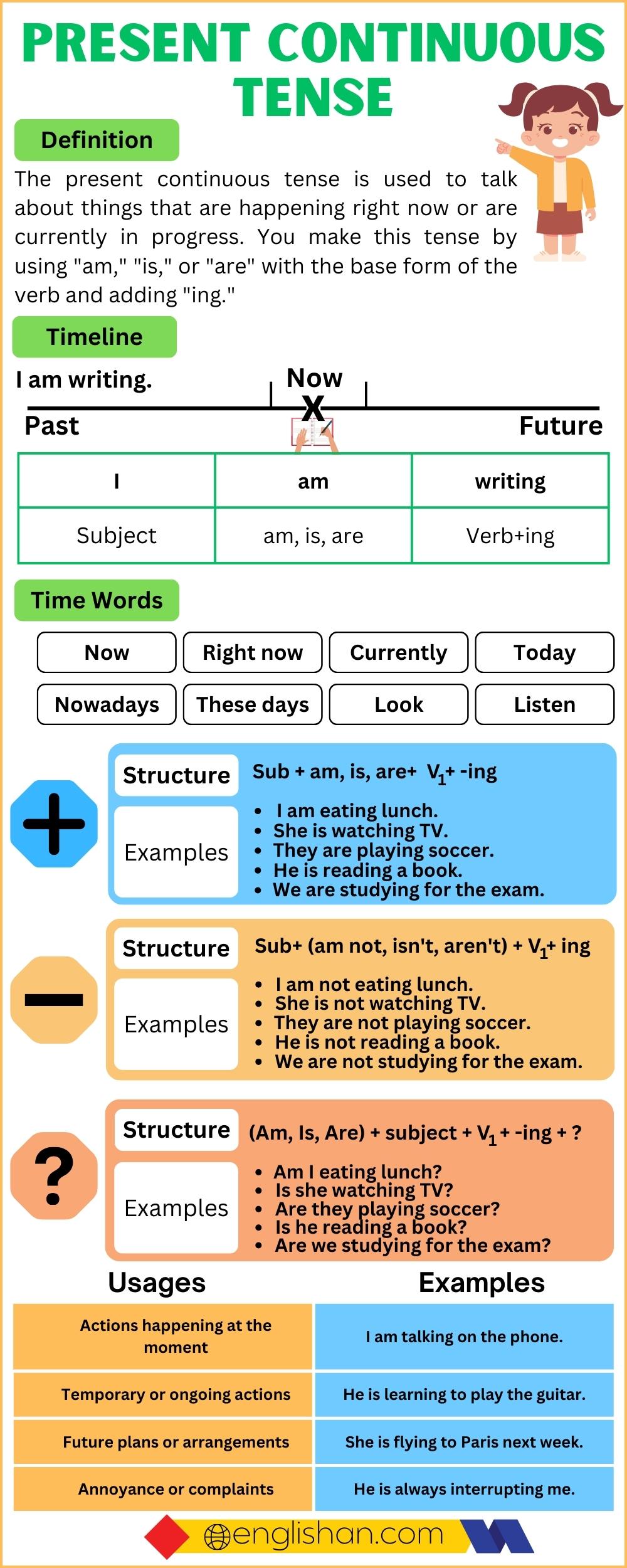
Formation of the Present Continuous Tense
Affirmative Sentences
Affirmative sentences are statements that tell us about something that is happening or true. They are positive statements without any negation or questioning.
Subject + is/am/are + verb(1st form) ing + object.
- She is reading a book.
- They are playing outside.
- He is cooking dinner.
- We are watching a movie.
- The cat is sleeping on the couch.
- I am listening to music.
- The children are laughing.
- She is writing a letter.
- They are dancing in the living room.
- He is studying for his exam.
- The birds are chirping in the trees.
- I am taking a walk in the park.
- He is running a marathon.
- She is painting a beautiful picture.
- They are building a sandcastle on the beach.
- We are having a picnic in the park.
- The students are participating in a quiz.
- She is playing the piano.
- They are baking a cake for the party.
- He is swimming in the pool.
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
| Subject | is/am/are | Verb(1st form) + ing | Object (if applicable). |
|---|---|---|---|
| She | is | reading | a book. |
| They | are | playing | outside. |
| He | is | cooking | dinner. |
| We | are | watching | a movie. |
| The cat | is | sleeping | on the couch. |
| I | am | listening | to music. |
| The children | are | laughing | . |
| She | is | writing | a letter. |
| They | are | dancing | in the living room. |
| He | is | studying | for his exam. |
| The birds | are | chirping | in the trees. |
| I | am | taking | a walk in the park. |
| He | is | running | a marathon. |
| She | is | painting | a beautiful picture. |
| They | are | building | a sandcastle on the beach. |
| We | are | having | a picnic in the park. |
| The students | are | participating | in a quiz. |
| She | is | playing | the piano. |
| They | are | baking | a cake for the party. |
| He | is | swimming | in the pool. |
Negative Sentences
Negative sentences are statements that say something is not true or not happening. They often include the word “not” to indicate the negation.
Subject + is/am/are + not + verb(1st form) ing + object.
- She is not watching TV.
- They are not playing video games.
- He is not eating chocolate.
- We are not going to the party.
- The cat is not chasing the mouse.
- I am not sleeping right now.
- The children are not fighting.
- She is not using her phone.
- They are not swimming in the pool.
- He is not wearing a hat.
- The birds are not singing.
- I am not playing soccer.
- She is not baking a cake.
- They are not studying for the test.
- He is not running in the race.
- We are not traveling to Europe.
- The dog is not barking.
- She is not taking a nap.
- They are not painting a picture.
- He is not playing the guitar.
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
| Subject | is/am/are | not | Verb(1st form) | Object (if applicable). |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| She | is | not | watching | TV. |
| They | are | not | playing | video games. |
| He | is | not | eating | chocolate. |
| We | are | not | going | to the party. |
| The cat | is | not | chasing | the mouse. |
| I | am | not | sleeping | right now. |
| The children | are | not | fighting | . |
| She | is | not | using | her phone. |
| They | are | not | swimming | in the pool. |
| He | is | not | wearing | a hat. |
| The birds | are | not | singing | . |
| I | am | not | playing | soccer. |
| She | is | not | baking | a cake. |
| They | are | not | studying | for the test. |
| He | is | not | running | in the race. |
| We | are | not | traveling | to Europe. |
| The dog | is | not | barking | . |
| She | is | not | taking | a nap. |
| They | are | not | painting | a picture. |
| He | is | not | playing | the guitar. |
Interrogative Sentences
Interrogative sentences are questions that seek information. They start with question words like who, what, when, where, and why, or by changing the order of the subject and verb.
Is/am/are + Subject + verb(1st form) ing + object?
- Is he watching TV right now?
- Are they playing soccer in the park?
- Is she cooking dinner for her family?
- Are we going to the movies tonight?
- Is the cat sleeping on the bed?
- Are you listening to music at the moment?
- Is the baby laughing in the other room?
- Are they studying for their exams?
- Is he writing a letter to his friend?
- Are they dancing at the party?
- Is the dog chasing its tail again?
- Are you having lunch with your colleagues?
- Is she swimming in the pool right now?
- Are they playing a board game together?
- Is he taking a walk in the park?
- Are we meeting for coffee tomorrow?
- Is the teacher explaining a new concept?
- Are they singing a song in the choir?
- Is she doing yoga in the living room?
- Are you attending the conference next week?
The sentences given above are broken down according to their grammatical structure.
| Is/am/are | Subject | Verb(1st form) + ing | Object | Complement?(if applicable) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Is | he | watching | TV | right now? |
| Are | they | playing | soccer | in the park? |
| Is | she | cooking | dinner | for her family? |
| Are | we | going | to the movies | tonight? |
| Is | the cat | sleeping | on the bed | ? |
| Are | you | listening | to music | at the moment? |
| Is | the baby | laughing | in the other room? | |
| Are | they | studying | for their exams | ? |
| Is | he | writing | a letter | to his friend? |
| Are | they | dancing | at the party | ? |
| Is | the dog | chasing | its tail | again? |
| Are | you | having | lunch with your colleagues | ? |
| Is | she | swimming | in the pool | right now? |
| Are | they | playing | a board game | together? |
| Is | he | taking | a walk in the park | ? |
| Are | we | meeting | for coffee | tomorrow? |
| Is | the teacher | explaining | a new concept | ? |
| Are | they | singing | a song in the choir | ? |
| Is | she | doing | yoga in the living room | ? |
| Are | you | attending | the conference | next week? |
Present Continuous Tense Example Sentences
Positive Sentences
- I am learning a new language.
- The dog is chasing its tail.
- We are planting flowers in the garden.
- She is giving a presentation at work.
- They are cleaning the house.
- He is fixing the car engine.
- The chef is preparing a special dish.
- I am attending a yoga class.
- She is knitting a scarf.
- They are hiking in the mountains.
- The birds are chirping.
- She is sewing the clothes.
- Ali is riding a bicycle.
- This cloth is selling cheap.
- The father is taking rest.
- They are vacating this house.
- Robbers are looting the carvan.
- Saba is knitting a sweater.
- It is raining cats and dogs.
- You are making excuses.
Negative Sentences
- I am not attending the concert.
- The students are not writing essays.
- We are not watching a play.
- She is not riding a bike.
- They are not gardening.
- He is not teaching a class.
- The chef is not cooking dinner.
- I am not practicing yoga.
- She is not reading a novel.
- They are not fishing in the lake.
- The sun is not shining.
- The well is not working.
- I am not feeling giddy.
- We are not printing a book.
- She is not waiting for you.
- The children are not making mischiefs.
- I am not shirking work.
- The jackals are not howling.
- She is not reading a book.
- We are not going to the party.
Interrogative Sentences
- Is he helping his parents with chores?
- Are they visiting their grandparents this weekend?
- Is she practicing the guitar for her recital?
- Are we having a family dinner tonight?
- Is the cat exploring the garden?
- Are they working on a group project?
- Is he playing a video game with his friends?
- Are you participating in the marathon?
- Is she giving a presentation to the team?
- Are they watching a documentary about wildlife?
- Is she telling a story?
- Is it drizzling?
- Is it blowing hard?
- When are the guests arriving here?
- Are they taking exercise?
- Is Kamran batting away?
- Is the baby sleeping?
- Who is running away?
- Why are you selling house?
- Is he reading a book?
Quiz:
- Is she ____________ a book? A) reading B) writing
- They are ____________ outside. A) playing B) sleeping
- He is ____________ dinner. A) cooking B) painting
- We are ____________ a movie. A) watching B) listening
- The cat is ____________ on the couch. A) sleeping B) swimming
- I am ____________ to music. A) listening B) dancing
- The children are ____________. A) laughing B) studying
- She is ____________ a letter. A) writing B) singing
- They are ____________ in the living room. A) dancing B) playing
- He is ____________ for his exam. A) studying B) running
- The birds are ____________ in the trees. A) chirping B) flying
- I am ____________ a walk in the park. A) taking B) driving
- He is ____________ a marathon. A) running B) cycling
- She is ____________ a beautiful picture. A) painting B) cooking
- They are ____________ a sandcastle on the beach. A) building B) sleeping
- We are ____________ a picnic in the park. A) having B) studying
- The students are ____________ in a quiz. A) participating B) sleeping
- She is ____________ the piano. A) playing B) swimming
- They are ____________ a cake for the party. A) baking B) reading
- He is ____________ in the pool. A) swimming B) dancing
- A) reading
- A) playing
- A) cooking
- A) watching
- B) sleeping
- A) Listening
- A) laughing
- A) writing
- A) dancing
- A) studying
- A) chirping
- A) taking
- A) running
- A) painting
- A) building
- A) having
- A) participating
- A) playing
- A) baking
- A) swimming
FAQs:
It is formed by using a form of the verb “to be” (am, is, are) followed by the base form of the main verb and “-ing” (e.g., “She is reading a book.”).
Yes, it can be used for future arrangements or plans, especially when they are fixed and confirmed (e.g., “We are meeting tomorrow.”).
Common time expressions include “now,” “at the moment,” “currently,” “right now,” “today,” and “this week/month/year.”
No, it is typically used for temporary or ongoing actions, not for habits or permanent states
Check Your Understanding by solving the following Exercises
You May Also Like