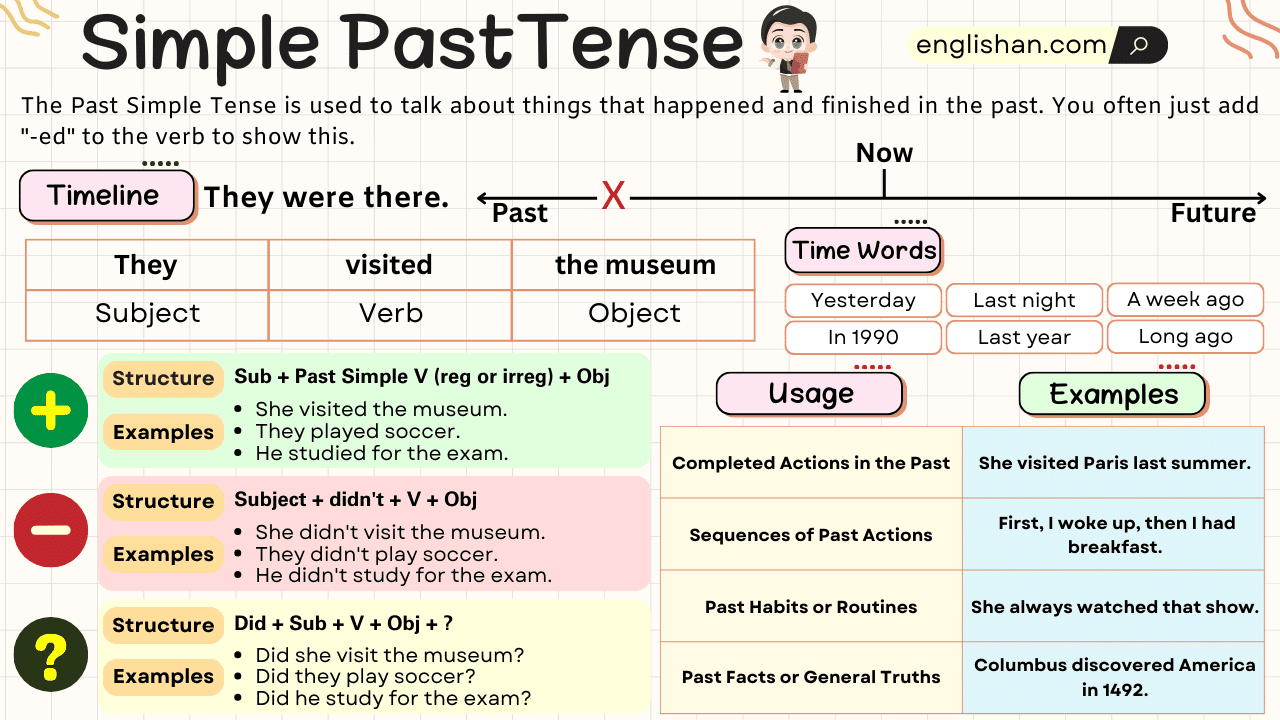
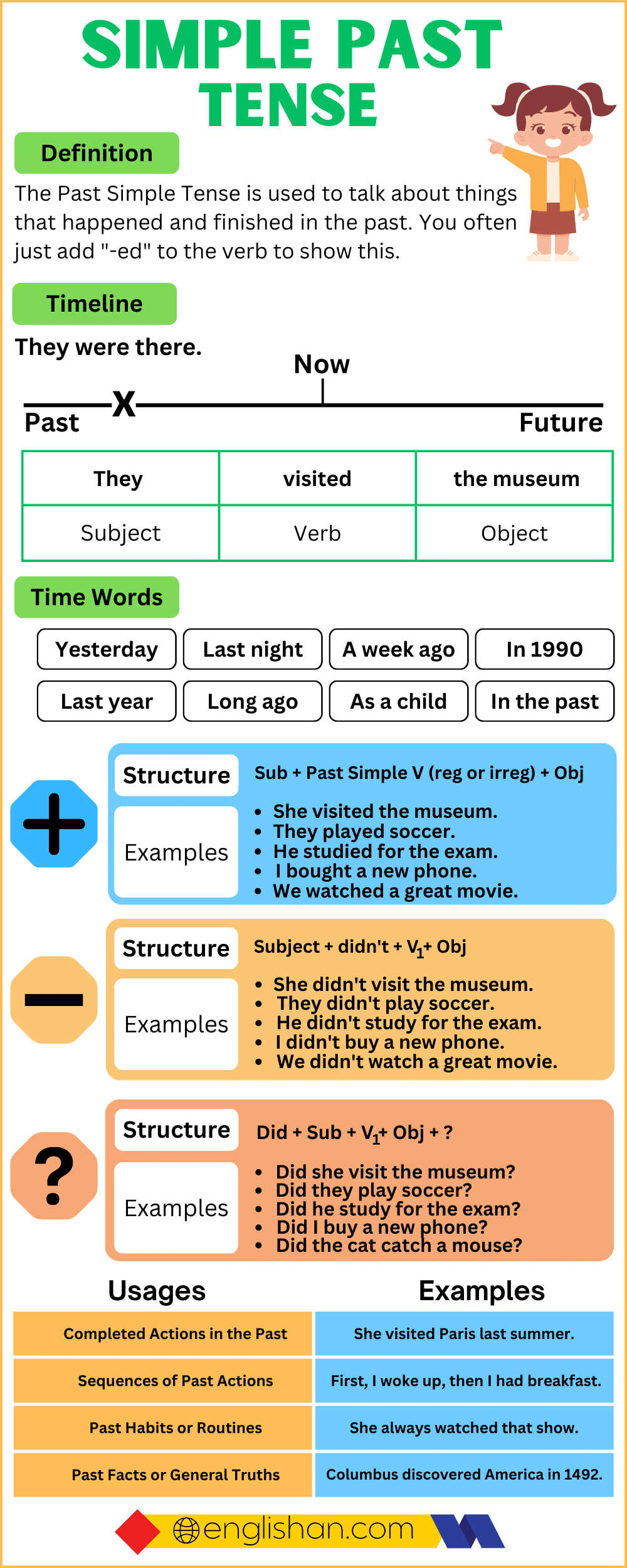
The Simple Past Tense (also called the Past Simple or Past Indefinite Tense) describes actions, events, or states that happened and were completed at a specific time in the past. It is used for finished activities, past habits, and historical facts.
Example:
- Ahmed visited Lahore last year.
- They played cricket yesterday.
Formula of the Simple Past Tense
Regular Verbs: Base verb + -ed
Irregular Verbs: Second form of the verb (unique past form)
Structures:
| Sentence Type | Formula | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | Subject + past verb + object | She cooked dinner last night. |
| Negative | Subject + did not + base verb + object | We did not go to the park. |
| Interrogative | Did + subject + base verb + object? | Did Ahmed write a letter? |
| Double Interrogative | Wh-word + did + subject + base verb + object? | Why did Sara leave early? |
Subject–Verb Agreement in Simple Past
The past verb form remains the same for all subjects. For negatives and questions, did + base verb is used.
| Subject/Noun | Affirmative Example | Negative Example |
|---|---|---|
| I / He / She / It | He played football. | He did not play football. |
| We / You / They | They watched TV. | They did not watch TV. |
| Singular Noun | The teacher taught math. | The teacher did not teach math. |
| Plural Noun | The students answered. | The students did not answer. |
Spelling Rules for Regular Verbs
| Rule | Base Form → Past Tense Examples |
|---|---|
| Add -ed | walk → walked, love → loved |
| Ending in “e” | bake → baked, arrive → arrived |
| CVC pattern (double consonant) | stop → stopped, plan → planned |
| Consonant + y → change y to i + ed | carry → carried, try → tried |
| Vowel + y → just add -ed | play → played, enjoy → enjoyed |
Irregular Verbs: go → went, have → had, eat → ate, see → saw
Time Expressions in the Simple Past Tense
Time words make it clear when the action happened.
| Time Expression | Example |
|---|---|
| yesterday | They went to the market yesterday. |
| last night/week/year | Ahmed studied late last night. |
| ago | She moved to Karachi three years ago. |
| in [year] | They traveled to Turkey in 2020. |
| at that time | He worked as a teacher at that time. |
Adverb Placement
Place adverbs after the main verb or at the end of the sentence.
Examples:
- She quickly finished her work.
- They happily played cricket in the street.
- Ahmed read the book yesterday.
Uses of the Simple Past Tense
- Completed Actions – She cooked dinner last night.
- Storytelling/Sequence of Events – The rain started, and the children ran inside.
- Past Habits – He woke up early every day when he was in school.
- Past Facts – The Wright brothers invented the airplane.
Comparison with Related Tenses
| Feature | Simple Past | Present Perfect |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Completed action in the past | Action completed with relevance to now |
| Helping Verb | None | Has / Have |
| Example | She read a book. | She has read the book. |
| Time Expressions | yesterday, last week, ago | since, for, already, just |
Short Answers in the Simple Past
- Did Ahmed complete his homework?
Yes, he did. / No, he did not. - Did they attend the meeting?
Yes, they did. / No, they didn’t.
Question Tags
- She finished her homework, didn’t she?
- They went to the park, didn’t they?
Examples in All Forms
Affirmative:
- Ahmed cleaned his room.
- They ate dinner together.
Negative:
- She did not go to the market.
- They did not attend the seminar.
Interrogative:
- Did she finish the assignment?
- Did they travel to Lahore?
Common Mistakes
- ❌ She goed to the park.
✅ She went to the park. - ❌ They drinked tea in the morning.
✅ They drank tea in the morning. - ❌ Did he wrote a letter?
✅ Did he write a letter.
Quick Recap
- Formula: Subject + past verb / Subject + did not + base verb / Did + subject + base verb
- Main Uses: Completed actions, storytelling, past habits, past facts
- Time Words: yesterday, ago, last week, in [year]
- Common Mistakes: Wrong past form, wrong question form
FAQs about Simple Past
The Simple Past Tense, also known as the Simple Past Tense, is a grammatical tense used to describe actions or events that occurred in the past and are now completed.
For regular verbs, the past tense is formed by adding “-ed” to the base form of the verb (e.g., walk -> walked, play -> played).
a) She visited the museum yesterday.
b) They played soccer in the park.
c) He finished his homework before dinner.
Irregular verbs have unique past tense forms that do not follow a regular pattern. For example, the past tense of “go” is “went” and the past tense of “eat” is “ate”.
No, the Simple Past Tense is used to describe completed actions in the past, not actions that were ongoing or continuous.
Yesterday, last week, two days ago, in 1995, when I was a child, etc.
You May Also Like