Contents
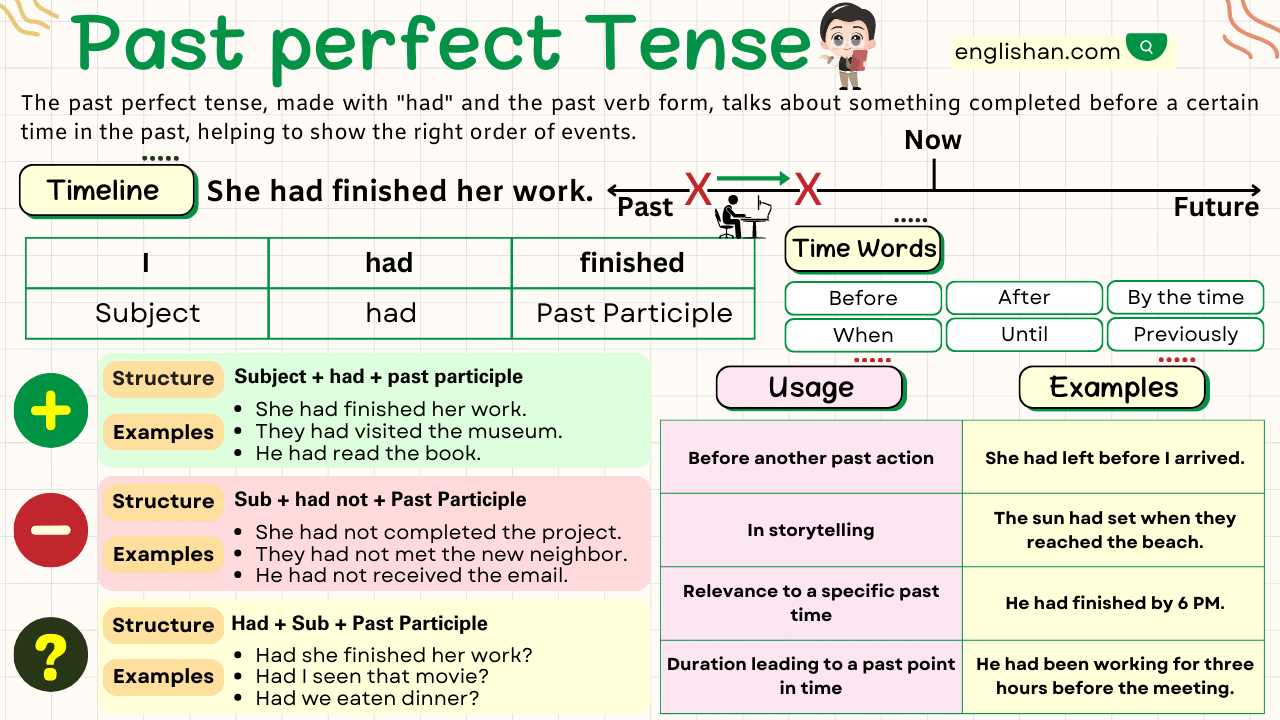
The Past Perfect Tense is used to talk about actions that were completed before another action in the past. It helps establish the sequence of events in past time. For example:
- Ahmed had finished his homework before his mother arrived.
Here, “had finished” shows that Ahmed’s action was completed before another past action.
This tense is essential for expressing clarity in storytelling, explaining past experiences, and sequencing events.
Structures of the Past Perfect Tense
The Past Perfect Tense is constructed using the auxiliary verb had followed by the past participle of the main verb. Let’s look at the different sentence structures:
Affirmative Sentences
Structure: Subject + had + past participle + object
Examples:
- Zainab had visited the museum before it closed.
- The dogs had eaten their food by the time Ali returned.
Zainab’s visit to the museum occurred before the museum’s closing. Similarly, the dogs completed their action before Ali’s return.
Negative Sentences
Structure: Subject + had not + past participle + object
Examples:
- Ahmed had not seen the movie before it was discussed.
- They had not completed their homework by the deadline.
Here, the actions (seeing the movie, completing homework) did not occur before the referenced times.
Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Had + subject + past participle + object?
Examples:
- Had Fatima called her sister before leaving?
- Had the teacher explained the concept before giving the test?
These questions ask if one action occurred before another.
Double Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Wh-question + had + subject + past participle + object?
Examples:
- Why had Ahmed left the room before the discussion started?
- Where had they gone before sunset?
These questions specify the reason or location related to the past actions.
Past Perfect Tense Chart
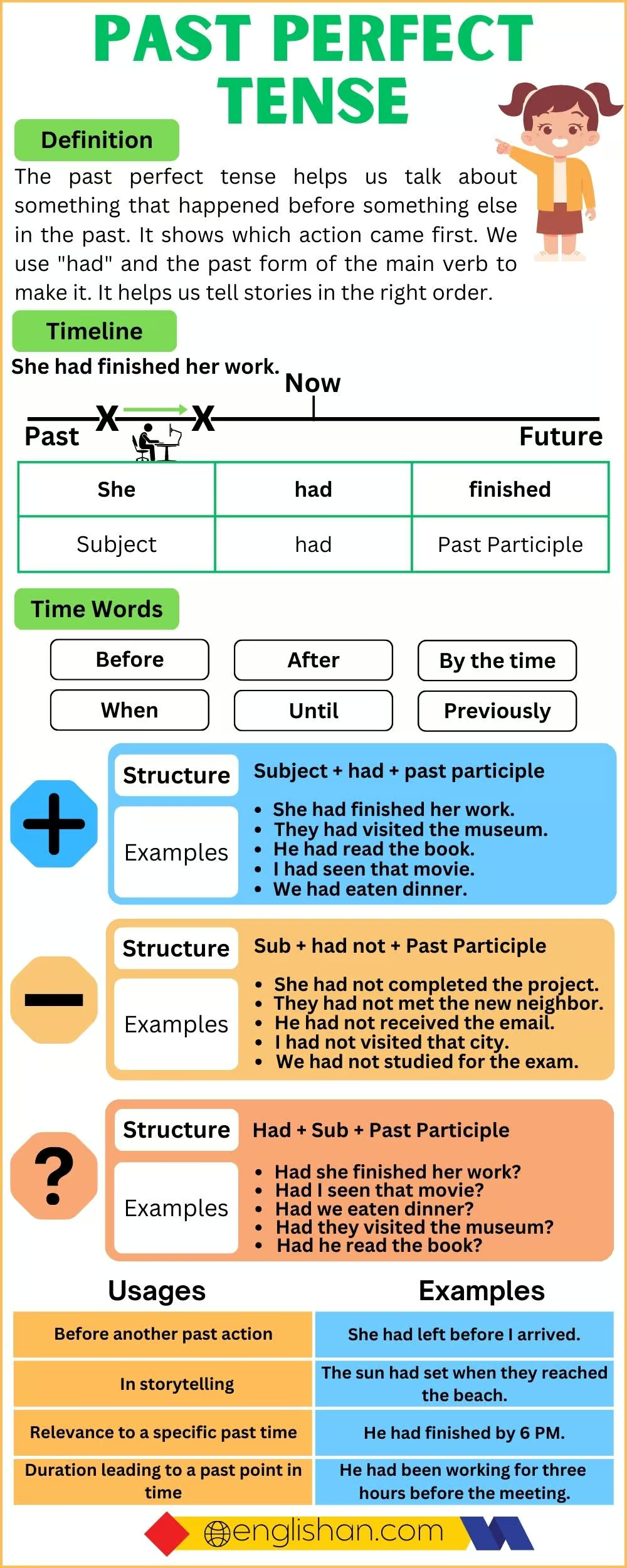
Subject-Verb Agreement
In the Past Perfect Tense, the helping verb had remains the same for all subjects. Below is a table to clarify:
| Subject | Helping Verb | Example |
| I | had | I had studied. |
| He/She/It | had | She had left. |
| We/You/They | had | They had traveled. |
| Singular Noun | had | The teacher had taught. |
| Plural Noun | had | The children had played. |
Time Expressions
Certain time expressions are often used with the Past Perfect Tense to show the order of events. Here are some examples:
- By the time: By the time Ahmed arrived, the meeting had ended.
- Before: Before Sara joined the party, she had prepared a cake.
- Already: He had already left before I reached his house.
- Just: The train had just departed when we reached the station.
- When: When I opened the door, they had left.
Adverb Placement
Adverbs are typically placed between “had” and the past participle in Past Perfect Tense.
Examples:
- Ahmed had already completed his task.
- They had never visited that park before.
- She had just arrived when the event started.
Uses of the Past Perfect Tense
The Past Perfect Tense has various uses that help in understanding past events better. Let’s learn these:
- Sequence of Actions:
The Past Perfect Tense highlights an action that occurred earlier than another action in the past. This helps establish a clear sequence of events.
- The guests had left before we arrived.
- Sara had completed her homework before her father returned.
- Reported Speech:
It is used in indirect speech to describe actions that were already completed at the time of reporting.
- He said he had finished his work before the deadline.
- She told me she had visited Lahore last year.
- Unreal Past Conditions:
This use describes hypothetical situations or conditions that did not happen in the past. It is often paired with conditional clauses.
- If she had studied, she would have passed the exam.
- If Ahmed had left earlier, he would have caught the train.
- Experience or Achievement:
It shows completion of actions or experiences before another point in the past.
- They had visited Mecca twice before moving to Karachi.
- The students had achieved remarkable results before the school’s anniversary.
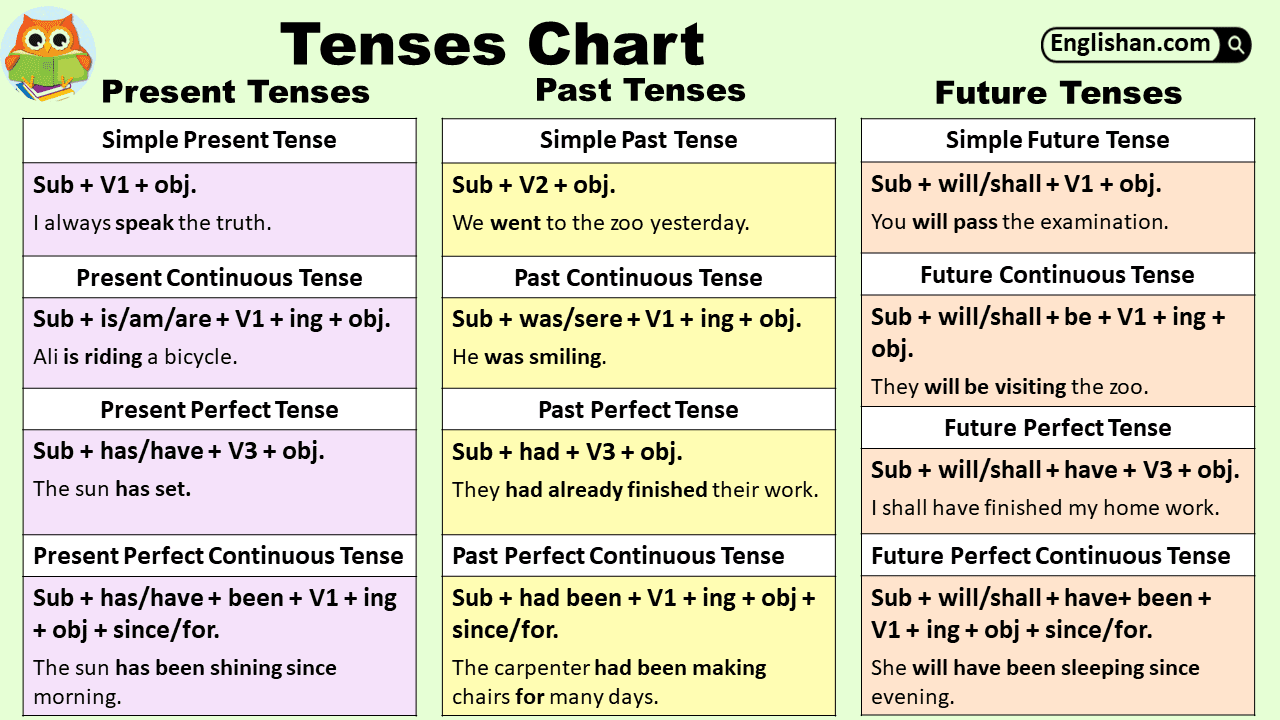
Comparison: Past Perfect vs. Simple Past
| Feature | Past Perfect | Simple Past |
| Definition | Action completed before another action | Action completed at a specific time |
| Helping Verb | Had | None |
| Example | Ahmed had left before I arrived. | Ahmed left at 7 p.m. |
| Sequence Emphasis | Yes | No |
| Time Expressions Used | Before, by the time, already, just | Yesterday, last week, at 5 p.m. |
Short Answers
In Past Perfect Tense, short answers are formed by using had or had not.
Examples:
- Question: Had Ahmed completed his homework?
- Yes, he had.
- No, he had not.
- Question: Had they left for the trip?
- Yes, they had.
- No, they had not.
Question Tags
Adding a question tag ensures confirmation in Past Perfect sentences. Use “had” in the tag.
Examples:
- She had finished her assignment, hadn’t she?
- They had left early, hadn’t they?
- Ahmed had forgotten his keys, hadn’t he?
Examples of the Past Perfect Tense in Use
Affirmative:
- Ahmed had cleaned his room before his guests arrived.
- The children had eaten lunch by the time their father came home.
- I had completed my project before the deadline.
Negative:
- Fatima had not gone to the market before her mother called her.
- The students had not finished their test when the bell rang.
- He had not returned the book before the library closed.
Interrogative:
- Had Sara taken the exam before the results were announced?
- Had the train departed before we reached the station?
- Had they visited Lahore before moving to Islamabad?
Common Mistakes with the Past Perfect Tense
Here are some frequent errors and their corrections:
- ❌ She had went to the market before it started raining.
- ✅ She had gone to the market before it started raining.
- ❌ The players had win the match before the crowd arrived.
- ✅ The players had won the match before the crowd arrived.
- ❌ Had they ate dinner before the guests came?
- ✅ Had they eaten dinner before the guests came?
FAQs
The Past Perfect Tense is used to show that one action was completed before another in the past. Example: Ahmed had eaten dinner before the guests arrived. It emphasizes the sequence of past events, helping create clarity in storytelling or explanations.
The Past Perfect Tense is formed using the auxiliary verb “had” followed by the past participle form of the main verb (e.g., had + eaten).
Time expressions like “before,” “by the time,” “already,” “until,” and “hadn’t” are commonly used with the Past Perfect Tense.
The Simple Past Tense describes an action that happened at a specific point in the past, while the Past Perfect Tense describes an action that occurred before another past action.
“Hadn’t” is the contraction of “had not” and is used in negative sentences (e.g., “She hadn’t finished her work.”). “Didn’t” is the contraction of “did not” and is used in negative sentences in the Simple Past Tense (e.g., “She didn’t finish her work.”).
Yes, the Past Perfect Tense can be used in reported speech to convey information that was said or thought in the past (e.g., “He said he had already seen the movie.”).
Yes, adverbs like “already,” “just,” “never,” “yet,” and others can be used with the Past Perfect Tense to provide additional information about the timing of the action.
Look for had followed by a past participle (e.g., finished, seen, gone). Example: She had completed her work before leaving the office. Use time expressions like before and by the time for added clarity.
Free Grammar and Vocabulary Worksheets Resources
You May Also Like