A tenses chart can be extremely helpful when learning English because it shows the different ways we talk about time. English has several tenses, and each one is used to explain events that happen in the past, present, or future. With this chart, you’ll find simple formulas and sentence examples that make it easier to master these tenses, making your speaking and writing clearer and more precise.
Present Simple Tense Chart
| Type | Formula | Examples |
| Affirmative | Subject + Base verb (+ “s/es” for 3rd person) | – She reads novels. – They watch movies. – I walk to school. |
| Negative | Subject + do/does + not + Base verb | – He doesn’t like coffee. – We don’t travel often. – I don’t eat meat. |
| Interrogative | Do/Does + Subject + Base verb? | – Does she play the guitar? – Do they enjoy hiking? – Does he work on Sundays? |
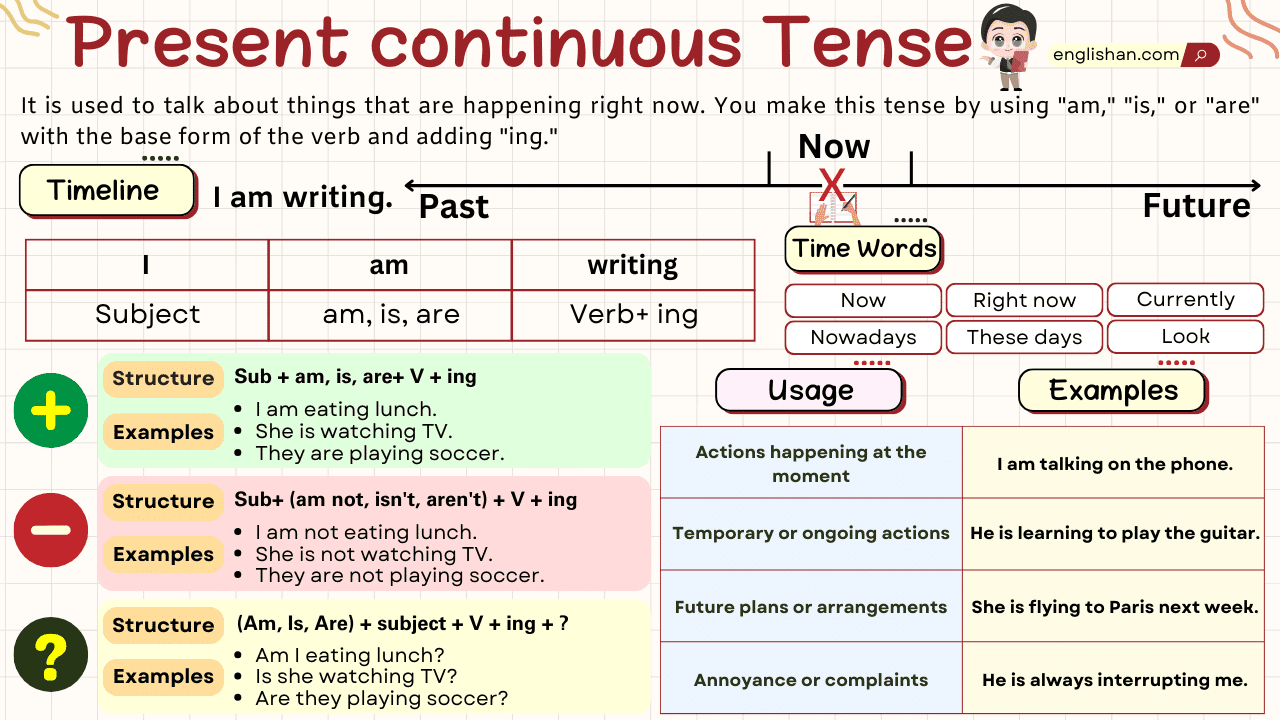
Present Continuous (Progressive) Tenses Chart
| Type | Formula | Examples |
| Affirmative | Subject + am/is/are + Base verb + ing | – I am studying for exams. – They are playing in the park. – She is reading a book. |
| Negative | Subject + am/is/are + not + Base verb + ing | – He isn’t driving right now. – We aren’t watching TV. – I’m not feeling well. |
| Interrogative | Am/Is/Are + Subject + Base verb + ing? | – Are they coming to the party? – Is she cooking dinner? – Am I speaking loudly? |
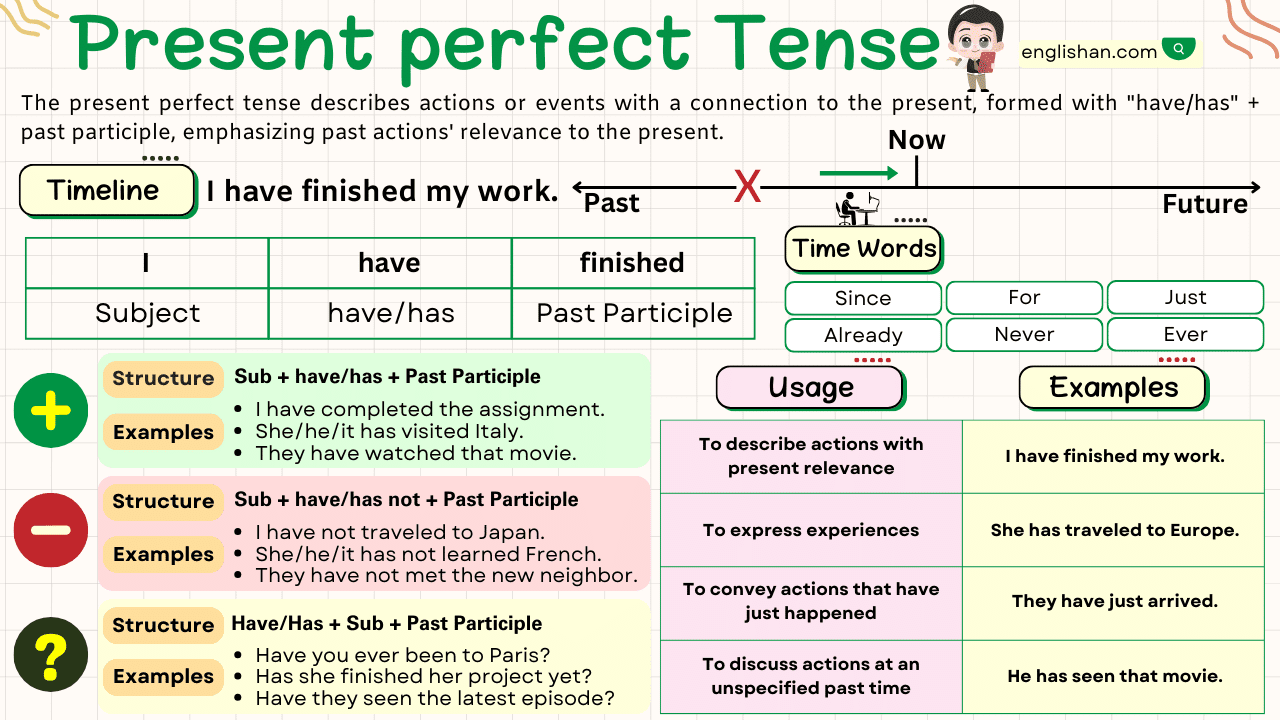
Present Perfect Tense
| Type | Formula | Examples |
| Affirmative | Subject + have/has + Past Participle (V3) | – I have finished my homework. – They have visited France. – She has baked a cake. |
| Negative | Subject + have/has + not + Past Participle | – He hasn’t met her before. – We haven’t seen that movie. – I haven’t been to the zoo recently. |
| Interrogative | Have/Has + Subject + Past Participle? | – Have they tried sushi? – Has she called you? – Have we lost the keys? |
Present Perfect Continuous Tense Chart
| Type | Formula | Examples |
| Affirmative | Subject + have/has + been + Base verb + ing | – I have been waiting here for over an hour. – They have been playing football since morning. – She has been working for three years. |
| Negative | Subject + have/has + not + been + Base verb + ing | – He hasn’t been feeling well lately. – We haven’t been going to the gym. – They haven’t been attending classes regularly. |
| Interrogative | Have/Has + Subject + been + Base verb + ing? | – Have you been reading this book for long? – Has she been sleeping since afternoon? – Have they been watching TV all day? |
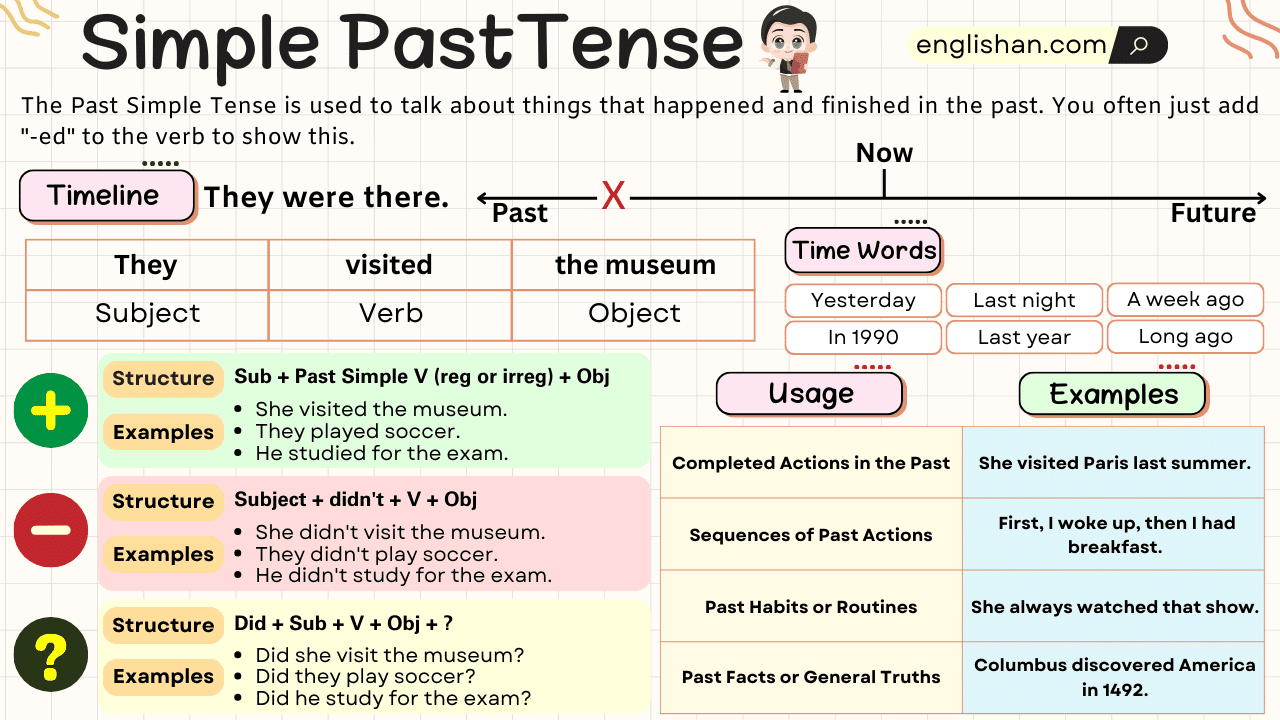
Past Simple Tenses Chart
| Type | Formula | Examples |
| Affirmative | Subject + Past Verb + Object | – She played football. – They watched a movie. – He read a book. |
| Negative | Subject + didn’t + Base Verb + Object | – She didn’t play football. – They didn’t watch a movie. – He didn’t read a book. |
| Interrogative | Did + Subject + Base Verb + Object? | – Did she play football? – Did they watch a movie? – Did he read a book? |
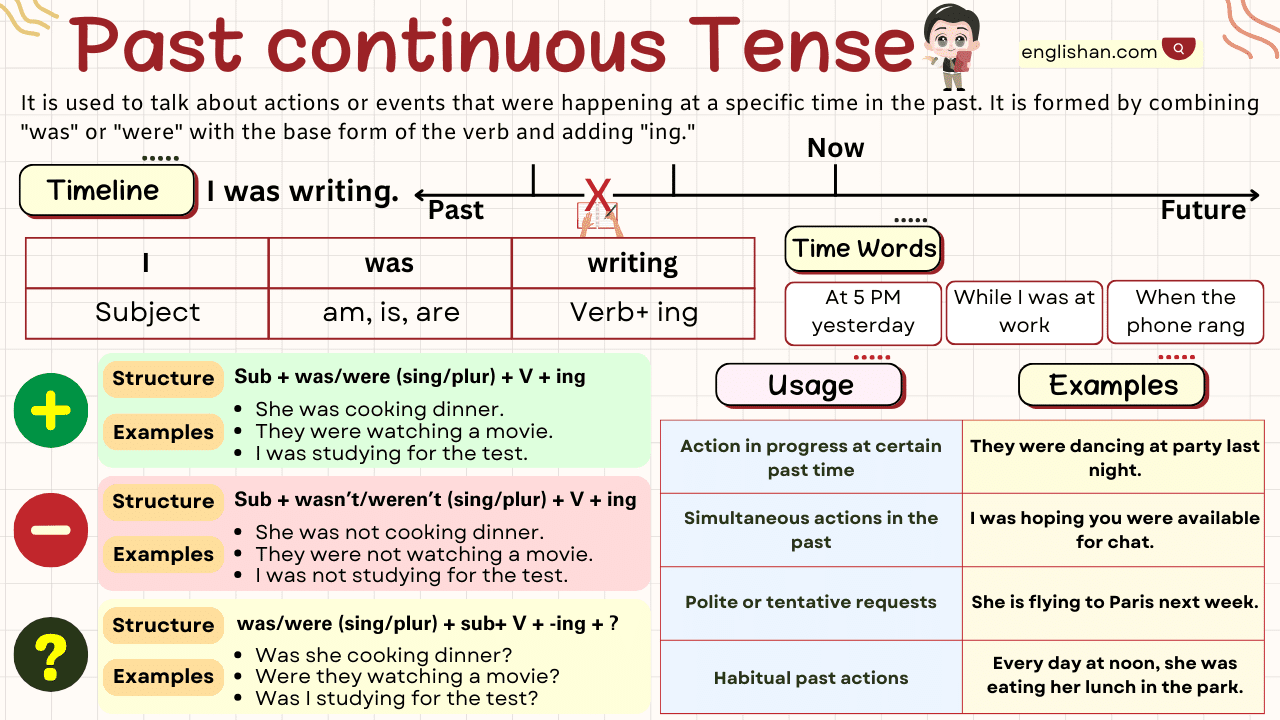
Past Continuous Tense
| Type | Formula | Examples |
| Affirmative | Subject + was/were + Verb-ing | – She was playing football. – They were watching a movie. – He was reading a book. |
| Negative | Subject + wasn’t/weren’t + Verb-ing | – She wasn’t playing football. – They weren’t watching a movie. – He wasn’t reading a book. |
| Interrogative | Was/Were + Subject + Verb-ing? | – Was she playing football? – Were they watching a movie? – Was he reading a book? |
Past Perfect Tense Chart
| Type | Formula | Examples |
| Affirmative | Subject + had + Past Participle | – She had played football. – They had watched a movie. – He had read a book. |
| Negative | Subject + hadn’t + Past Participle | – She hadn’t played football. – They hadn’t watched a movie. – He hadn’t read a book. |
| Interrogative | Had + Subject + Past Participle? | – Had she played football? – Had they watched a movie? – Had he read a book? |
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
| Type | Formula | Examples |
| Affirmative | Subject + had been + Verb-ing + time | – She had been playing football for an hour. – They had been watching a movie since evening. – He had been reading for two hours. |
| Negative | Subject + hadn’t been + Verb-ing + time | – She hadn’t been playing football for an hour. – They hadn’t been watching a movie since evening. – He hadn’t been reading for two hours. |
| Interrogative | Had + Subject + been + Verb-ing + time? | – Had she been playing football for an hour? – Had they been watching a movie? – Had he been reading for two hours? |
Simple Future Tenses Chart
| Type | Formula | Examples |
| Affirmative | Subject + will/shall + Base verb + Object | – She will play football tomorrow. – They will visit the museum next week. – He shall write a letter. |
| Negative | Subject + will/shall + not + Base verb + Object | – She will not play football tomorrow. – They won’t visit the museum next week. – He shall not write a letter. |
| Interrogative | Will/Shall + Subject + Base verb + Object? | – Will she play football tomorrow? – Will they visit the museum next week? – Shall he write a letter? |
Future Continuous Tense Chart
| Type | Formula | Examples |
| Affirmative | Subject + will/shall + be + Present Participle | – She will be playing football at this time tomorrow. – They will be visiting the museum when you arrive. – He shall be writing a letter when we call. |
| Negative | Subject + will/shall + not + be + Present Participle | – She will not be playing football at 4 PM. – They won’t be visiting the museum. – He shall not be writing a letter tonight. |
| Interrogative | Will/Shall + Subject + be + Present Participle? | – Will she be playing football at 3 PM? – Will they be visiting the museum on Friday? – Shall he be writing a letter in the evening? |
Future Perfect Tense
| Type | Formula | Examples |
| Affirmative | Subject + will/shall + have + Past Participle | – She will have played football by the time you arrive. – They will have visited all museums by the end of their trip. – He shall have written three letters by noon. |
| Negative | Subject + will/shall + not + have + Past Participle | – She will not have played football by 5 PM. – They won’t have visited the museum by then. – He shall not have written the letters. |
| Interrogative | Will/Shall + Subject + have + Past Participle? | – Will she have played football by evening? – Will they have visited the museum? – Shall he have written all letters by Friday? |
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
| Type | Formula | Examples |
| Affirmative | Subject + will/shall + have + been + Present Participle | – She will have been playing football for two hours by 5 PM. – They shall have been visiting museums all day. – He will have been writing the report for three hours. |
| Negative | Subject + will/shall + not + have + been + Present Participle | – She will not have been playing football for long. – They shall not have been visiting museums for a week. – He will not have been writing for long. |
| Interrogative | Will/Shall + Subject + have + been + Present Participle? | – Will she have been playing football for an hour? – Shall they have been visiting museums for a while? – Will he have been writing the report for long? |
Each tense has been separated into individual tables for clarity and ease of understanding.
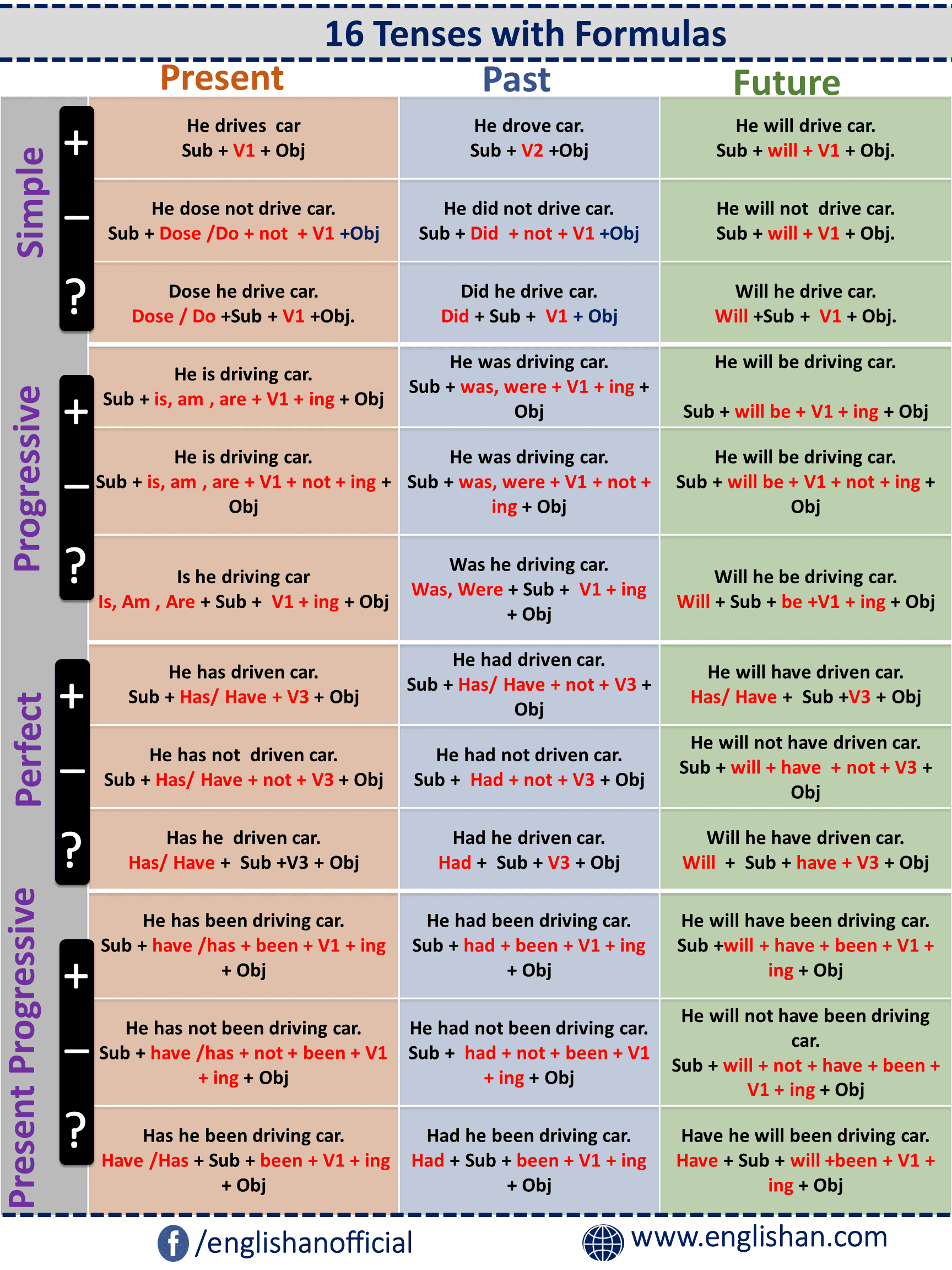
All Tenses Chart
FAQs:
The 12 forms of tense in English are:
1. Simple Present: She reads.
2. Present Continuous: She is reading.
3. Present Perfect: She has read.
4. Present Perfect Continuous: She has been reading.
5. Simple Past: She read.
6. Past Continuous: She was reading.
7. Past Perfect: She had read.
8. Past Perfect Continuous: She had been reading.
9. Simple Future: She will read.
10. Future Continuous: She will be reading.
11. Future Perfect: She will have read.
12. Future Perfect Continuous: She will have been reading.
These tenses show when an action happens—now, in the past, or in the future.
Here are the 12 tense formulas:
1. Simple Present: Subject + Base verb (s/es)
2. Present Continuous: Subject + is/am/are + verb (ing)
3. Present Perfect: Subject + has/have + past participle
4. Present Perfect Continuous: Subject + has/have + been + verb (ing)
5. Simple Past: Subject + Past verb
6. Past Continuous: Subject + was/were + verb (ing)
7. Past Perfect: Subject + had + past participle
8. Past Perfect Continuous: Subject + had + been + verb (ing)
9. Simple Future: Subject + will/shall + base verb
10. Future Continuous: Subject + will/shall + be + verb (ing)
11. Future Perfect: Subject + will/shall + have + past participle
12. Future Perfect Continuous: Subject + will/shall + have + been + verb (ing)
A tense shows when an action happens: in the past, present, or future.
1. Present tense: Action happening now.
2. Past tense: Action that already happened.
3. Future tense: Action that will happen.
You May Also Like