Contents
Transitional words and phrases are important because they help connect ideas, sentences, and paragraphs. They make writing flow smoothly and are like signposts that guide readers through your thoughts.
Using transitional words and phrases can make your writing clearer and easier to understand. In this article, we will explain what they are, why they matter, and share examples to show how you can use them to improve your writing.
What are Transitional Words?
Transitional words, also known as connectors or linking words, are single words that connect ideas and help to create a smooth flow between sentences and paragraphs. Transitional words can signal relationships between ideas, such as time, cause and effect, comparison, contrast, addition, and concession. Using transitional words can help to avoid repetition and make your writing more concise and clear. Instead of repeating the same idea or phrase multiple times, you can use a transitional word to signal the relationship between the ideas and move smoothly from one sentence or paragraph to the next.
Examples of Transitional Words:
- Additionally
- Similarly
- However
- Therefore
- Meanwhile
- For example
- In conclusion
- First
- Indeed
- In other words
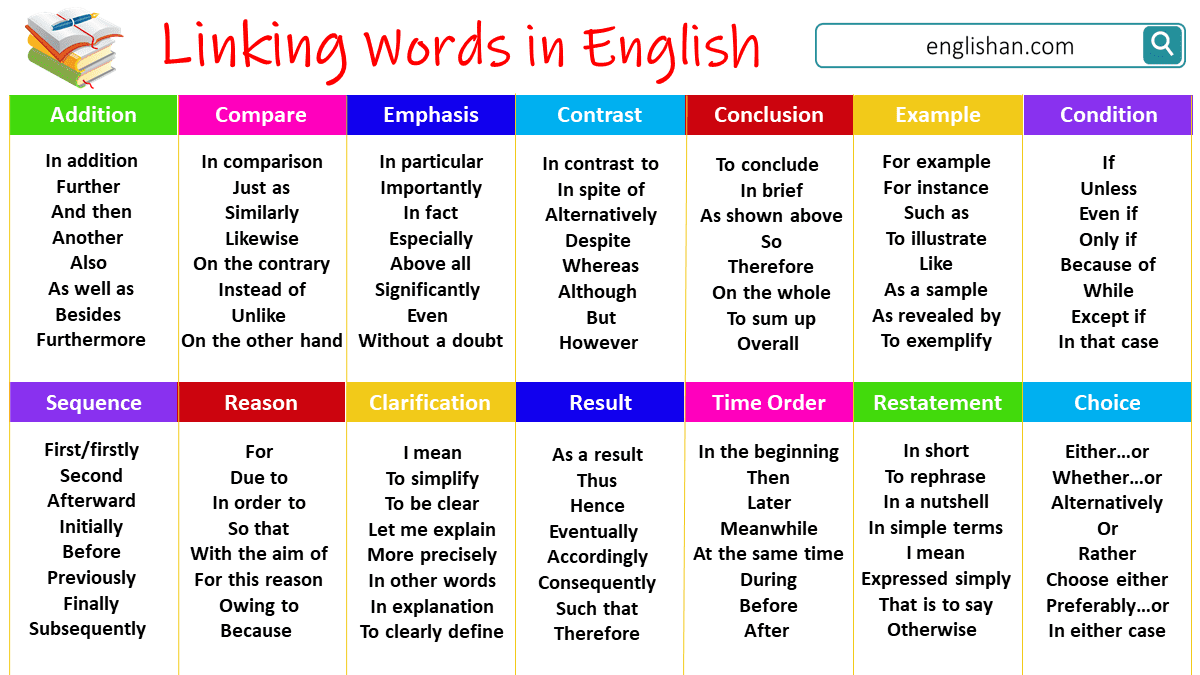
What are Transitional Phrases?
Transitional phrases are groups of words that function as transitional elements. They are more complex than transitional words because they consist of multiple words, but serve the same purpose of guiding the reader or listener through the text. Transitional phrases serve similar functions to transitional words, such as adding information, contrasting ideas, showing time relationships, indicating cause and effect, emphasizing important points, and providing examples.
Examples of Transitional Phrases:
- On the other hand
- As a result
- In the same way
- In other words
- Such as
- To sum up
- Next to
- Without a doubt
- During that time
- Just as
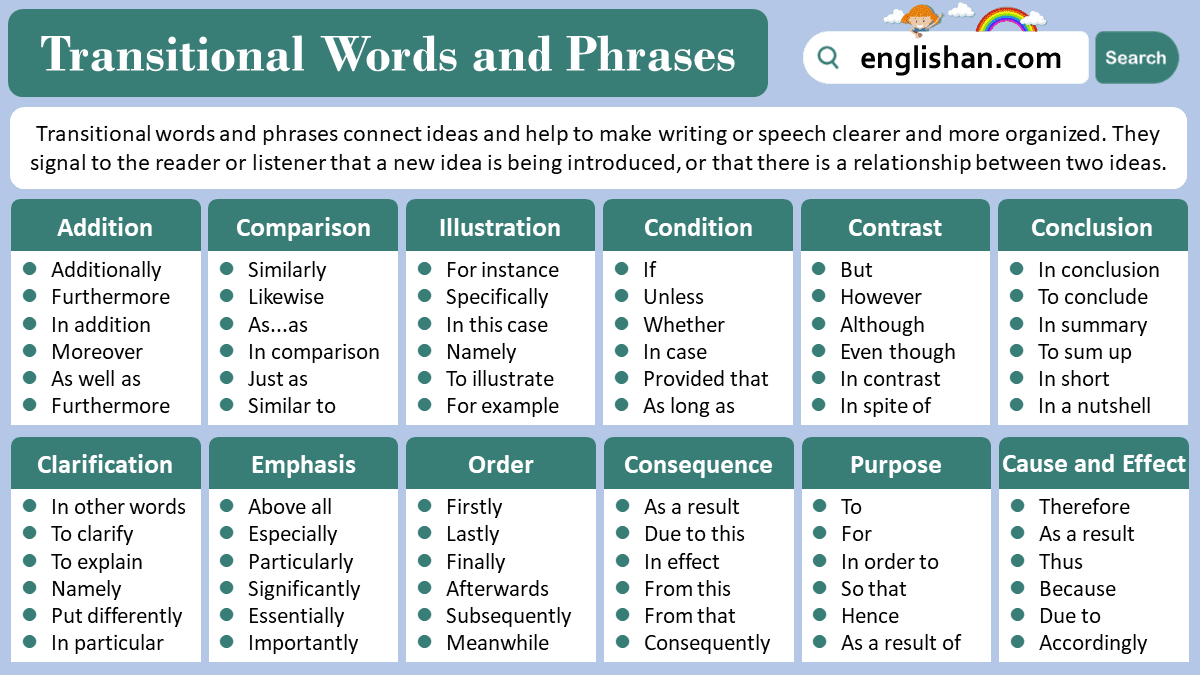
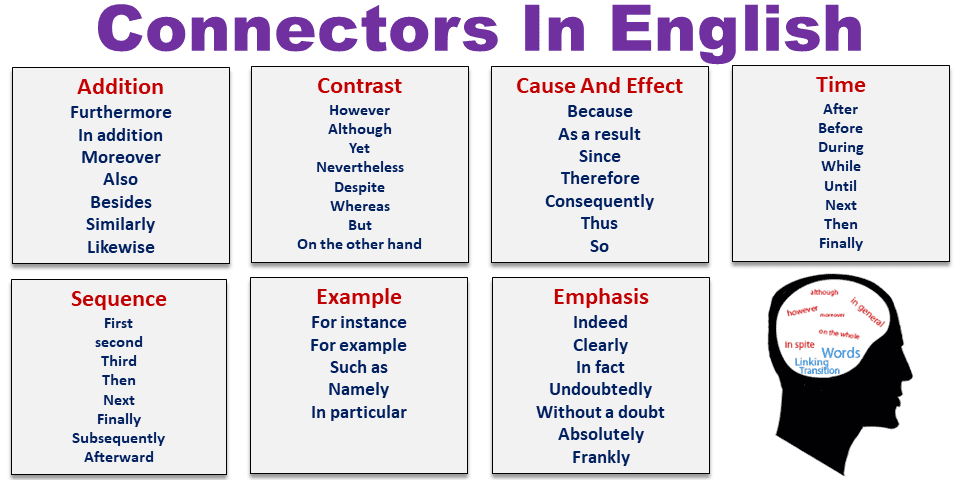
Types of Transitional Words and Phrases
Transitional words help make your writing smoother by connecting ideas clearly. Below are different types of transitional words and how they can be used effectively.
Addition Words
Addition words help add new ideas or information that support what you’ve already said. They make your writing flow better and connect similar ideas.
Examples:
- Additionally
- Also
- Furthermore
- In addition
- Moreover
- Not only…but also
- On top of that
- As well as
- Besides
- Coupled with
- In the same way
- Likewise
- To add on
- In a similar vein
- Equally important
- Along with
- In like manner
- Plus
- And
Comparison Words
Comparison words show how things are similar. They help the reader understand how different ideas are alike.
Examples:
- Similarly
- Likewise
- In comparison
- Just as
- As…as
- Comparable to
- Correspondingly
- In the same manner
- Similarly to
- Likewise
Contrast Words
Contrast words show how things are different. They help explain different points of view or opposing ideas.
Examples:
- However
- On the other hand
- Nevertheless
- Nonetheless
- But
- Yet
- Although
- Even though
- In contrast
- Conversely
- Whereas
- While
- On the contrary
- In spite of
- Despite
Cause and Effect Words
Cause and effect words explain why something happens and what happens because of it. They help make connections clear.
Examples:
- Because
- Since
- Therefore
- As a result
- Consequently
- Thus
- Due to
- Hence
- Owing to
- For this reason
- On account of
- Resulting from
Time Words
Time words show when things happen. They help put events in the right order so the reader can follow along easily.
Examples:
- Now
- Today
- Tomorrow
- Yesterday
- Currently
- Presently
- Meanwhile
- In the meantime
- Soon
- Later
- Afterwards
- Before
- After
- Then
- At that time
- At the same time
- In the past
- In the future
- Ultimately
Example Words
Example words help give specific examples to make your ideas clearer. They make abstract ideas easier to understand.
Examples:
- For example
- For instance
- Such as
- Like
- Namely
- In particular
- Specifically
- To illustrate
- As an illustration
- As a case in point
- In other words
- To clarify
- To demonstrate
- To exemplify
- To elaborate
- To put it differently
- For one thing
- For another thing
- As revealed by
- As shown by
Conclusion Words
Conclusion words help wrap up your ideas. They let the reader know you are finishing your thoughts.
Examples:
- In conclusion
- To conclude
- Ultimately
- In summary
- To sum up
- In short
- Finally
- In a nutshell
- Overall
- Therefore
Sequence Words
Sequence words show the order of steps or events. They help guide the reader through a process step by step.
Examples:
- First
- Firstly
- Second
- Secondly
- Third
- Thirdly
- Next
- Then
- Afterward
- Subsequently
- Finally
- Last
- In the meantime
- Meanwhile
- Following this
- Concurrently
- Simultaneously
- Eventually
- Ultimately
- In the end
- At last
- Lastly
Emphasis Words
Emphasis words highlight important points. They help make sure the reader notices key information.
Examples:
- Importantly
- Indeed
- Notably
- Chiefly
- Particularly
- Especially
- In particular
- Above all
- Specifically
- Essentially
- Significantly
- Crucially
- Primarily
- Basically
- In essence
- Substantially
- Undoubtedly
- Surely
- Clearly
Clarification Words
Clarification words help explain things more clearly or in a different way so the reader understands better.
Examples:
- In other words
- That is to say
- To clarify
- Simply put
- Because
- Since
- For this reason
- As
- Owing to
- Due to
- In other words
- Seeing that
- Given that
- To put it differently
- In order to
- So
Condition Words
Condition words show that something will happen only if certain conditions are met. They are used to set limits or requirements.
Examples:
- If
- Unless
- Provided that
- As long as
- Assuming that
- On the condition that
- Only if
- In case
Purpose Words
Purpose words explain why something is done or the goal behind an action. They show intention or aim.
Examples:
- So that
- In order to
- For the purpose of
- To
- With this in mind
- With the aim of
- For this reason
- In an effort to
FAQs
Transitional words are connectors that create flow and coherence in writing. They link ideas, sentences, and paragraphs, helping readers follow the logical progression of a text.
Transitional phrases are groups of words that work like transitional words. They typically consist of two or more words, such as “on the other hand,” “as a result,” and “in the same way.” These phrases enhance the clarity and cohesion of your writing by linking ideas effectively.
Transitional words improve the readability of your text. They establish connections between ideas, create smooth transitions between sentences and paragraphs, and ensure overall coherence.
Transitional words make writing more organized and reader-friendly. They help ideas flow logically, reducing confusion and keeping readers engaged with your arguments and points.
Transitional words are categorized by their functions:
Addition: furthermore, moreover, in addition
Contrast: however, on the other hand, yet
Comparison: similarly, likewise
Cause and Effect: therefore, consequently, as a result
Time/Sequence: first, meanwhile, afterward
You May Also Like