Attributive adjectives play a significant role in English grammar. They are adjectives placed directly before nouns to describe or modify them. For example, in the phrase “a red apple,” the word “red” describes the noun “apple.” Understanding these adjectives helps create clearer, more detailed sentences, enriching both writing and speech. In this article, we will explore their usage, rules, and examples.
What Are Attributive Adjectives?
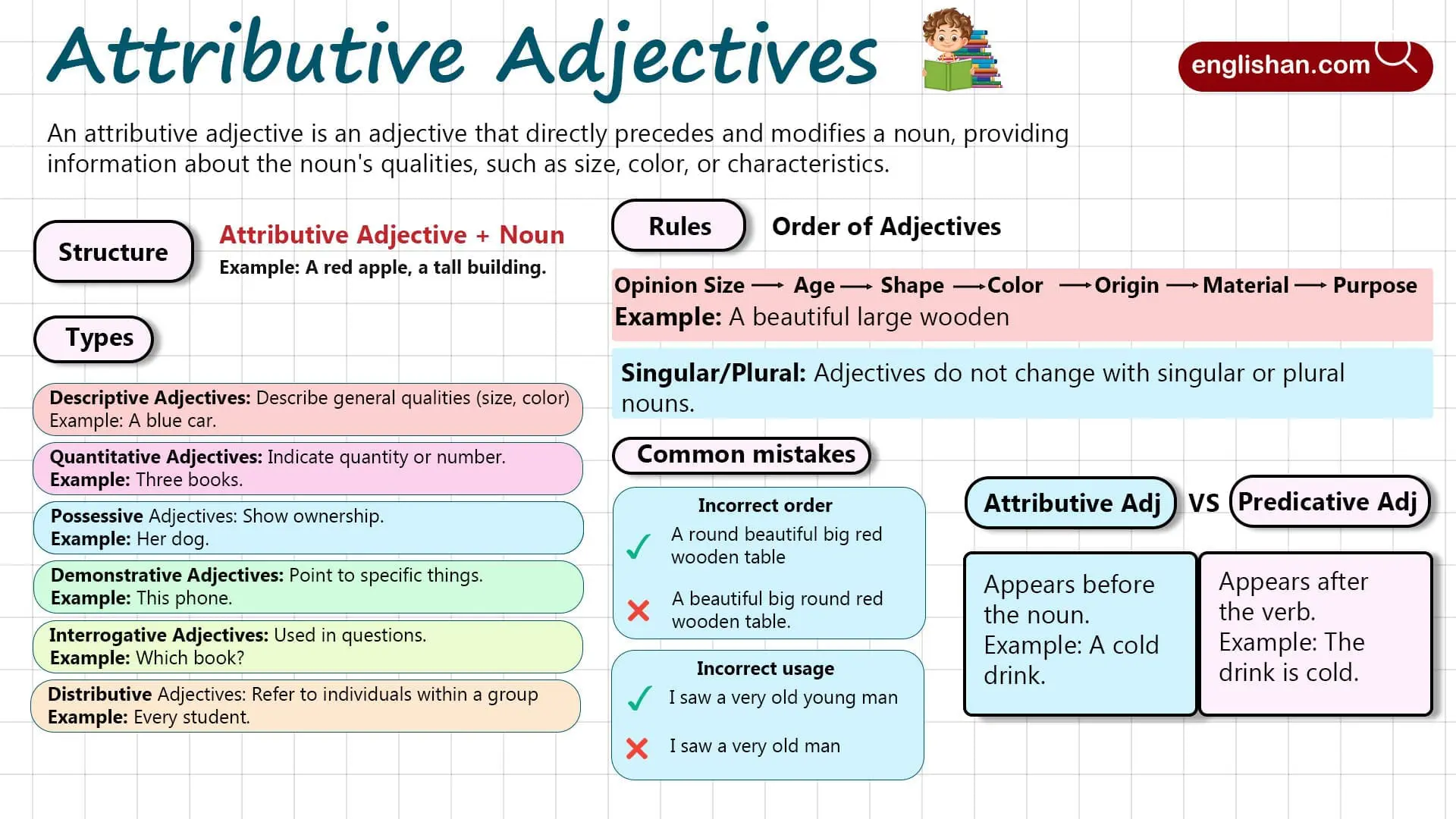
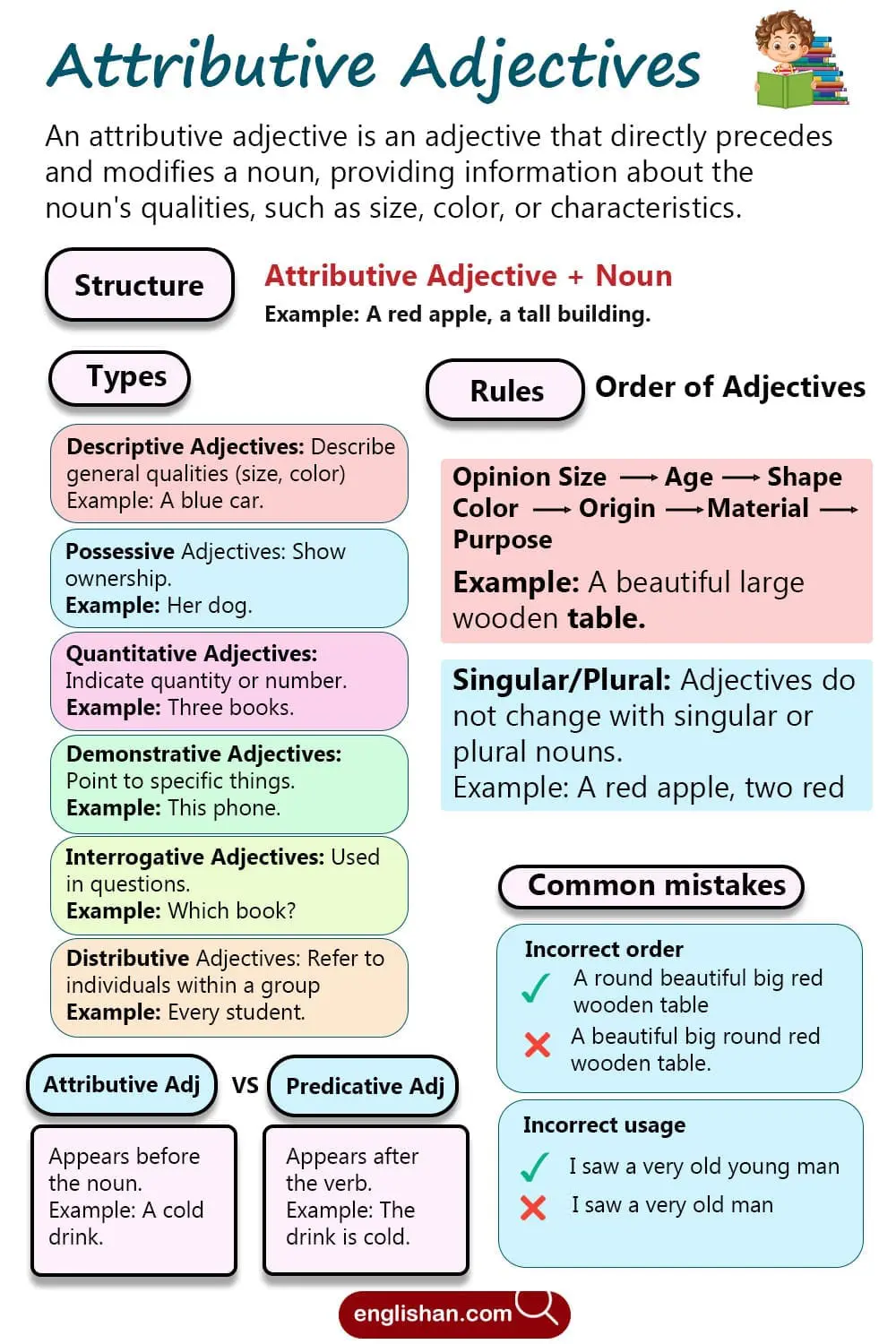
An attributive adjective is an adjective that directly precedes and modifies a noun, providing information about qualities like size, color, or attributes.
For example:
- A tall building
- A delicious cake
- The happy child
In these sentences, tall, delicious, and happy modify building, cake, and child. These adjectives help convey more specific details, improving communication.
Attributive vs. Predicative Adjectives
Adjectives can appear in two forms: attributive and predicative.
- Attributive: These adjectives appear before the noun they describe. For example, “a cold drink.”
- Predicative: These adjectives follow the verb, describing the noun indirectly. For example, “The drink is cold.” Here, “cold” is predicative because it follows the verb “is.”
Both forms serve descriptive purposes, but attributive ones offer immediate detail by directly preceding the noun.
Types of Attributive Adjectives
There are different types of attributive adjectives, each serving a unique purpose when modifying nouns:
- Descriptive Adjectives: Describe general characteristics like size, color, or quality.
- Example: A beautiful flower, a blue car
- Quantitative Adjectives: Indicate quantity or number.
- Example: Five apples, many books
- Possessive Adjectives: Show ownership or possession.
- Example: My house, her dog
- Demonstrative Adjectives: Point out specific things.
- Example: This phone, those shoes
- Interrogative Adjectives: Used to ask questions about nouns.
- Example: Which book is yours?
- Distributive Adjectives: Refer to individual nouns within a group.
- Example: Each student, every person
Examples of Attributive Adjectives in Sentences
Here are examples of how these adjectives function in sentences:
- She wore a beautiful dress.
- The tall man entered the room.
- We have three cats at home.
- My brother loves to travel.
- That car is very fast.
- Which movie are we watching tonight?
In each sentence, the adjective appears right before the noun it modifies.
Rules for Using Attributive Adjectives
Here are some key rules to remember when using attributive adjectives:
- Order of Adjectives: When using multiple adjectives, they follow a specific order:
- Opinion → Size → Age → Shape → Color → Origin → Material → Purpose
- Example: A beautiful (opinion) big (size) round (shape) red (color) wooden (material) table.
- Singular and Plural Nouns: Adjectives do not change based on whether the noun is singular or plural.
- Example: A red apple, three red apples.
- No Comparison: Adjectives describe a noun but do not compare unless used in comparative or superlative forms.
- Example: A faster car (comparative), the fastest car (superlative).
Common Mistakes with Attributive Adjectives
Here are common mistakes learners make with attributive adjectives:
- Incorrect order of adjectives:
❌ A round beautiful big red wooden table.
✅ A beautiful big round red wooden table. - Using the wrong adjective for the context:
❌ I saw a very old young man.
✅ I saw a very old man. - Forgetting the adjective:
❌ The child is running in dress.
✅ The child is running in a blue dress.
Remember, these adjectives must always be placed before the noun they describe.
Importance of Attributive Adjectives in Writing and Speaking
Attributive adjectives are essential because they provide more information about the noun, creating vivid and clear imagery. Imagine describing a car without adjectives: I have a car is vague, but I have a shiny red sports car is much more descriptive and engaging.
Using these adjectives effectively will make your communication more precise and interesting, whether in writing or speaking.
Conclusion
Attributive adjectives are a fundamental part of English, adding richness and detail to nouns. Mastering their usage will enhance both your speaking and writing skills.
FAQs
An attributive adjective is a word that describes a noun and usually comes before it.
Examples:
1. A red apple – “Red” describes the apple.
2. A tall building – “Tall” describes the building.
3. A happy dog – “Happy” describes the dog.
4. An old car – “Old” describes the car.
The adjective tells us more about the noun.
Here are 6 examples of attributive nouns:
1. School bus
2. Coffee cup
3. Dinner plate
4. Water bottle
5. Football team
6. Movie ticket
The first noun describes the second noun.
Here are 12 examples of adjectives:
1. Happy
2. Tall
3. Blue
4. Fast
5. Soft
6. Old
7. Beautiful
8. Friendly
9. Smart
10. Warm
11. Loud
12. Strong
These words describe or modify nouns, telling us more about them.
Here are some adjectives that are attributive only (they usually come before a noun and don’t work well after “is” or “are”):
1. Main – The main reason (not “The reason is main”).
2. Former – The former president (not “The president is former”).
3. Dead – The dead animal (not “The animal is dead”).
4. Industrial – The industrial area (not “The area is industrial”).
5. Rural – The rural village (not “The village is rural”).
These adjectives are mostly used before nouns.
A predicative adjective comes after a linking verb and describes the subject.
Example:
The flower is beautiful.
(“Beautiful” describes the flower after the verb “is.”)
Read More