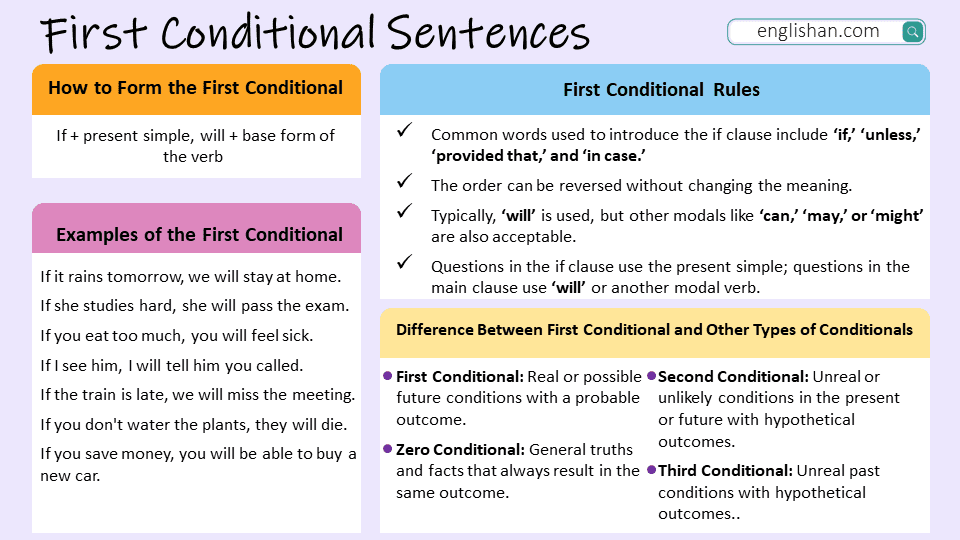
The first conditional is a sentence structure used to talk about future possibilities that are likely to happen if a certain condition is met. It follows this pattern: If + present simple, will + base verb. This helps English learners express likely results of real situations.
Structure of a First Conditional Sentence
A first conditional sentence has two parts: an if clause (condition) and a main clause (result).
Structure: If + present simple, will + base form of the verb
If Clause (Condition)
- Begins with the word if to introduce a condition.
- Uses a present simple verb.
Examples:
- If it rains, we will stay at home.
- If clause: If it rains
- Main clause: we will stay at home
- If she calls me, I will answer.
- If clause: If she calls me
- Main clause: I will answer
- If you eat too much, you will feel sick.
- If clause: If you eat too much
- Main clause: you will feel sick
Main Clause (Result)
- Begins with will or another modal verb like can, may, or might
- Followed by the base form of the verb
Examples:
- If it rains, we will stay at home.
- If she calls me, I will answer.
- If you eat too much, you will feel sick.
Distinction from Other Conditional Structures
| Conditional Type | Usage | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| First Conditional | Real and possible future events | If + present simple, will/modal + base verb | If it rains, we will stay at home. |
| Zero Conditional | General truths or scientific facts | If + present simple, present simple | If you heat water, it boils. |
| Second Conditional | Unreal or unlikely present/future situations | If + past simple, would/modal + base verb | If I won the lottery, I would travel. |
| Third Conditional | Unreal past situations | If + past perfect, would have + past participle | If he had studied, he would have passed. |
How to Identify First Conditional
‘If’ at the Start
- Look for if at the beginning. It signals a condition.
Present Simple in Condition
- The if clause should use a present simple verb.
‘Will’ or Modals in Result
- The main clause should have will or modals like can, may, might.
Realistic Future Event
- It should describe a possible future situation.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with First Conditional Rules
Incorrect Verb Tense in If Clause
Always use present simple in the if clause, not future tense.
- Correct: If it rains, we will stay home.
- Incorrect: If it will rain, we will stay home.
Misplacing the Comma
Use a comma only when the if clause comes first.
- Correct: If you study, you will pass.
- Correct: You will pass if you study.
- Incorrect: You will pass, if you study.
Using ‘Will’ in Both Clauses
The word will must appear only in the main clause, not in the if clause.
- Correct: If she calls, I will answer.
- Incorrect: If she will call, I will answer.
Using First Conditional for Unreal Situations
Do not use the first conditional for imaginary or impossible events. Use it only for real and possible future situations.
- Correct: If I finish early, I will help you.
- Incorrect: If I were rich, I will buy a car. (Use second conditional here)
Confusing ‘If’ with ‘When’
Use if for conditions, not when. “If” suggests uncertainty. “When” suggests certainty.
- Correct: If he comes, we will eat together.
- Incorrect: When he comes, we will eat together. (only correct if you’re sure he will come)
20 Example Sentences of First Conditional
- If it rains, we will cancel the picnic.
- If you study, you will pass the test.
- If she calls, I will answer.
- If they invite us, we will go.
- If I wake up late, I will miss the bus.
- If you don’t eat, you will get hungry.
- If he drives fast, he might crash.
- If we leave now, we will catch the train.
- If it gets cold, I will wear a jacket.
- If she finishes her work, she can rest.
- If you touch that wire, you will get shocked.
- If they win, they will celebrate.
- If you don’t water the plants, they will die.
- If we hurry, we can be on time.
- If I see him, I will tell him.
- If the sun shines, we will go swimming.
- If you read more, you will improve.
- If she gets sick, she might stay home.
- If you forget, I will remind you.
- If the store closes, we will come tomorrow.
FAQs:
A first conditional sentence is a grammatical structure in English used to express a possible or likely future outcome based on a specific condition. It typically consists of an if clause in the present simple tense and a main clause with will or another modal verb, followed by the base form of the verb.
Form a first conditional sentence by starting with an if clause, using the present simple tense. Follow this with a main clause using will or a modal verb, along with the base form of the verb.
First conditionals express real and possible future situations, while zero conditionals are used for general truths and facts. The if clause in a zero conditional also uses the present simple tense.
You May Also Like