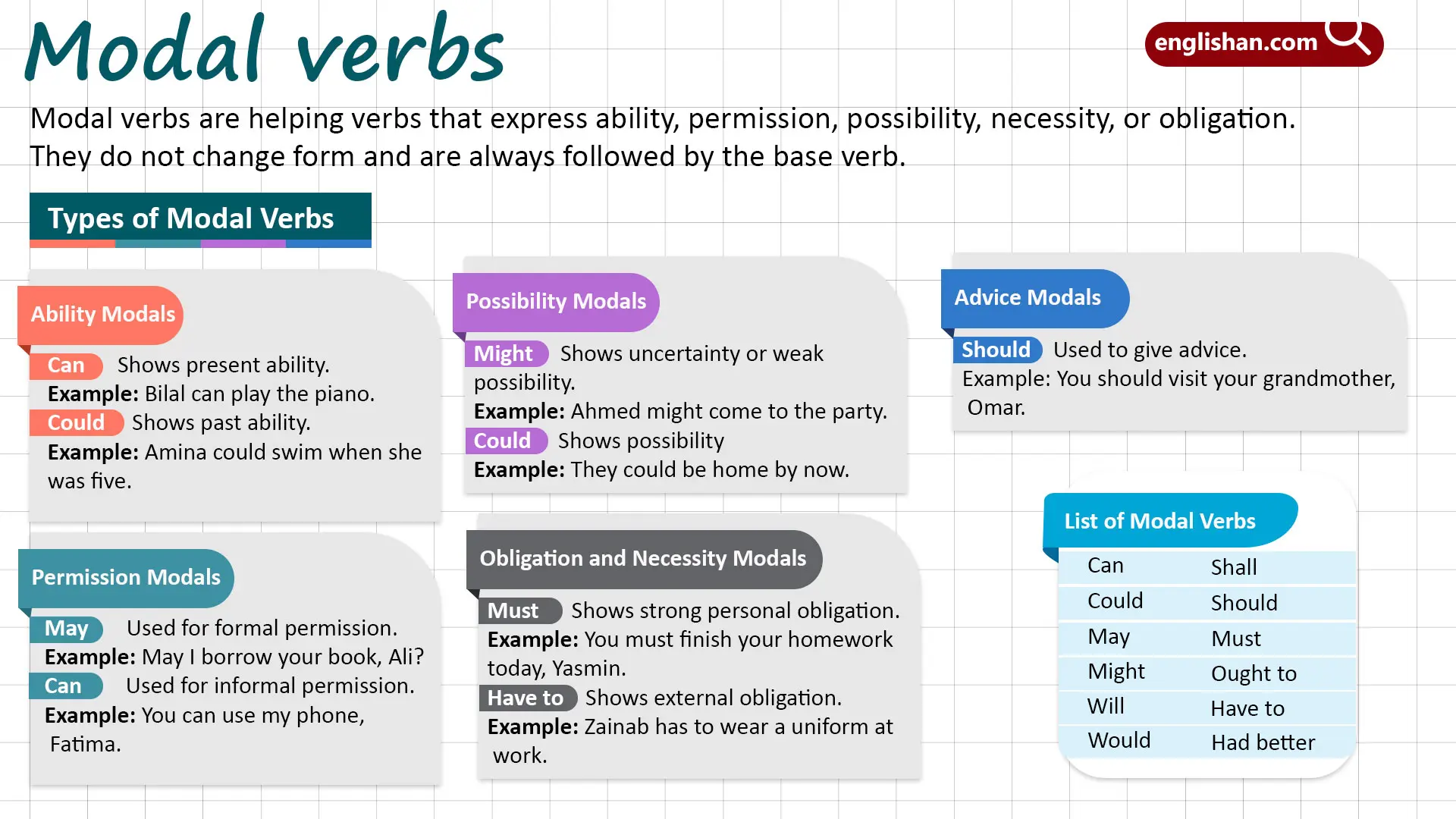
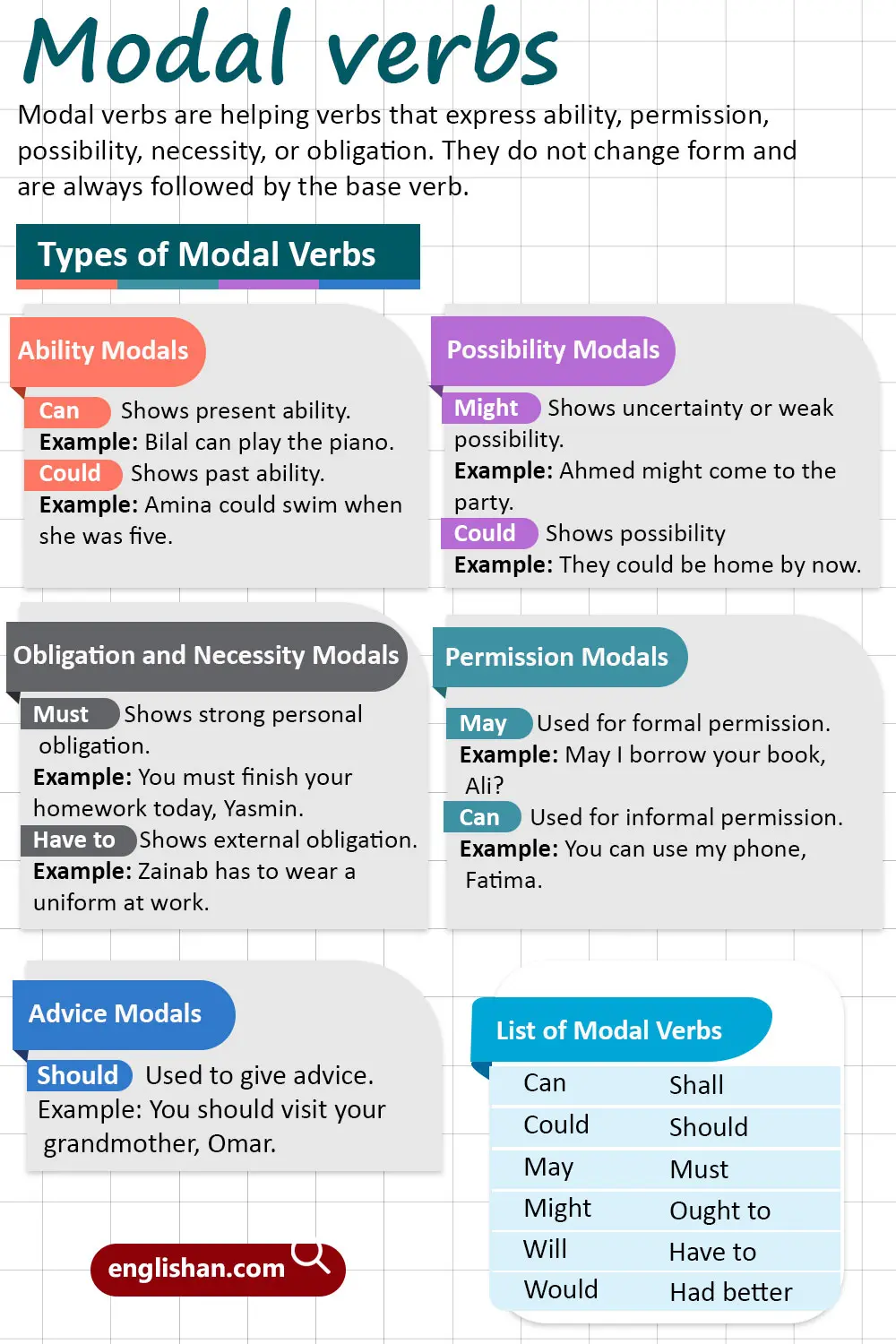
A modal verb is a type of auxiliary verb that expresses possibility, ability, necessity, or permission. It always works with a main verb to complete meaning in a sentence. Unlike other verbs, modals do not change form with subjects or tenses.
In this lesson, you will study the definition, rules, and types of modal verbs. You will also see examples, mistakes, practice sentences to master their correct usage.
Definition of Modal Verbs
A modal verb is an auxiliary verb that adds meaning to the main verb by showing ability, permission, necessity, probability, or obligation. Common modals include can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would. They do not take -s endings and are always followed by a base verb.
Functions of Modal Verbs in English
Modal verbs express different functions in sentences:
- Ability: She can swim across the river.
- Possibility: It might rain tomorrow.
- Necessity/Obligation: You must wear a seatbelt.
- Permission: You may leave early today.
- Advice: You should see a doctor.
- Prediction: The train will arrive at six.
Did you know? The modal shall was once very common in British English but is now rare in everyday speech.
Rules of Using Modal Verbs
- Use base form of main verb after a modal.
- She can drive a car.
- Modals do not take -s or -ed endings.
- ❌ He cans swim. → ✅ He can swim.
- No “to” after true modals.
- ❌ She must to go. → ✅ She must go.
- Negative form is made with “not.”
- He cannot play guitar.
- Questions are formed by inversion.
- Can she dance?
- Only one modal in a clause.
- ❌ He will can come. → ✅ He will be able to come.
- Past meaning may use could, might, should, would.
- She could sing when she was younger.
Types of Modal Verbs
Modal Verbs
The main set of modal verbs includes can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would. These are true modals because they never change form, never add -s, and are always followed by the base form of the main verb.
- Can: shows ability or permission.
- She can solve the puzzle easily.
- You can borrow my book tomorrow.
- Could: expresses past ability, polite requests, or possibility.
- He could run very fast when he was a child.
- Could you help me with this task?
- May: gives permission or shows possibility.
- You may leave once you finish your work.
- It may rain later this evening.
- Might: weaker possibility than may.
- He might join us for dinner.
- She might call you tomorrow.
- Must: shows necessity, obligation, or strong certainty.
- He must finish the project today.
- That must be the new teacher.
- Shall: expresses future intention (formal or British use).
- We shall meet again.
- I shall return the book tomorrow.
- Should: used for advice, expectations, or mild obligation.
- You should wear a jacket in winter.
- The train should arrive at seven.
- Will: expresses future certainty or willingness.
- They will travel next week.
- I will help you with your homework.
- Would: shows polite requests, hypothetical situations, or repeated past actions.
- I would help if I had time.
- When we were young, we would play outside every evening.
Semi-Modal Verbs
Semi-modals are verbs that act like modals but are formed differently. They often use “to” or have verb-like endings. Common semi-modals include have to, need to, ought to, dare to, used to.
- Have to: shows necessity or external obligation.
- She has to wear a uniform at school.
- We have to finish the report by Monday.
- Need to: indicates necessity or requirement.
- You need to study for the exam.
- I need to call my parents today.
- Ought to: expresses moral duty, advice, or strong probability.
- You ought to respect your parents.
- She ought to pass with all her preparation.
- Dare to: shows courage or boldness.
- He dared to question the manager.
- I don’t dare to speak in front of a large crowd.
- Used to: describes past habits or states that no longer exist.
- He used to play cricket every weekend.
- They used to live in this town.
Modal Verbs in Different Tenses
- Present/Future: She can play the piano.
- Past ability: He could run fast when young.
- Past necessity: We had to wait in line.
- Future reference: She will call you tomorrow.
- Unreal/conditional: I would go if I had time.
Sentence Structures with Modal Verbs
| Structure | Example |
|---|---|
| Affirmative | She can sing beautifully. |
| Negative | He cannot drive a truck. |
| Interrogative | May I come in? |
| Past Reference | When I was young, I could run fast. |
| Conditional | I would help if you asked. |
Examples of Modal Verbs in Sentences
- She can solve this problem quickly.
- They might come to the party tonight.
- He must wear a helmet while riding.
- You may sit here.
- She should drink more water.
- The students will complete their work.
- I would travel more if I had money.
- He could sing when he was a child.
- You have to pay attention in class.
- We ought to be kind to others.
- She used to play the piano.
- He shall answer for his actions.
- They need to leave soon.
- I might read that book later.
- She will succeed with hard work.
Common Mistakes with Modal Verbs
❌ He cans play guitar.
✅ He can play guitar.
(Modals never take -s endings.)
❌ She must to go now.
✅ She must go now.
(Do not use “to” after true modals.)
❌ He will can help you.
✅ He will be able to help you.
(Do not use two modals together.)
Modal Verbs vs Auxiliary Verbs
- Modal verbs add meaning (necessity, ability, permission). She can dance well.
- Primary auxiliaries (be, have, do) form tenses, voices, and questions. She is dancing.
Thus, modals are a subset of auxiliaries but perform different functions.
Exceptions and Special Notes
- Dare and need sometimes act like modals (e.g., Need you ask?).
- In informal English, gonna, wanna sometimes replace modal-like meanings but are not standard.
- Some modals express politeness rather than strict grammar: “Could you pass the salt?”
Differences Between Common Modal Verbs
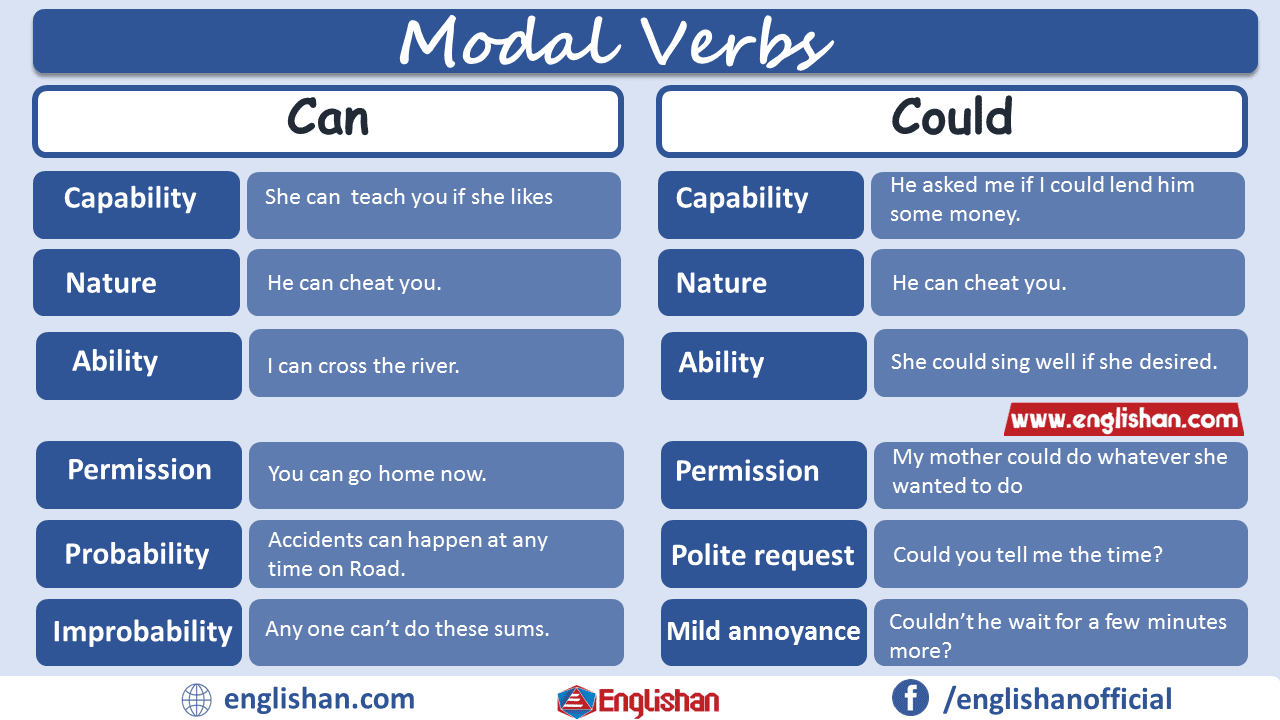
Can vs Could
- Can: shows present ability or permission.
- She can speak three languages.
- You can borrow this book.
- Could: expresses past ability, polite requests, or possibility.
- When I was young, I could run fast.
- Could you help me with this task?
Key point: Can = present/fact; Could = past, polite, or uncertain possibility.
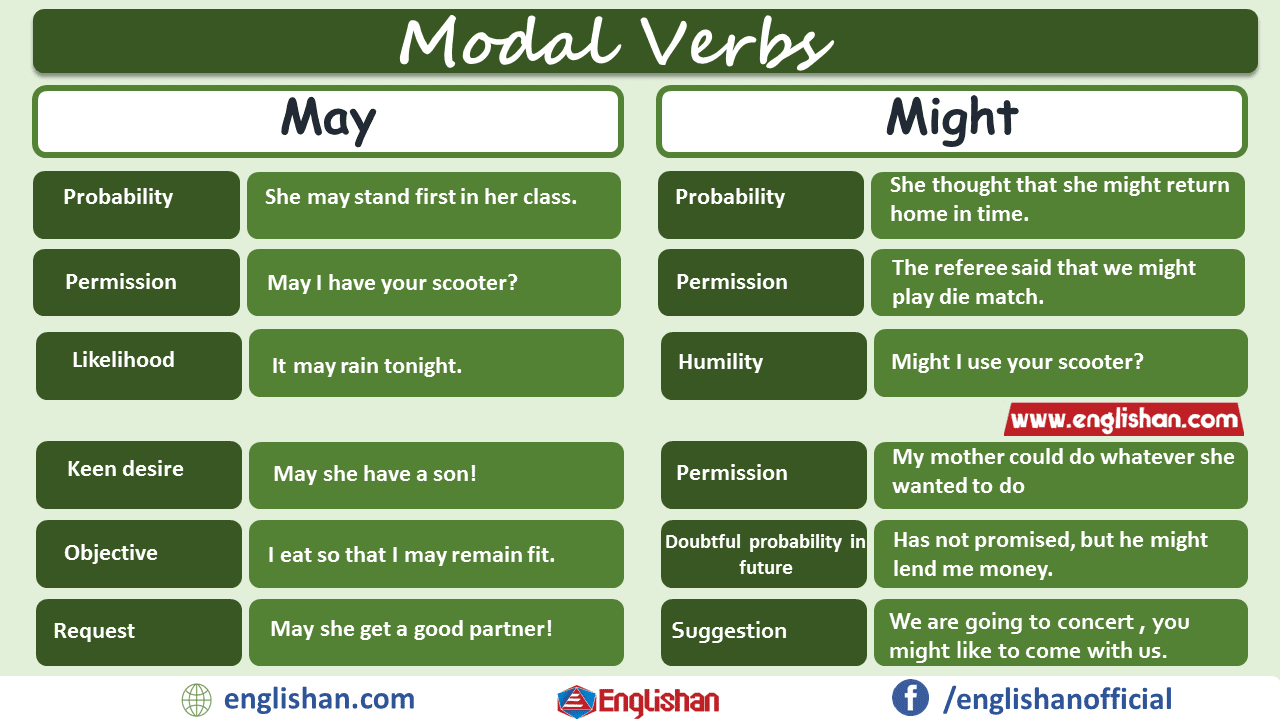
May vs Might
- May: expresses permission or strong possibility.
- You may leave the class now.
- It may rain this afternoon.
- Might: shows weaker or more uncertain possibility.
- She might come to the party.
- He might win if he trains harder.
Key point: May is slightly stronger than might in showing possibility.
Will vs Would
- Will: expresses certainty, willingness, or definite future.
- They will arrive at six.
- I will help you with your homework.
- Would: used for hypothetical, polite, or conditional situations.
- I would buy that car if I had money.
- She would like some tea, please.
Key point: Will = definite action; Would = imagined, polite, or conditional.

Shall vs Should
- Shall: expresses formal intention or offers (mainly British English).
- We shall overcome this problem.
- Shall I open the window?
- Should: used for advice, recommendations, or expectations.
- You should eat more vegetables.
- The train should arrive on time.
Key point: Shall = formal future or offers; Should = advice or likelihood.

Exercises and Practice with Modal Verbs
- Fill in the blank: She ___ play the piano when she was five.
- Identify the modal: He must finish his work today.
- Correct the mistake: She shoulds drink more water.
- Make a question with may.
- Rewrite using a modal: It is necessary for you to leave now.
- Join: He was tired. He continued working. → Use must or should.
- Write a sentence with would in a conditional form.
FAQs on Modal Verbs
What are modal verbs in English grammar?
Modal verbs are auxiliaries like can, may, must, will that show ability, necessity, permission, or possibility. She can ride a bike.
Can modal verbs be used in past tense?
Yes, some modals have past forms. She could sing well when she was young. Semi-modals like had to also show past necessity.
Do modal verbs change with subjects?
No. Modal verbs remain the same for all subjects. I can swim. She can swim. Unlike normal verbs, they do not take -s.
What is the difference between modal verbs and auxiliaries?
Auxiliaries form tense and voice, while modals express meaning such as possibility. She is singing (auxiliary). She must sing (modal).
Can we use two modals together?
Generally no. ❌ He will can come. → ✅ He will be able to come. Instead, replace one modal with a phrase.
Final Thought
A modal verb strengthens grammar by expressing meanings like ability, necessity, or possibility. By learning its rules, types, and exceptions, learners can avoid mistakes and write accurately. With practice, modals become natural tools for fluent communication.
FAQs About Modal Verbs
A modal verb is a type of auxiliary verb that expresses necessity, possibility, permission, ability, or obligation. They are used with the main verb to add meaning to the action.
Types:
1. Can
2. Could
3. May
4. Might
5. Shall
6. Should
7. Will
8. Would
9. Must
10. Ought to
Here are 12 modal verbs with simple examples:
1. Can’t – Impossibility.
Example: She can’t be serious.
2. Couldn’t – Past impossibility.
Example: I couldn’t find it.
3. May not – Prohibition.
Example: You may not go.
4. Might not – Small chance of something not happening.
Example: I might not come.
5. Shan’t – Refusal (British).
Example: I shan’t do that.
6. Shouldn’t – Negative advice or obligation.
Example: You shouldn’t eat too much.
7. Will not – Refusal.
Example: I will not help.
8. Won’t – Short for “will not.”
Example: She won’t agree.
9. Would not – Refusal or hypothetical.
Example: I would not go there.
10. Wouldn’t – Short for “would not.”
Example: He wouldn’t listen.
11. Mustn’t – Prohibition.
Example: You mustn’t shout.
12. Need – Necessity or obligation (semi-modal).
Example: You need to hurry.
You May Also Like