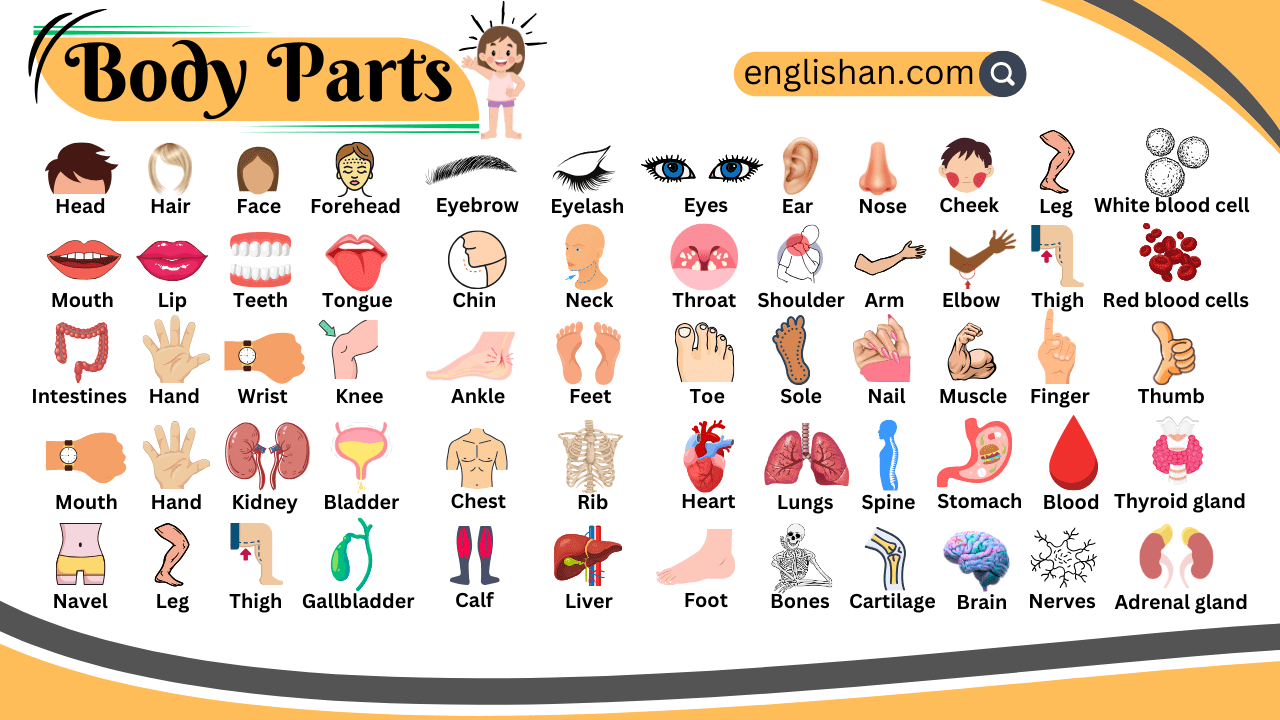
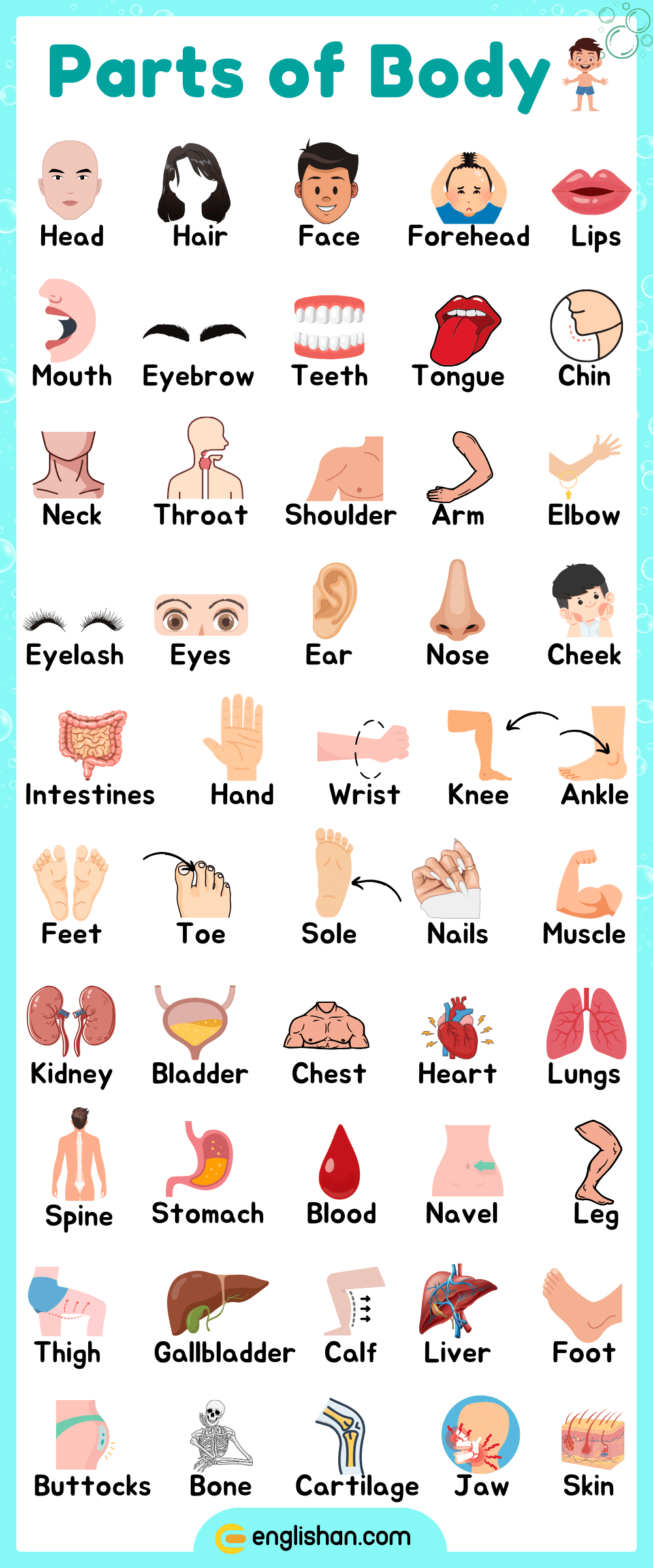
We use body parts names when talking about how we feel, move, or play. This post helps you learn words like head, knees, and fingers using fun pictures and short facts. These names are important when you’re at school, visiting the doctor, or just learning about your own body. The list below shows what each part does, how it helps us, and where it is found. It’s perfect for kids, students, and ESL learners who want to speak about the body with more confidence. At the end, you’ll remember all the key body parts names in English.
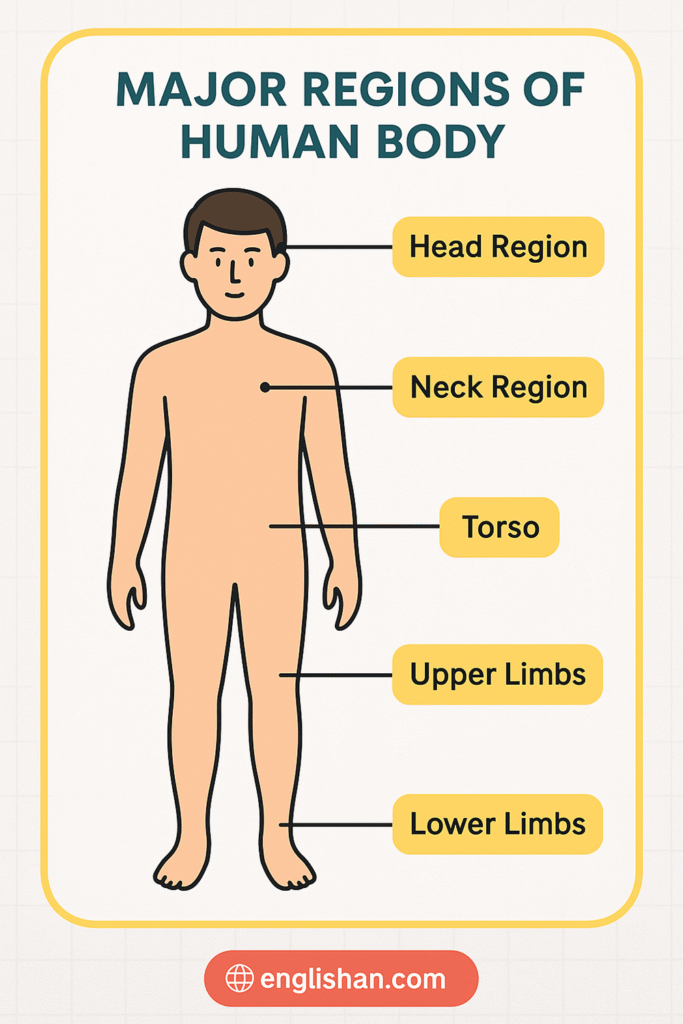
Major Body Regions in the Human Body
The human body is divided into five major regions. Knowing these helps us talk clearly about different body parts name and how each one works and moves.
Head
- The head has the brain, eyes, ears, nose, and mouth.
- It controls thinking, feeling, and sensing.
Neck
- The neck links the head to the torso.
- It contains the windpipe, food pipe, and major blood vessels.
Torso
- The torso includes the chest, abdomen, and back.
- It protects the heart, lungs, and digestive organs.
Upper Limbs
- The arms, from shoulder to hand, help us lift, hold, and write.
Lower Limbs
The legs, from hip to foot, support our weight and help us walk, run, and balance.
Head and Neck Body Parts Name

Scalp
The scalp covers the top of the head and is the skin that supports hair growth.
Skull
The skull is the bony structure that forms the head, protecting the brain and supporting the face.
Face
The face includes the forehead, cheeks, eyes, nose, mouth, and chin.

Forehead
The forehead is the area above the eyes, extending to the hairline.

Eyebrows
Eyebrows are the strips of hair above the eyes that help prevent sweat and debris from entering the eyes.

Eyelashes
Eyelashes are the short, curved hairs growing on the edge of the eyelids, protecting the eyes from dust and particles.

Eyelids
Eyelids are the movable skin folds that cover and protect the eyes.

Eyes
The eyes are the organs of sight, responsible for vision.
Nose
The nose is the organ responsible for smell and breathing. It also filters the air we breathe.

Nostrils
Nostrils are the two openings of the nose through which air enters and exits.

Mouth
The mouth is used for speaking, eating, and breathing. It contains the teeth, tongue, and gums.

Lips
Lips are the soft, movable parts that form the opening of the mouth.
Teeth
Teeth are hard, calcified structures used for chewing food.

Tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth, essential for tasting, chewing, swallowing, and speaking.
Chin
The chin is the lower part of the face below the mouth.

Jaw (Mandible)
The jaw is the bone that forms the lower part of the face, holding the lower teeth.

Cheeks
Cheeks are the soft areas of the face below the eyes and between the nose and ears.
Ears
Ears are the organs responsible for hearing and balance. They consist of the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear.
Earlobes
Earlobes are the soft, fleshy parts at the bottom of the ears.

Neck
The neck supports the head and contains structures like the trachea, esophagus, and major blood vessels.
Throat
The throat includes the pharynx and larynx, which are involved in swallowing, breathing, and speaking.
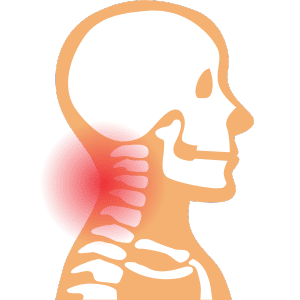
Nape
The nape is the back of the neck, below the hairline.
Torso – Upper Body Parts Vocabulary
The torso, often referred to as the trunk, is one of the most important parts of body as it contains the heart, lungs, and digestive organs. These parts of body are central to maintaining life, processing nutrients, and providing energy.
Shoulders
The shoulders connect the arms to the torso, providing a wide range of motion.
Collarbone (Clavicle)
The collarbone is the bone that connects the shoulder to the sternum (breastbone).
Chest (Thorax)
The chest contains the heart, lungs, and ribcage.

Ribcage
The ribcage is a set of bones that protect the heart and lungs.
Breastbone (Sternum)
The sternum is the flat bone in the center of the chest that connects to the ribs.
Breasts
Breasts are located on the chest and contain mammary glands in females.
Abdomen
The abdomen is the area between the chest and pelvis, containing the stomach, intestines, liver, and other digestive organs.
Navel (Belly Button)
The navel is the scar on the abdomen marking the point where the umbilical cord was attached before birth.
Waist
The waist is the narrow part of the torso between the ribs and hips.
Back
The back extends from the neck to the lower torso and includes the spine (backbone).
Spine (Vertebral Column)
The spine is the bony structure that runs down the back, protecting the spinal cord and supporting the body.
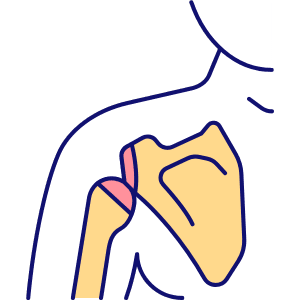
Shoulder Blades (Scapulae)
Shoulder blades are the flat bones on the upper back that connect the arms to the torso.
Lower Back (Lumbar Region)
The lower back is the area of the back between the ribcage and the pelvis.
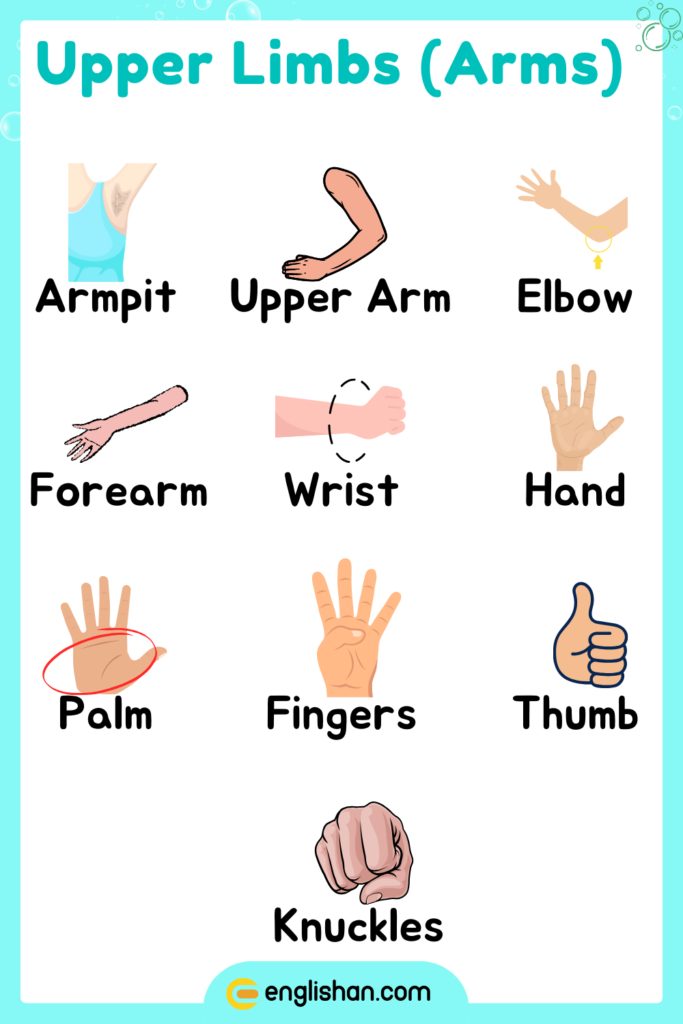
Upper Limbs Body Parts in English
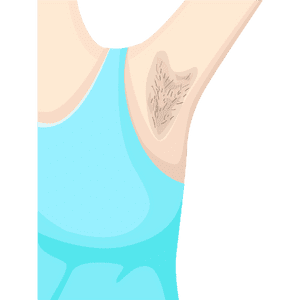
Armpit (Axilla)
The armpit is the hollow area under the arm where it meets the shoulder.

Upper Arm
The upper arm is the part of the arm between the shoulder and elbow.

Elbow
The elbow is the joint connecting the upper arm to the forearm.

Forearm
The forearm is the part of the arm between the elbow and wrist.
Wrist
The wrist is the joint connecting the forearm to the hand.

Hand
The hand includes the palm, fingers, and thumb.

Palm
The palm is the inner surface of the hand.

Fingers
Fingers are the digits of the hand, used for grasping and manipulating objects.

Thumb
The thumb is the short, thick first digit of the hand, allowing for grasping and dexterity.

Knuckles
Knuckles are the joints of the fingers, where the bones of the hand meet the bones of the fingers.
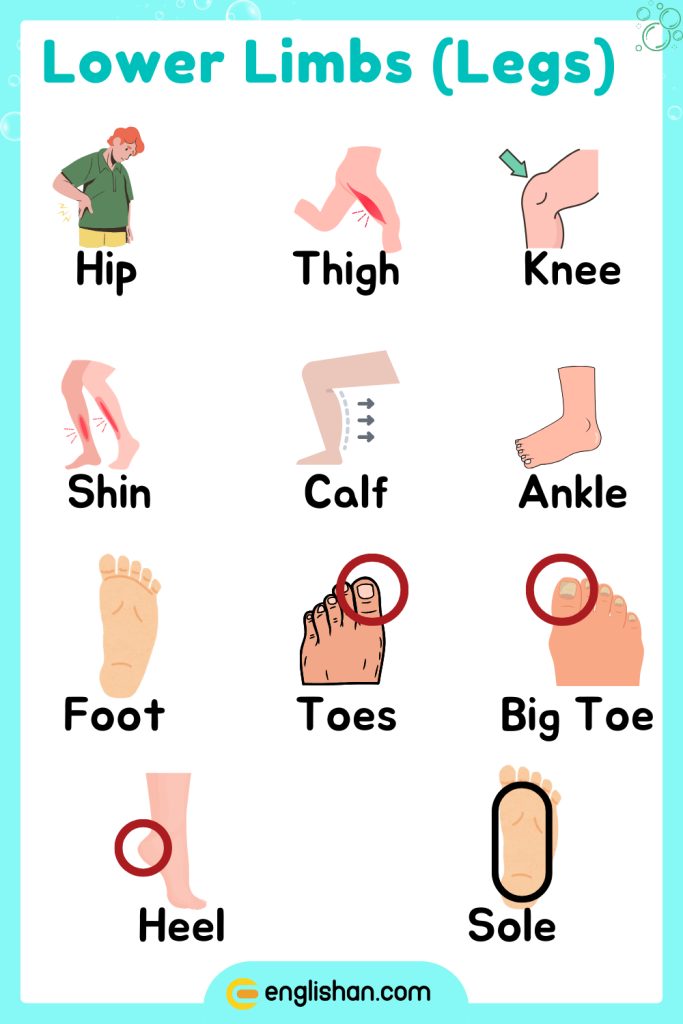
Lower Limbs Body Parts for Students

Hip
The hip is the joint connecting the leg to the pelvis, allowing for movement and weight-bearing.
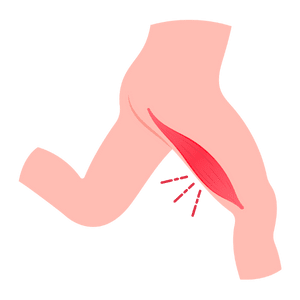
Thigh
The thigh is the upper part of the leg between the hip and knee.
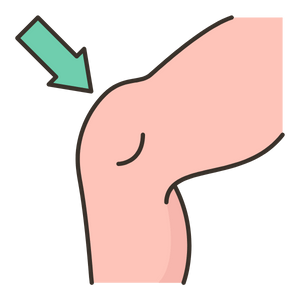
Knee
The knee is the joint connecting the thigh to the lower leg, allowing for movement and weight-bearing.
Shin
The shin is the front part of the lower leg, between the knee and ankle.
Calf
The calf is the back part of the lower leg, between the knee and ankle.
Ankle
The ankle is the joint connecting the lower leg to the foot, allowing for movement and balance.
Foot
The foot includes the toes, arch, and heel, supporting the body’s weight and allowing for movement.
Toes
Toes are the digits of the foot, helping with balance and movement.
Big Toe
The big toe is the largest toe, playing a key role in balance.
Heel
The heel is the back part of the foot, supporting the body’s weight.
Sole
The sole is the bottom surface of the foot.
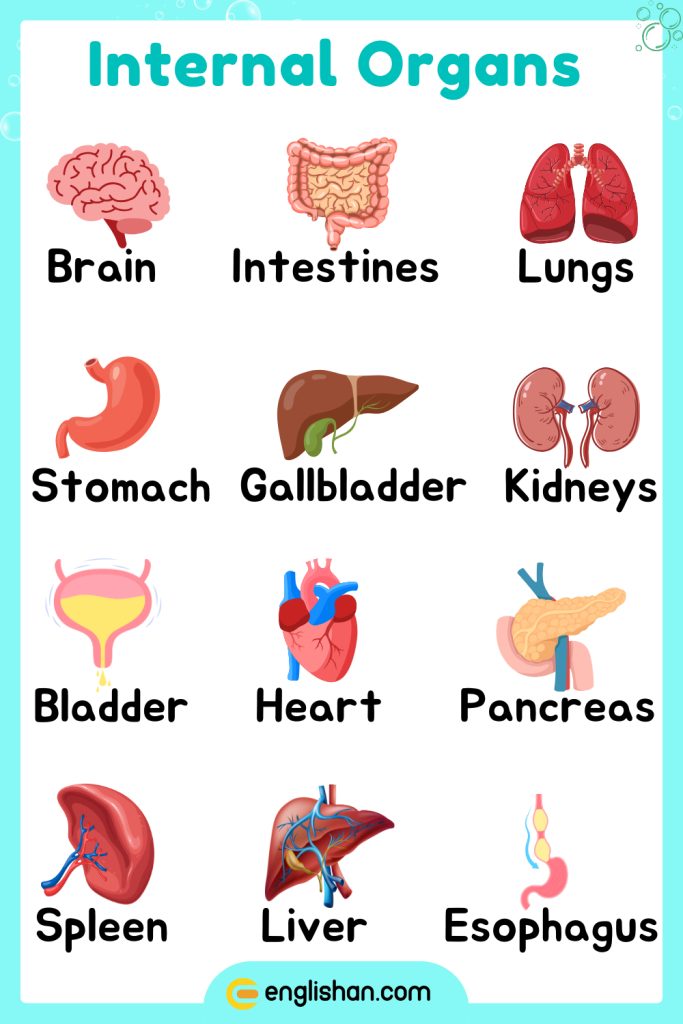
Internal Organs of Body
Internal organs are the hidden yet vital parts of body that regulate bodily functions. These parts of body include the heart, lungs, liver, and kidneys, all of which are necessary for survival and maintaining health.

Brain
The brain is the organ responsible for thought, memory, emotion, and controlling bodily functions.
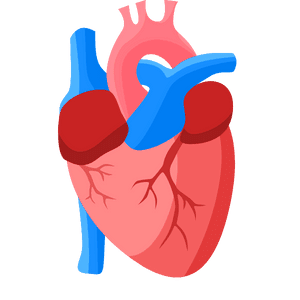
Heart
The heart is the muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
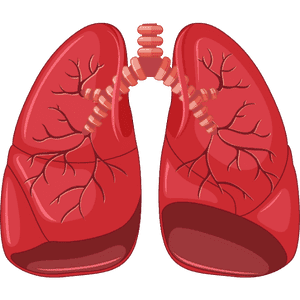
Lungs
The lungs are the organs responsible for breathing, taking in oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide.

Stomach
The stomach is the organ that breaks down food through digestion.
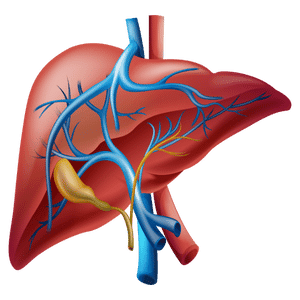
Liver
The liver processes nutrients, detoxifies substances, and produces bile.
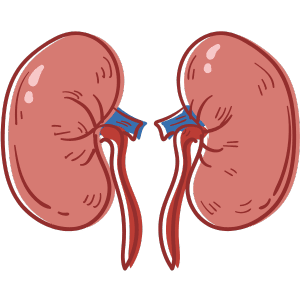
Kidneys
The kidneys filter waste from the blood and produce urine.

Bladder
The bladder stores urine until it is expelled from the body.
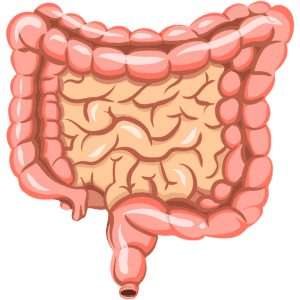
Intestines
The pancreas produces enzymes for digestion and hormones like insulin.The pancreas produces enzymes for digestion and hormones like insulin.
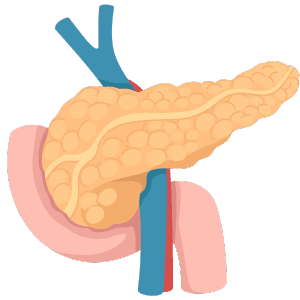
Pancreas
The pancreas produces enzymes for digestion and hormones like insulin.
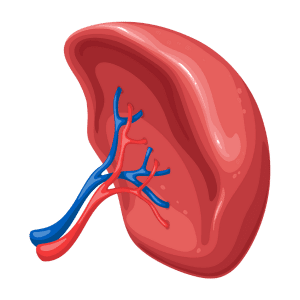
Spleen
The spleen filters blood and helps fight infections.
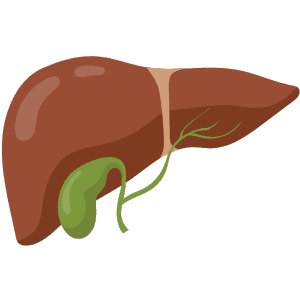
Gallbladder
The gallbladder stores bile produced by the liver, which helps digest fats.
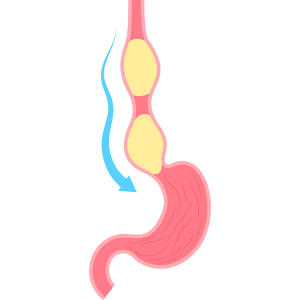
Esophagus
The esophagus is the tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach.
Fema
Other Important Parts
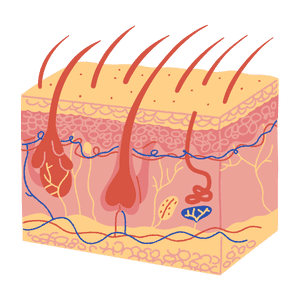
Skin
The skin is the body’s largest organ, covering and protecting the body.

Hair
Hair grows from the skin and provides protection and insulation.

Nails
Nails are the hard coverings on the tips of fingers and toes, protecting the digits and aiding in manipulation.

Blood Vessels
Blood vessels, including arteries, veins, and capillaries, carry blood throughout the body.
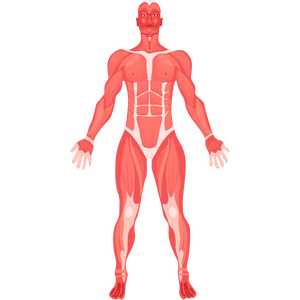
Muscles
Muscles are tissues that contract to produce movement.

Bones
Bones provide structure and support for the body, protecting organs and allowing for movement.
Joints
Joints are where two bones meet, allowing for movement.
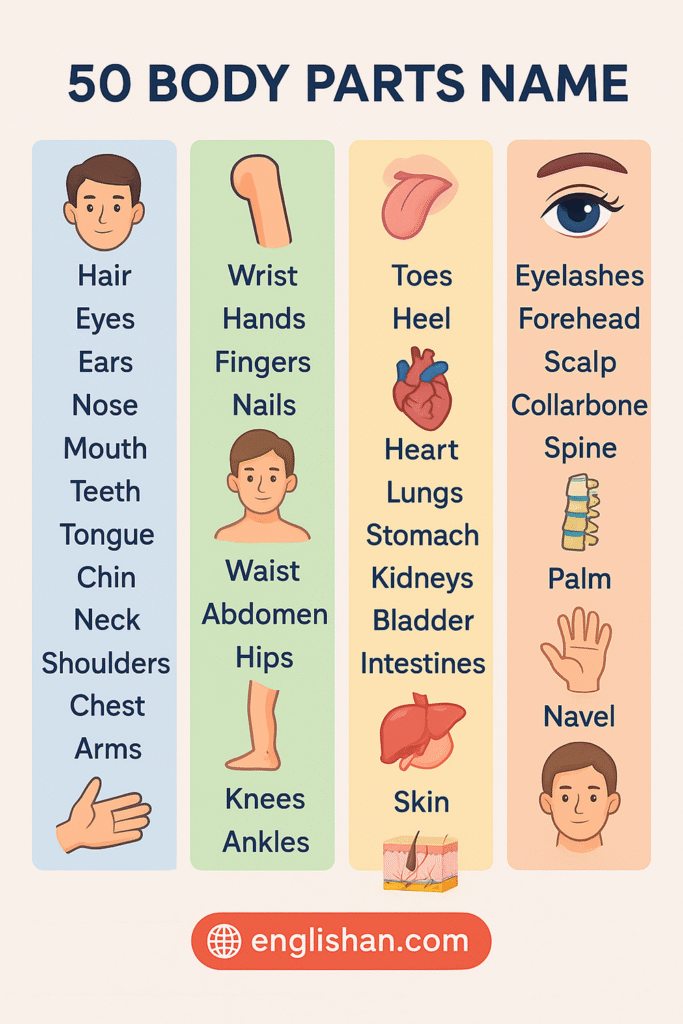
List of 50 Body Parts Names
Here is a list of 50 commonly known body parts in English:
- Head
- Hair
- Eyes
- Ears
- Nose
- Mouth
- Teeth
- Tongue
- Chin
- Neck
- Shoulders
- Chest
- Arms
- Elbow
- Wrist
- Hands
- Fingers
- Nails
- Back
- Waist
- Abdomen
- Hips
- Legs
- Thighs
- Knees
- Ankles
- Feet
- Toes
- Heel
- Brain
- Heart
- Lungs
- Liver
- Stomach
- Kidneys
- Bladder
- Intestines
- Skin
- Eyebrows
- Eyelashes
- Forehead
- Scalp
- Collarbone
- Spine
- Palm
- Navel
- Vulva
- Penis
- Breasts
- Groin
Body Parts Vocabulary with Functions and Use Cases
Each body part has a special job to do.
- Eyes: To see clearly.
- Hands: To hold, write, and touch.
- Legs: To walk, run, and support movement.
- Mouth: To eat, drink, and speak.
- Ears: To hear sounds and words.
- Heart: To pump blood through the body.
- Lungs: To breathe in oxygen and out carbon dioxide.
- Brain: To think, control actions, and manage the body.
- Teeth: To chew food for digestion.
- Tongue: To taste and assist in speaking.
- Stomach: To digest food and begin absorption.
- Fingers: To write, pick, and feel objects.
Body Parts Name Activities for Kids and Learners
Body Parts Song
Use songs like “Head, Shoulders, Knees, and Toes” to learn names easily.
Matching & Coloring
Match names with pictures and color each part correctly.
Labeling Worksheets
Use worksheets to write the correct name next to each body part.
Body Part Game Ideas
Play games like Simon Says, flashcards, and puzzles to review and remember body part names.
Conclusion
Learning the body parts name in English helps you speak about your body confidently. It improves understanding in daily life, school, and healthcare. Keep practicing with songs, games, and visuals to remember them well.
FAQs
Here are 12 body parts in English:
1. Head
2. Eyes
3. Ears
4. Nose
5. Mouth
6. Neck
7. Shoulders
8. Arms
9. Hands
10. Legs
Feet
12. Back
These are some basic body parts that are commonly used in English.
Here’s a short and simple list of body parts:
1. Head: eyes, nose, mouth, ears, hair
2. Neck: throat
3. Upper body: chest, stomach, back
4. Arms and hands: shoulder, arm, elbow, wrist, fingers
5. Lower body: thigh, knee, leg, ankle, toes
6. Inside: brain, heart, lungs, stomach, kidneys
The body part “Jigar” in English refers to the liver.
The body part “Takhna” in English is called the ankle.
The body part “Pitta” in English refers to bile or the gallbladder, depending on the context.
You May Also Like
- Human Body Sound
- Name of Diseases in Humans
- Internal Body Parts Names
- Human Body Parts Worksheet
- Parts of BP Apparatus Names
- Parts of Ear and their Functions