The ear is a complex organ responsible for the sense of hearing and plays a crucial role in maintaining balance. It consists of three main parts: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. Each part has specific structures and functions that contribute to the overall auditory and vestibular processes.
What is the Ear?
The ear is a complex organ responsible for the sense of hearing and plays a crucial role in maintaining balance. It is divided into three main parts: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear.
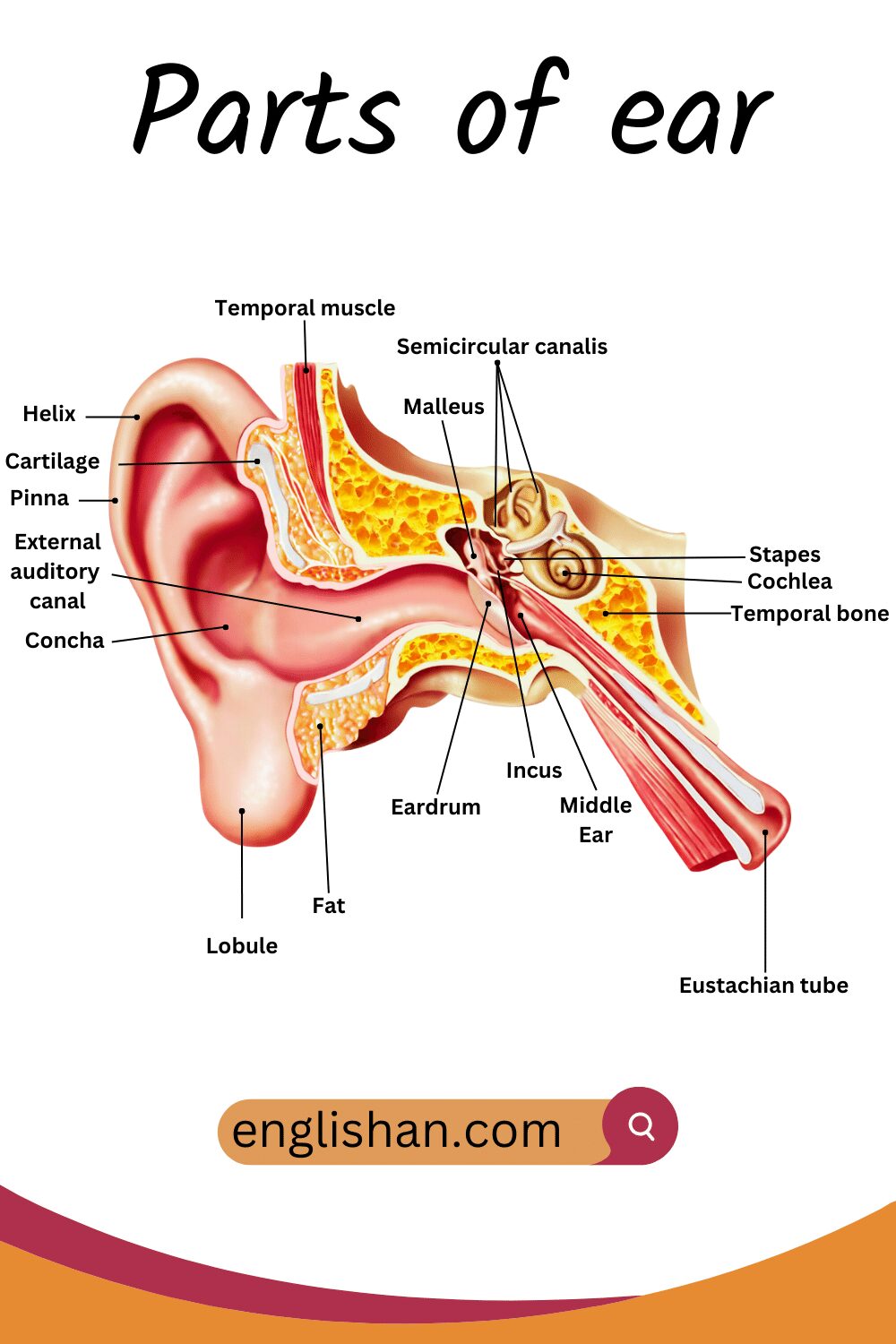
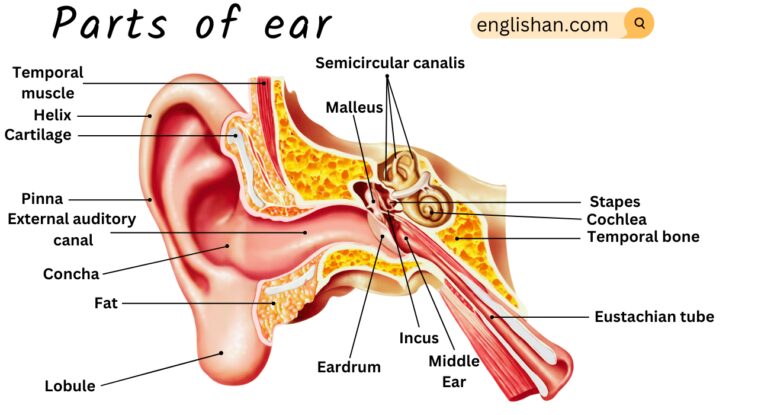
What are the Parts of the Ear?
The ear is a complex organ with three main parts: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear.
1. Outer Ear:
- Pinna (Auricle): This is the visible part of the ear that collects and funnels sound waves into the ear canal.
- Ear Canal (External Auditory Meatus): A tube-like structure that directs sound waves toward the eardrum.
- Eardrum (Tympanic Membrane): A thin membrane that vibrates in response to sound waves, transmitting them to the middle ear.
2. Middle Ear:
- Ossicles: These are three small bones (malleus, incus, and stapes) that amplify and transmit vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear.
- Eustachian Tube: A narrow tube connecting the middle ear to the back of the throat, maintaining air pressure on both sides of the eardrum.
3. Inner Ear:
- Cochlea: A snail-shaped, fluid-filled structure responsible for converting sound vibrations into electrical signals sent to the brain.
- Vestibular System: This includes structures like semicircular canals, utricle, and saccule, contributing to balance and detecting changes in head position.
- Auditory Nerve: It transmits electrical signals from the cochlea to the brain, enabling the perception of sound.
What is the Main Function of the Ear?
The ear serves two main functions: hearing and balance.
1. Hearing: It helps us listen to and understand sounds around us. The outer ear catches sounds, the middle ear amplifies them, and the inner ear turns them into signals for our brain to recognize.
2. Balance: Inside the ear, there’s a system that helps us stay steady and not fall over. It senses our head’s position and movements, making sure we can walk, run, and stand without losing balance.
Anatomy
Where are my ears located?
Your ears are on the sides of your head. They’re the parts you can see on the outside (the ears you wear earrings on), and there’s more inside your head too, helping you hear and stay balanced.
Conditions and Disorders
What are some Ear Problems?
There are various ear problems that can affect the outer, middle, or inner parts of the ear. Some common ear issues include:
1. Ear Infections: Infections can occur in the outer ear (otitis externa) or the middle ear (otitis media) and are often associated with pain, swelling, and sometimes discharge.
2. Tinnitus: This is the perception of noise or ringing in the ears when there is no external sound. It can be a symptom of various underlying conditions.
3. Hearing Loss: Loss of hearing can be temporary or permanent and may result from factors such as aging, exposure to loud noise, infections, or certain medical conditions.
4. Earwax Buildup: Excessive earwax can block the ear canal, leading to hearing problems or discomfort. Cleaning the ears improperly can also contribute to the issue.
5. Vertigo and Dizziness: Inner ear problems, such as issues with the vestibular system, can cause symptoms like vertigo and dizziness.
6. Meniere’s Disease: This is a disorder of the inner ear that can cause episodes of vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus, and a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear.
7. Eardrum Perforation: A hole or tear in the eardrum can occur due to infection, injury, or changes in air pressure. It may lead to hearing loss and increased susceptibility to infections.
8. Swimmer’s Ear: This is an infection of the outer ear canal often caused by water remaining in the ear after swimming, creating a favorable environment for bacterial growth.
9. Otosclerosis: An abnormal bone growth in the middle ear that can cause hearing loss.
10. Cholesteatoma: An abnormal, noncancerous skin growth that can develop in the middle ear behind the eardrum.
What are some symptoms of common ear conditions?
Different ear conditions can manifest with various symptoms. Here are some common ear-related symptoms associated with different conditions:
1. Ear Infections:
- Pain or discomfort in the ear
- Fluid drainage from the ear
- Reduced hearing
- Feeling of fullness in the ear
- Fever (especially in middle ear infections)
2. Tinnitus:
- Ringing, buzzing, or hissing sounds in the ears
- Perception of noise without an external source
3. Hearing Loss:
- Gradual or sudden decrease in hearing
- Difficulty understanding speech, especially in noisy environments
4. Earwax Buildup:
- Earache
- Tinnitus
- Feeling of fullness or blockage in the ear
- Hearing loss
5. Vertigo and Dizziness:
- Spinning sensation (vertigo)
- Imbalance or unsteadiness
- Nausea and vomiting
6. Meniere’s Disease:
- Episodes of vertigo
- Hearing loss, usually fluctuating
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- Feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear
7. Eardrum Perforation:
- Ear pain
- Hearing loss
- Tinnitus
- Discharge from the ear
8. Swimmer’s Ear:
- Itching in the ear canal
- Redness and swelling
- Pain, especially when moving the ear or jaw
9. Otosclerosis:
- Gradual hearing loss, often in both ears
- Tinnitus
10. Cholesteatoma:
- Chronic ear infections
- Foul-smelling ear drainage
- Hearing loss
- Tinnitus
What Tests will my Healthcare Provider Use to Check my Ears?
Healthcare providers use various tests to assess the health of your ears and diagnose any potential issues. The specific tests may depend on the symptoms you’re experiencing and the suspected ear condition. Here are some common tests used to check the ears:
Otoscopic Examination:
- A visual inspection of the ear canal and eardrum using an otoscope. This helps identify issues such as earwax buildup, infections, or abnormalities.
Audiometry:
- A hearing test that measures your ability to hear sounds of different frequencies and volumes. It helps assess the degree and type of hearing loss.
Tympanometry:
- This test measures the movement of the eardrum in response to changes in air pressure. It helps evaluate middle ear function and can identify issues like fluid behind the eardrum.
Pure-tone Audiometry:
- A more detailed hearing test that determines the softest sounds you can hear at different frequencies. It provides a comprehensive assessment of your hearing abilities.
Speech Audiometry:
- This test evaluates your ability to hear and understand speech at different volumes. It helps assess how well you can comprehend spoken language.
Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE) Test:
- This measures the sounds produced by the inner ear in response to a stimulus. It is often used to assess the function of the cochlea.
Vestibular Function Tests:
- These tests assess the function of the inner ear’s vestibular system and may include the Dix-Hallpike maneuver, caloric testing, or rotary chair testing. They help diagnose conditions related to balance and dizziness.
CT Scan or MRI:
- Imaging tests that provide detailed pictures of the ear structures. They are used to investigate issues such as tumors, infections, or abnormalities in the ear and surrounding areas.
Electrocochleography (ECochG):
- This test measures electrical potentials generated in the inner ear in response to sound stimuli. It can help diagnose certain inner ear disorders.
Care
How can I Properly Care for my Ears?
Proper care is essential for maintaining good ear health. Here are some tips to help you care for your ears:
Keep Your Ears Dry: Dry your ears thoroughly after swimming or showering.
Avoid Inserting Objects: Do not use cotton swabs or other objects in the ear canal.
Protect from Loud Noise: Use ear protection in noisy environments.
Clean Ears Safely: Clean the outer ear with a washcloth; consult a professional for earwax removal.
Limit Earphone Use: Avoid high volumes and take breaks from earphones.
Manage Allergies: Effectively manage allergies to prevent their issues.
Stay Smoke-Free: Quit smoking to reduce the risk of infections.
Ear Health During Air Travel: Chew gum or swallow during takeoff and landing.
Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with a healthcare provider.
Protect Ears in Cold Weather: Wear a hat or earmuffs in cold and windy weather.
Quiz:
1. What is the visible part of the ear called?
- a) Tympanic Membrane
- b) Pinna (Auricle)
2. Which part of the ear is responsible for converting sound vibrations into electrical signals?
- a) Ossicles
- b) Cochlea
3. What is the primary function of the outer ear?
- a) Balance
- b) Collecting sound waves
4. What connects the middle ear to the back of the throat and helps equalize air pressure?
- a) Auditory Nerve
- b) Eustachian Tube
5. Which test measures the softest sounds a person can hear at different frequencies?
- a) Tympanometry
- b) Pure-Tone Audiometry
6. What is the primary symptom of tinnitus?
- a) Vertigo
- b) Ringing in the ears
7. Which part of the ear is affected by swimmer’s ear?
- a) Inner Ear
- b) Outer Ear
8. What condition is characterized by a hole or tear in the eardrum?
- a) Otitis Media
- b) Eardrum Perforation
9. What test records eye movements to evaluate balance function?
- a) Electrocochleography
- b) Videonystagmography
10. What is the main function of the vestibular system in the inner ear?
- a) Smell
- b) Balance
11. Which habit should be avoided for proper ear care?
- a) Regular ear cleaning
- b) Inserting objects into the ear canal
12. What can protect your ears from loud noises?
- a) Earplugs
- b) Cotton swabs
13. What symptom is associated with an ear infection?
- a) Itching
- b) Pain
14. Which imaging test provides detailed pictures of the ear structures?
- a) MRI
- b) CT Scan
Answers:
- b) Pinna (Auricle)
- b) Cochlea
- b) Collecting sound waves
- b) Eustachian Tube
- b) Pure-Tone Audiometry
- b) Ringing in the ears
- b) Outer Ear
- b) Eardrum Perforation
- b) Videonystagmography
- b) Balance
- b) Inserting objects into the ear canal
- a) Earplugs
- b) Pain
- a) MRI
FAQS:
1. Q: How often should I clean my ears?
Clean the outer part regularly with a washcloth. Avoid inserting objects into the canal. If you have excessive earwax, consult a healthcare provider.
2. Q: Can earwax cause hearing loss?
Yes, impacted earwax can cause hearing loss. It is important not to insert objects into the canal for cleaning.
3. Q: What are the signs of an ear infection?
Signs of an infection include pain, fluid drainage, reduced hearing, and fever in some cases.
4. Q: How can I protect my ears from loud noises?
Use its protection, such as earplugs or earmuffs, in noisy environments to prevent hearing damage.
5. Q: Is it safe to use cotton swabs to clean my ears?
No, inserting cotton swabs into the canal can push earwax further inside and increase the risk of injury or infection.
6. Q: How can I prevent swimmer’s ear?
Keep it dry after swimming by tilting your head to let water drain out and using a towel.
7. Q: What should I do if I have tinnitus (ringing in the ears)?
If you experience persistent tinnitus, consult a healthcare professional for an evaluation, as it can be a symptom of various underlying conditions.
8. Q: Can allergies affect my ears?
Yes, allergies can contribute to issues. Managing allergies effectively may help prevent related problems.
You May Also Like:
- Parts of Eye and their Functions
- Five Fingers Names in English with Pictures
- Body Parts: List of Human Body Parts in English
- Past Perfect Tense With Examples, Rules, Usage
- Human Body Sounds List in English
- 60 Examples of Metaphor Sentences