Pronouns are words used to replace nouns in a sentence to avoid repetition. Among the different types of pronouns, there are relative pronouns that connect two ideas, phrases, or clauses in a sentence, providing additional information about a person, place, thing, or idea mentioned earlier. Examples of relative pronouns include ‘who’, ‘whom’, ‘whose’, ‘which’, and ‘that’. In this article, we will discuss relative pronouns, their types, uses, and examples to help you master this essential aspect of English.
What Are Relative Pronouns?
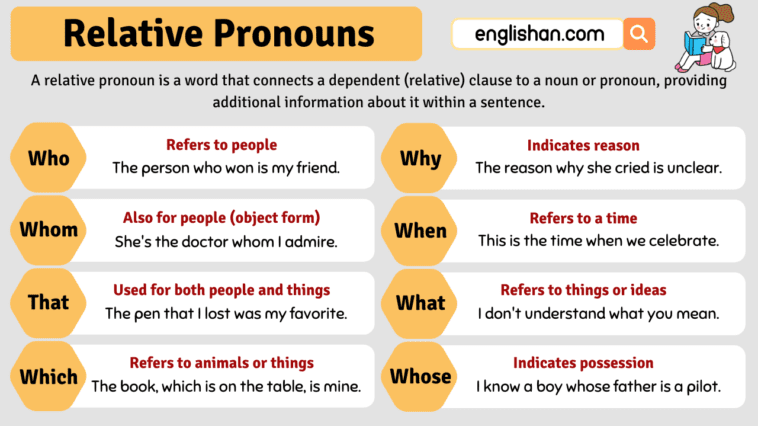
Relative pronouns connect a clause or phrase to a noun or pronoun in a sentence. They introduce a relative clause that describes or identifies it further. Common relative pronouns include “who,” “whom,” “whose,” “which,” and “that.” These pronouns make our sentences clearer and more informative by connecting related ideas.
Here are some simple example sentences:
- This is the house where I grew up.
- The girl who lives next door is my friend.
- I know a man whose car is blue.
- The book which is on the table is mine.
- Do you know anyone whom I can ask for help?
In each sentence, the relative pronoun introduces a clause that provides additional information about the noun or pronoun in the main clause. For example, in the first sentence, “where” connects the clause “I grow up” to the noun “house,” telling us more about the house.
Common Relative Pronouns
- Who: Used for people: Sarah is a girl who loves to read books.
- Whom: Also for people: She’s the doctor whom I admire.
- That: Works for both people and things: The book that I’m reading is exciting.
- Which: Points to things: The cake, which she baked, smells delicious.
- Whose: Shows possession: I know a boy whose father is a pilot.
- Where: Tells us about places: This is the place where we first met.
- When: Talks about time: This is the time when we celebrate.
- Why: Explains reasons: She explained the reason why she was late.
- What: Refers to things: I don’t understand what you mean.
- Whichever: Offers choices: You can pick whichever color you like.
- Whatever: Means anything: You can choose whatever flavor you like.
- Whoever: Refers to any person: Whoever needs help can ask me.
- Whichever: Refers to any thing or choice: Choose whichever color you like.
- Whatsoever: General reference to anything: I’ll accept whatsoever you decide.

Types of Relative Pronouns
Relative pronouns can be categorized into different types based on their usage and the information they provide.
- Personal Pronouns: These relative pronouns include “who,” “whom,” and “whose.” They refer to specific people or, in some cases, animals with names. Example: The woman who lives next door is a doctor.
- Demonstrative Pronouns: “Which” falls under this category. It refers to animals and things. Example: The book, which is on the table, is mine.
- Possessive Pronouns: “Whose” is the only relative pronoun in this category. It shows possession. Example: She is the girl, whose bag got stolen.
- Non-restrictive Pronouns: These relative pronouns provide additional, non-essential information. They are set off by commas and can be omitted without changing the meaning of the sentence. Example: Sarah, who is my neighbor, invited me to her party.
- Restrictive Pronouns: These pronouns provide essential information about the noun they modify and cannot be omitted without altering the sentence’s meaning. Example: The car that is parked in front of the house belongs to Asim.
Functions of Relative Pronouns
Relative pronouns have several functions within a sentence:
- Connecting Clauses: They connect the dependent clause to the main clause, providing additional information about the noun or pronoun mentioned in the main clause.
- I know a person who can help us.
- Introducing Essential Information: They introduce information that is essential for understanding the sentence’s meaning.
- The man who lives next door is a doctor.
- Showing Possession: Relative pronouns like “whose” indicate possession.
- This is the girl whose bag was stolen.
- Referring to Whole Groups: They can refer to a whole group rather than a specific individual.
- Dogs that bark loudly can be annoying.
Usage of Relative Pronouns
- Identify the Noun: Find the noun in your sentence that you want to give more information about.
- Choose the Right Pronoun: Select a relative pronoun based on the type of noun – use “who” for people, “which” for things, and “whose” for possession.
- Introduce the Relative Clause: Place the relative pronoun at the beginning of a new clause to add extra details about the noun.
- Connect Ideas: Use the relative pronoun to connect the two parts of the sentence, showing how they are related.
- Keep It Clear and Simple: Use relative pronouns to make your sentences more straightforward and avoid repeating the same words.
- Use “Who” for People: When talking about people, use “who” to connect the sentences smoothly.
- Use “Which” for Things: If you’re describing things or animals, go for “which” to link your ideas.
- Show Possession with “Whose”: When indicating possession, choose “whose” to clarify ownership.
- Use Commas for Non-Restrictive Clauses: If the information is extra and not essential, set it off with commas.
- Don’t Use a Comma for Restrictive Clauses: If the information is crucial, don’t use commas before and after the relative clause.
Relative Pronouns List
Here is the list of common relative pronouns:
- Who
- Whom
- Whose
- Which
- That
- Where
- When
- Why
- What
- Whoever
- Whomever
- Whichever
- Whatever
- Whosoever
Relative Pronouns Examples
- The book which I read is interesting.
- The car that I drive is fast.
- The park where we play is big.
- The day when we met was sunny.
- The reason why she cried is unclear.
- Whoever comes early gets a prize.
- She is the girl who won the race.
- The man whom I saw is a doctor.
- Whichever path you take, be careful.
- The reason why he left is unknown.
- The place where we met is special.
- Whatever you decide, I’ll support you.
- This is the tree that gives juicy fruits.
- She is the one who always helps.
- This is the bus which goes to the city.
- I’ll eat whatever you cook for dinner.
- He is the one who scored the highest.
- This is the pen whose ink is black.
- The girl whom I met is my cousin.
- The restaurant, which serves pizza, is nearby.
Relative Pronouns Exercises
Fill in the blanks with the correct relative pronoun:
- The man __________ lives next door is a doctor.
- Do you know __________ took my pen?
- This is the restaurant __________ serves delicious food.
- She is the one __________ won the award.
- The movie __________ we watched last night was amazing.
- Tell me __________ you want for your birthday.
- Can you show me __________ book you’re reading?
- The reason __________ he left early is unclear.
- He is the student __________ bag got stolen.
- Is he the teacher __________ you admire?
- Is this __________ you were looking for?
- We should appreciate __________ helps us.
- __________ goes there should be careful.
- I don’t understand __________ you’re saying.
- This is the park __________ we used to play as kids.
Answers:
- who
- who
- that
- who
- that
- what
- which
- why
- whose
- whom
- what
- whoever
- Whoever
- what
- where
FAQs
Q1: What are relative pronouns?
Relative pronouns are words used to introduce a subordinate clause (also called a relative clause) that gives more information about a noun in the main clause. They include “who,” “whom,” “whose,” “which,” “that,” and sometimes “what.”
Q2: How do relative pronouns work?
Relative pronouns serve as connectors between different parts of a sentence. They link the main clause with a subordinate clause, providing additional details about the noun mentioned in the main clause.
Q3: What is the difference between restrictive and non-restrictive relative clauses?
Restrictive relative clauses provide essential information about the noun, and they are not set off by commas. Non-restrictive relative clauses provide additional, non-essential information and are set off by commas. For example, “The boy who is tall is my friend” (no commas), and “My sister, who is a doctor, is coming” (commas).
Q4: What’s the difference between “that” and “which”?
“That” is used in restrictive clauses, essential for the sentence’s meaning, while “which” is used in non-restrictive clauses, providing additional, non-essential information. For example:
- The book that I read is interesting (restrictive).
- The book, which I read, is interesting (non-restrictive).
Q5: Give example sentences of relative pronouns:
Relative pronouns example sentences include:
- This is the street where I live.
- I will eat whatever you cook.
- She is the girl who won the race.
- The pen that I lost was my favorite.
- She is the one whose phone rang.
You May Also Like:
- Relative Clauses | Definition, Types, Usage & Examples
- 60 Examples of Pronouns in Sentences
- Noun Clauses | Definition, Types, Usage & Examples
- Dependent Clauses: Examples and a Quiz
- Worksheets of Pronoun: Use of Pronouns in Sentences