A subject complement is a word or group of words that follows a linking verb and gives more information about the subject. It can rename, identify, or describe the subject, completing the meaning of the sentence.
In this article, you will learn the definition, rules, types, examples, and common mistakes with subject complements. You will also practice with exercises and review FAQs to master this key grammar concept.
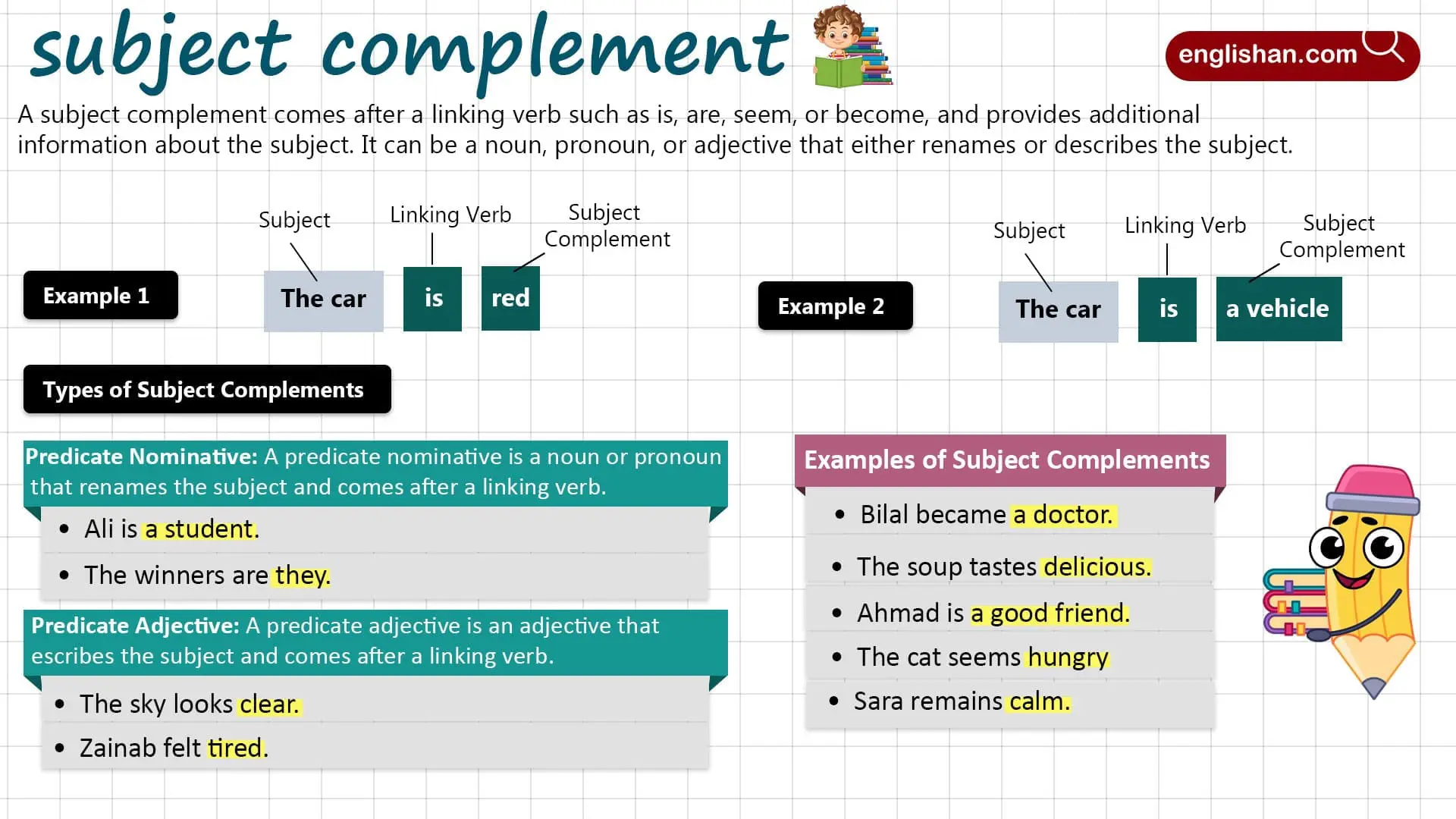
What is Subject Complement?
A subject complement is a noun, pronoun, or adjective that follows a linking verb and either renames the subject or describes its state. It is different from an object because it does not receive the action of the verb. Instead, it completes the meaning of the subject by providing identity or description.
For example:
- “My brother is a teacher.” (Here, a teacher renames brother.)
- “The flowers are beautiful.” (Here, beautiful describes flowers.)
Rules of Using Subject Complement
- Use only after linking verbs
Linking verbs such as be, seem, become, appear, look, feel, taste are followed by subject complements.- Example: “She seems tired.”
- It must refer back to the subject
The complement always gives meaning to the subject, not the object.- Example: “The winner is he.”
- It can be a noun, pronoun, or adjective
Subject complements may rename or describe the subject in different forms.- Example: “This is she.”
- Agreement with the subject
When the complement is a noun, it must agree in number and meaning with the subject.- Example: “My friends are students.”
Subject Complement and Linking Verbs
The subject complement always follows a linking verb. Linking verbs do not express action but show the condition or state of the subject. Without the complement, the sentence feels incomplete.
Examples:
- “The sky became dark.”
- “The actor is a hero.”
Types of Subject Complement
Predicate Nominative
A predicate nominative is a noun or pronoun that renames or identifies the subject.
- “Mr. Khan is a doctor.”
- “It was she who called you.”
Predicate Adjective
A predicate adjective is an adjective that describes the subject.
- “The soup tastes delicious.”
- “They are happy with the results.”
Structure of Subject Complement in a Sentence
A typical structure is:
Subject + Linking Verb + Subject Complement
Examples:
- “Ali is a student.”
- “The test seems easy.”
- “Her smile became brighter.”
Examples of Subject Complement in Sentences
- The manager is a leader.
- This book is interesting.
- The culprit was he.
- Their new car looks expensive.
- She became the class representative.
- The garden appears fresh after the rain.
- That singer is famous worldwide.
- The children are quiet today.
- The exam seemed difficult for everyone.
- This house is ours.
- The story remains unbelievable.
- He turned an honest man.
- The idea sounds brilliant.
- Our neighbors are friendly people.
- The winner is you.
Difference Between Subject Complement and Direct Object
- A subject complement gives meaning to the subject.
- A direct object receives the action of the verb.
Examples:
- “She is a teacher.” → Subject complement (renames subject).
- “She teaches students.” → Direct object (receives action).
Subject Complement vs Object Complement
- Subject complement: follows a linking verb and describes the subject.
- Object complement: follows a direct object and describes or renames it.
Examples:
- Subject complement: “The room is clean.”
- Object complement: “We painted the room clean.”
Subject Complement vs Predicate
- Predicate: everything in the sentence except the subject.
- Subject complement: part of the predicate that specifically describes or renames the subject.
Example:
- In “The sky is blue,” the predicate is is blue, and the subject complement is blue.
Common Mistakes with Subject Complement
❌ Wrong: “It is him.”
✅ Correct: “It is he.”
Explanation: Subject complement after be must be in subject form.
❌ Wrong: “They are them.”
✅ Correct: “They are they.”
Explanation: A pronoun as subject complement must match subject case.
❌ Wrong: “She looks happily.”
✅ Correct: “She looks happy.”
Explanation: Subject complements use adjectives, not adverbs.
Exercises and Practice Sentences on Subject Complement
- Fill in the blank: “This building is ____.” (old / quickly)
- Choose the correct option: “The winners are (they / them).”
- Transform: “The soup tastes salty.” → Change complement to describe taste differently.
- Identify: Underline the subject complement in the sentence: “The children became noisy.”
- Correct the mistake: “It is him who called.”
Final Thought
The subject complement is a vital element that connects the subject with a descriptive or identifying expression. By understanding its rules, forms, and common mistakes, learners can write and analyze sentences with confidence. Mastery of this topic ensures accuracy and clarity in both spoken and written English.
FAQs on Subject Complement
A subject complement is a word that comes after a linking verb and tells you more about the subject.
Example:
She is happy.
“Happy” is the subject complement because it tells us more about “she.” The linking verb is “is.”
A complement is a word that completes a sentence by describing the subject or object.
Examples:
She is a teacher. (Subject complement)
They called him funny. (Object complement)
Here are some examples of object complements:
They named the dog Max.
(“Max” describes the object “dog.”)
She painted the wall blue.
(“Blue” describes the object “wall.”)
The teacher called him smart.
(“Smart” describes the object “him.”)
Object complements give more information about the object in a sentence.
A complement completes the meaning of a sentence.
Subject complement: Follows a linking verb and describes the subject. Example: She is tired.
Object complement: Follows the object and describes it. Example: They made him leader.
In English grammar:
Subject is the person or thing doing the action.
Example: Tom eats an apple. (Tom is the subject.)
Object is the person or thing that receives the action.
Example: Tom eats an apple. (An apple is the object.)
The subject performs the action, and the object receives it.
Read More