Contents
Correlative conjunctions, also known as parallel conjunctions, are an essential part of the English language, as they help to connect words, phrases, and clauses in a sentence. They are often used in pairs, with each part of the pair introducing a new idea. These pairs create a sense of balance and clarity in writing or speaking. In this article, we will explore the different types of correlative conjunctions, their functions, and how to use them effectively. So let’s get started!
What are Correlative Conjunctions?
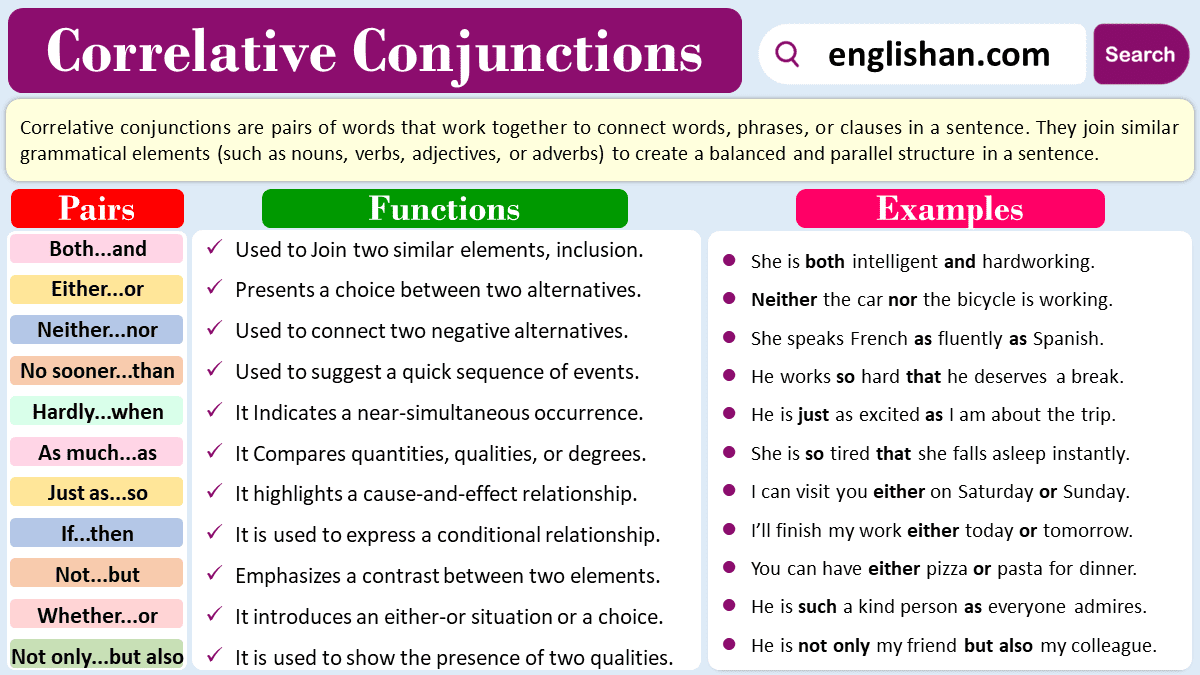
Correlative conjunctions are pairs of words that work together to connect elements in a sentence. These pairs of conjunctions are used to join similar grammatical structures, such as words, phrases, or clauses. Correlative conjunctions are important for creating balance, making comparisons, expressing choices, and showing relationships between different parts of a sentence. Some common examples of correlative conjunctions include “both…and,” “either…or,” “neither…nor,” “not only…but also,” “whether…or,” and “as…as.”
For example In the sentence “You can have either tea or coffee,” the correlative conjunction “either…or” introduces a choice between two alternatives. The word “either” signals a choice, and “or” emphasizes that we can pick one option from the given alternatives. This pair ensures that the sentence is well-organized, making it easy for the reader or listener to understand the available choices.
Structure of Correlative Conjunctions
It’s crucial to remember that the elements connected by correlative conjunctions should be grammatically parallel, meaning they should have the same grammatical structure. Let’s understand the structure of a sentence using a correlative conjunction:
- Both [Element A] and [Element B].
In this structure, “both” and “and” work together to connect two equal elements. The same principle applies to other correlative conjunction pairs. Now, let’s explore each pair in more detail:
Both…and: This pair indicates the presence of two qualities, actions, or characteristics. It’s used when you want to emphasize the combination of two elements.
- She is both intelligent and creative.
Here “Both…and” connects two qualities, indicating that the person possesses both intelligence and creativity.
Either…or: This pair presents a choice between two alternatives. It’s commonly used when describing options or decisions.
- You can eat either now or later.
Here correlative conjunction Either…Or presents a choice between two options, suggesting that the action can happen at one time or another.
Neither…nor: This pair expresses a negative condition contrast, stating that neither of the two connected elements is true or present.
- Neither the sun nor the moon is out right now.
Here the pair “Neither…Nor” expresses a negative condition, indicating that both the sun and the moon are absent there.
Not only…but also: This pair emphasizes the presence of two qualities or actions, suggesting that both are true or happening.
- She is not only smart but also kind.
This pair emphasizes the presence of two qualities, highlighting both the smartness and kindness of the person.
Whether…or: This pair introduces alternatives or possibilities, often used in situations of uncertainty or decision-making.
- I don’t know whether to laugh or cry.
This pair “Whether…Or” introduces alternative possibilities, indicating uncertainty or a decision to be made between laughing and crying.
Common Correlative Conjunctions
- Both…and: Connects two similar elements.
- Either…or: Presents a choice between two alternatives.
- Neither…nor: Connects two negative alternatives.
- Not only…but also: Emphasizes the presence of two qualities.
- So…as: Compares the degree of similarity or dissimilarity.
- Such…that: Shows a result or consequence.
- Scarcely…when: Implies an action immediately follows another.
- Rather…than: Expresses a preference for one thing over another.
- No sooner…than: Suggests a quick sequence of events.
- Hardly…when: Indicates a near-simultaneous occurrence.
- As much…as: Compares quantities or degrees.
- Just as…so: Highlights a cause-and-effect relationship.
- More…than: Compares quantities, indicating excess.
- As…as: Indicates equality or similarity.
- The…the: Shows a proportional relationship.
- Rather…or: Presents alternatives with a preference.
- Whether…or not: Introduces a condition with or without an option.
- If…then: Expresses a conditional relationship.
- Not…but: Emphasizes a contrast between two elements.
- Whether…or: Introduces alternatives, indicating a common outcome.
Functions of Correlative Conjunctions
Here are some basic functions of correlative conjunctions:
- Show Relationship: Correlative conjunctions highlight connections between ideas, emphasizing how two elements are related within a sentence.
- Offer Choices: They present alternatives, helping to express choices or options available in a situation.
- Indicate Similarity: They compare similar qualities or characteristics, illustrating the likeness between two elements.
- Establishing Balance: Correlative conjunctions create a sense of balance by connecting similar elements in a sentence.
- Express Contrast: These conjunctions emphasize differences, signaling a contrast between two ideas or actions.
- Emphasizing Dual Aspects: Correlative conjunctions stress the presence of two qualities or conditions simultaneously.
- Create Balance: They contribute to the overall balance of a sentence by connecting parallel structures and maintaining symmetry.
- Establish Conditions: Correlative conjunctions introduce conditions or scenarios, specifying the circumstances under which something may happen.
- Demonstrate Cause and Effect: They highlight a cause-and-effect relationship between different elements in a sentence.
- Provide Emphasis: By using pairs like “not only…but also,” correlative conjunctions amplify the importance of certain qualities or actions.
Rules of Correlative Conjunctions
Here are some basic rules:
Always in Pairs:
Correlative conjunctions come in pairs, always working together to connect elements in a sentence.
-
- Both…and, Either…or, Neither…nor, Not only…but also, Whether…or, So…as.
Parallel Structure:
Elements connected by correlative conjunctions should be grammatically and structurally parallel.
-
- He likes both reading and to write.❎
- He likes both reading and writing.✅
No Mixing:
Don’t mix different pairs of correlative conjunctions. Stick to the chosen pair throughout the sentence.
-
- Either you don’t study nor pass the exam.❎
- Either you don’t study or you don’t pass the exam.✅
Clear Placement:
Place correlative conjunctions before the elements they connect.
-
- She is not funny only but smart.❎
- She is not only smart but also funny.✅
Punctuation:
Use appropriate punctuation to separate the elements connected by correlative conjunctions.
-
- Whether it’s raining, or not we’ll go out.❎
- Whether it’s raining or not, we’ll go out.✅
Double Negatives:
Avoid using double negatives with correlative conjunctions, as they can create confusion.
-
- I don’t want neither pizza nor pasta.❎
- I want neither pizza nor pasta.✅
Wrong Word Order:
Maintain the correct word order to ensure clarity and proper sentence structure.
-
- I neither want tea or coffee.❎
- I want neither tea nor coffee.✅
List of Correlative Conjunctions
- Both…and
- Either…or
- Neither…nor
- Not only…but also
- Whether…or
- As…as
- So…as
- Such…that
- Scarcely…when
- No sooner…than
- Hardly…when
- The more…the more
- Rather…than
- Whether…or not
- Rather…or
- Not…but
- Just as…so
- Not…nor
- Not…but rather
- From…to
- Too…to
- Enough…to
- As much…as
- Not so much…as
- As soon as…sooner than
- As many…as
- Just so…as
- No less…than
- So much…that
- As far…as
- Even though…yet
- Such…as
- Whether…or not
- As if…so too
- Just as…so too
- So much…that
- Rather…than
- Such…that
- Too…to
- Either…or else
- Just as…so
- Whether…or not
- So…that
- Too…to
- Not only…but also
- Such…that
- Not…but
- Not so much…as
- As soon as…sooner than
- As far…as
Correlative Conjunctions Examples
- She is either at home or at work.
- He is both a teacher and a painter.
- You can have either tea or coffee.
- He runs as fast as his older brother.
- The more you study, the more you’ll learn.
- She is both intelligent and hardworking.
- I will go to the store whether it rains or not.
- He is not only my neighbor but also my friend.
- He was not so much angry as disappointed.
- Neither the car nor the bicycle is working.
- I will go to the party whether you come or not.
- You can have either pizza or pasta for dinner.
- She speaks French as fluently as Spanish.
- He works so hard that he deserves a break.
- Neither the book nor the movie was interesting.
Correlative Conjunctions Exercises
- She is ______ intelligent ______ creative.
- both…and
- either…or
- not only…but also
- neither…nor
- You can either join us now ______ come later.
- or
- nor
- and
- but
- She was so tired ______ she couldn’t stay awake.
- both
- as
- and
- nor
- I want neither tea ______ coffee.
- or
- nor
- but
- and
- ______ it rains ______ shines, we’ll have the picnic.
- Whether…or
- Neither…nor
- Both…and
- So…as
- He is not only a doctor ______ a teacher.
- and
- but also
- nor
- either
- We can either go to the beach ______ to the mountains.
- and
- or
- but also
- neither
- She not only plays cricket ______ also football.
- and
- or
- but also
- nor
- ______ you finish your homework ______ you can go out.
- If…then
- So…as
- Either…or
- Neither…nor
- She is such ______ excellent student ______ everyone admires her.
- a…that
- not only…but also
- more…than
- whether…or
Answers:
- a) both…and
- a) or
- b) that
- b) nor
- a) Whether…or
- b) but also
- b) or
- b) but also
- a) If…then
- a) a…that
FAQs:
Correlative conjunctions are pairs of words that work together to connect similar elements within a sentence. These pairs include “both…and,” “either…or,” “neither…nor,” “not only…but also,” “whether…or,” and others.
Correlative conjunctions, unlike regular conjunctions, always come in pairs. They join similar grammatical elements and create a balanced and parallel structure in a sentence.
Common correlative conjunctions include:
1. Both…and
2. Either…or
3. Neither…nor
4. Not only…but also
5. Whether…or
6. As…as
7. Such…as
8. So…that
Correlative conjunctions serve various purposes, such as expressing choices, indicating alternatives, making comparisons, and emphasizing inclusion or exclusion in a sentence.
Yes, correlative conjunctions can connect different types of words, including nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs, as long as the elements being connected are similar in structure.
She is both a doctor and a teacher.
She is as friendly as her sister.
So tired that he fell asleep instantly.
She is just as kind as her brother..
She is so busy that she forgets things.
You May Also Like