Contents
Adverbs play a crucial role in our language by providing additional information about verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. Among the various types of adverbs, “adverbs of time” hold a special significance. They give us essential details about when an action occurs, allowing us to construct clear and precise sentences. In this article, we will explore what adverbs of time are with their types uses, and examples. So let’s get started!
What Are Adverbs of Time?
As the name suggests, adverbs of time tell us when an action happened. tells us when she arrived, giving us a sense of time. They provide us with valuable information about the timing and duration of an event, helping us create a clearer and more detailed picture when we communicate. These adverbs can refer to specific points in time, like today or tomorrow, or to more general time frames, like now or soon. They often answer questions like “When did it happen?” or “How often does it happen?” For instance, consider the sentence: “She arrived early.” Here, the adverb “early” tells us when she arrived, giving us a sense of time.
Here are some other examples of adverb of time:
- Now: I am writing this article now.
- Yesterday: I went to the park yesterday.
- Soon: I will finish my homework soon.
- Today: We have a meeting today.
- Always: She always arrives on time.
- Never: He never eats spicy food.
- Early: I woke up early.
- Late: She arrived late to the party.
- Always: He always arrives on time.
Types of Adverbs of Time
Adverbs of time can be categorized into three main groups:
Definite Time
Definite time adverbs specify an exact moment or duration. They tell us precisely when an action happened. Here are some examples:
- Today: Refers to the current day.
- Tomorrow: Means the day after today.
- Yesterday: Indicates the day before today.
Indefinite Time
Indefinite-time adverbs give a more general idea of when something happened. They don’t specify an exact moment. For Example:
- Now: This refers to the present moment.
- Later: Refers to a time after the present, but not immediately.
- Soon: Means in a short time from now.
- Always: He always arrives early.
Frequency
Frequency adverbs tell us how often or frequently an action occurs. They are a subset of adverbs of time and provide crucial information in various contexts. For Example:
- Always: Signifies at all times.
- Often: Means many times.
- Sometimes: Indicates at certain times.
- Never: Signifies not at any time.
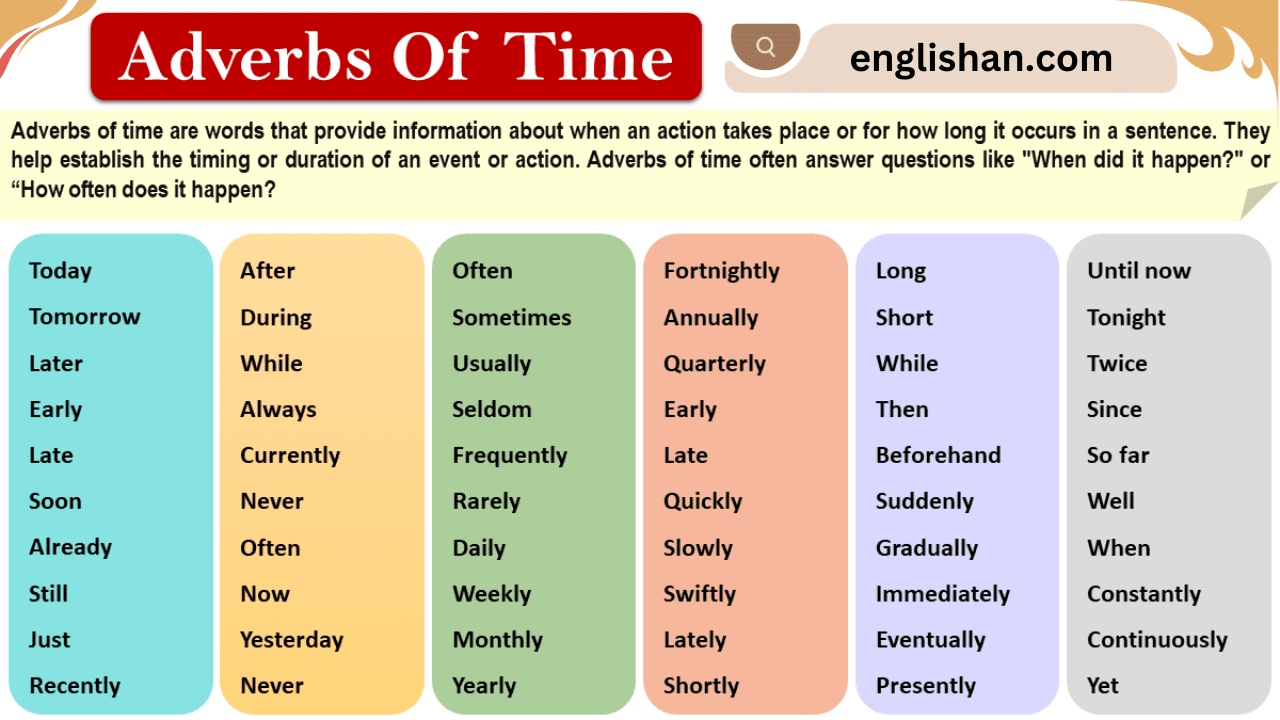
List of Adverbs of Time
Here is a list of some of the most common adverbs of time:
- Now
- Yesterday
- Today
- Tomorrow
- Later
- Early
- Late
- Soon
- Already
- Still
- Just
- Recently
- Before
- After
- During
- While
- Always
- Currently
- Never
- Often
- Sometimes
- Usually
- Seldom
- Frequently
- Rarely
- Daily
- Weekly
- Monthly
- Yearly
- Fortnightly
- Annually
- Quarterly
- Early
- Late
- Quickly
- Slowly
- Swiftly
- Lately
- Shortly
- Long
- Short
- While
- Then
- Beforehand
- Suddenly
- Gradually
- Immediately
- Eventually
- Presently
- Constantly
- Continuously
Adverbs of Time Example Sentences
To understand how adverbs of time are used, let’s look at some examples:
- Now: I am eating lunch now.
- Today, we visited the museum.
- She always arrives early for class.
- I will call you later.
- They sometimes go for a walk in the evening.
- She went to the market yesterday.
- Finish your homework before dinner.
- First, we’ll eat, then we’ll play.
- We’ll be there soon.
- They often go for a walk in the park.
- She rarely eats junk food.
- Typically, the store closes at 9 p.m.
- The movie is mainly about friendship.
- One day, I’ll travel the world.
- He rarely watches TV.
- I read a book while waiting for the bus.
- Nowadays, people use smartphones.
- We have a family meeting monthly.
- They celebrate their anniversary yearly.
- She goes swimming weekly.
- He exercises daily.
- She finished her homework quickly.
- The turtle moves slowly.
- The phone rang suddenly.
- He finally arrived at the party.
- She has already eaten lunch.
Position of Adverbs of Time
Adverbs of time can appear at the beginning, middle, or end of a sentence, depending on the emphasis you want to give:
- Before the main verb:
- She always smiles.
- They will leave soon.
- At the beginning of a sentence (followed by a comma):
- Yesterday, I went to the park.
- Now I am studying.
- At the end of a sentence:
- She arrived late.
- We’ll meet tomorrow.
FAQs:
These are two words that provide information about when an action takes place or for how long it occurs in a sentence. They help establish the timing or duration of an event or action.
Yes, it can be used in almost any sentence to provide information about when an action occurs.
Adverbs of time indicate when an action occurred (e.g., now, yesterday), while adverbs of frequency indicate how often an action happens (e.g., always, rarely).
Common examples of adverbs of time include now, yesterday, today, tomorrow, soon, always, never, often, sometimes, usually, etc.
Look for words that answer questions like “When did it happen?” or “How often does it happen?” An adverb of time often modifies verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
Here are some examples:
1. I will call you later.
2. She always arrives on time.
3. He never eats spicy food.
4. The concert will start soon.
5. I’m studying for my exam now.
You May Also Like