Contents
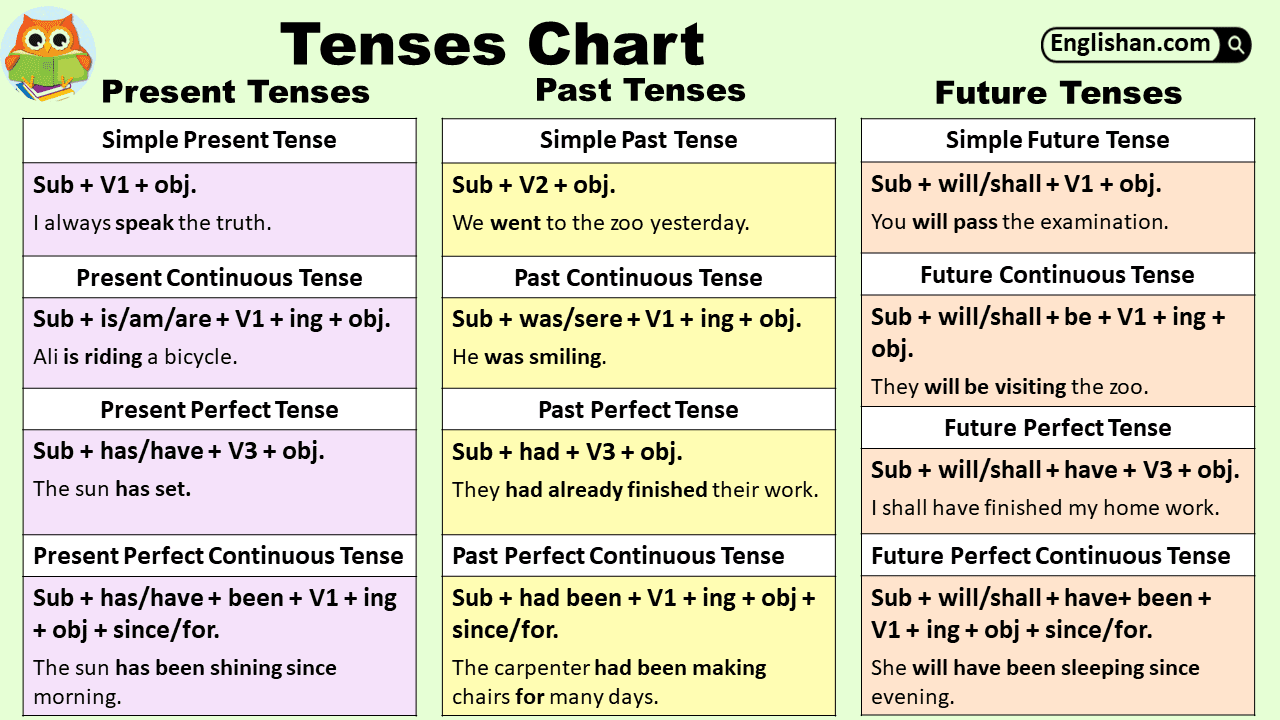
Understanding future tenses is an essential part of mastering English grammar. Future tenses allow us to talk about events, actions, or plans that will happen after the present moment. In this guide, we will learn the structures, uses, and examples of future tenses to help learners communicate effectively and confidently.
What Are Future Tenses?
Future tenses are used to describe actions, events, or states that will happen after the present moment. In English, there are four main future tenses:

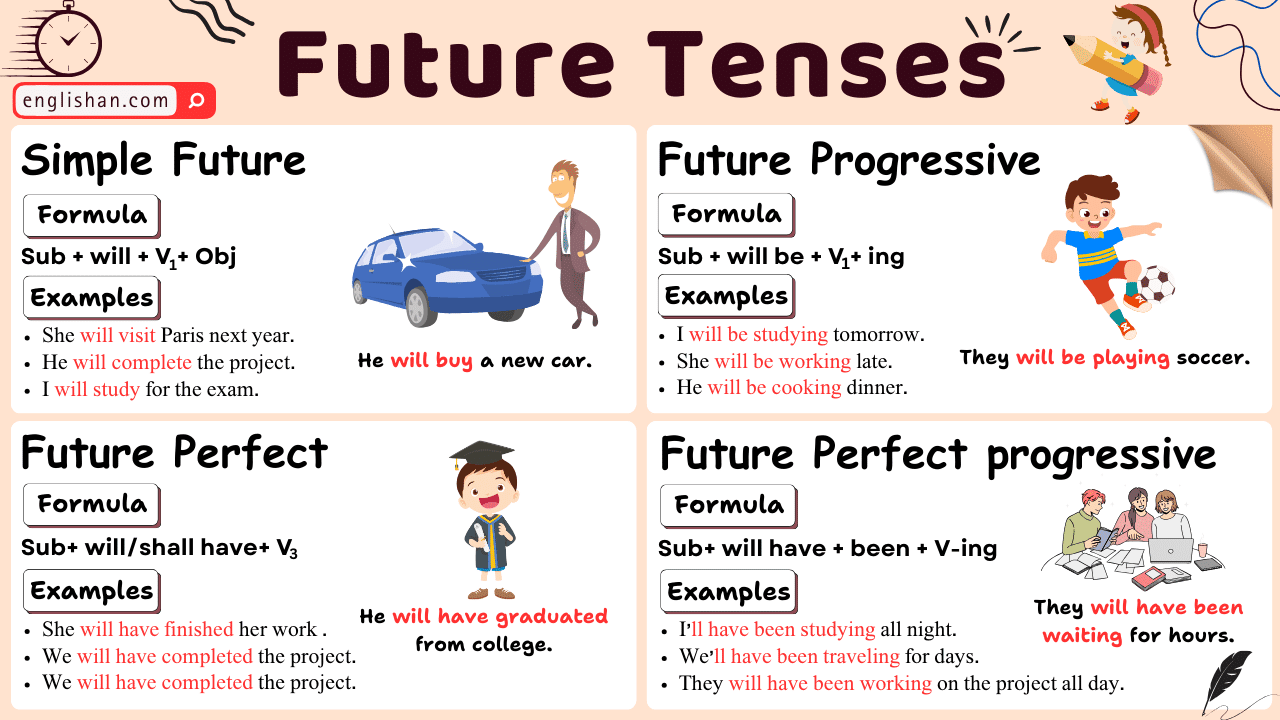
Simple Future Tense
Structure of the Simple Future Tense
The simple future tense is used to express actions that will happen at a later time. It is formed using the auxiliary verb “will” followed by the base form of the main verb.
Affirmative: Subject + will + base verb
- Ahmed will study tomorrow.
- Ali will play football next week.
Negative: Subject + will not (won’t) + base verb
- Ahmed will not study tomorrow.
- Ali won’t play football next week.
Interrogative: Will + subject + base verb?
- Will Ahmed study tomorrow?
- Will Ali play football next week?
Double Interrogative: Question word + will + subject + base verb?
- When will Ahmed study?
- Why will Ali play football?
Uses of the Simple Future Tense
The simple future tense is used in the following cases:
| Uses | Example |
| To express future actions or events | Ayesha will visit her grandmother next month. |
| To make predictions about the future | It will rain tomorrow. |
| To express decisions made at the moment of speaking | I will help you with your homework. |
| To express promises or offers | I will call you later. |
Examples of the Simple Future Tense in Use
Affirmative:
- Fatima will bake a cake for the party.
- Bilal will drive to Karachi tomorrow.
- They will join us for lunch.
Negative:
- Fatima will not bake a cake for the party.
- Bilal won’t drive to Karachi tomorrow.
- They will not join us for lunch.
Interrogative:
Will Fatima bake a cake for the party?
Will Bilal drive to Karachi tomorrow?
Will they join us for lunch?
Future Continuous Tense
Structure of the Future Continuous Tense
The future continuous tense describes ongoing actions that will be happening at a specific time in the future. It is formed using “will be” followed by the present participle (verb+ing).
Affirmative: Subject + will be + present participle
- Ahmed will be studying at 8 PM.
- Ayesha will be cooking dinner tonight.
Negative: Subject + will not (won’t) be + present participle
- Ahmed will not be studying at 8 PM.
- Ayesha won’t be cooking dinner tonight.
Interrogative: Will + subject + be + present participle?
- Will Ahmed be studying at 8 PM?
- Will Ayesha be cooking dinner tonight?
Double Interrogative: Question word + will + subject + be + present participle?
- What will Ahmed be studying at 8 PM?
- Where will Ayesha be cooking dinner?
Uses of the Future Continuous Tense
The future continuous tense is used in the following cases:
| Uses | Example |
| To describe actions that will be ongoing at a specific time in the future | At 7 PM, they will be watching a movie. |
| To predict future events that are already planned or expected | She will be traveling to Islamabad next week. |
| To indicate polite inquiries about someone’s future actions | Will you be attending the meeting tomorrow? |
Examples of the Future Continuous Tense in Use
Affirmative:
- Bilal will be playing cricket in the afternoon.
- Fatima will be reading her favorite book this evening.
- Ahmed will be working on his project all night.
Negative:
- Bilal will not be playing cricket in the afternoon.
- Fatima won’t be reading her favorite book this evening.
- Ahmed will not be working on his project all night.
Interrogative:
- Will Bilal be playing cricket in the afternoon?
- Will Fatima be reading her favorite book this evening?
- Will Ahmed be working on his project all night?
Future Perfect Tense
Structure of the Future Perfect Tense
The future perfect tense describes actions that will be completed before a specific time in the future. It is formed using “will have” followed by the past participle of the main verb.
Affirmative: Subject + will have + past participle
- Ahmed will have completed his assignment by 9 PM.
- Fatima will have finished her dinner before the meeting.
Negative: Subject + will not (won’t) have + past participle
- Ahmed will not have completed his assignment by 9 PM.
- Fatima won’t have finished her dinner before the meeting.
Interrogative: Will + subject + have + past participle?
- Will Ahmed have completed his assignment by 9 PM?
- Will Fatima have finished her dinner before the meeting?
Double Interrogative: Question word + will + subject + have + past participle?
- What will Ahmed have completed by 9 PM?
- When will Fatima have finished her dinner?
Uses of the Future Perfect Tense
The future perfect tense is used in the following cases:
| Uses | Example |
| To indicate actions that will be completed before a specific time in the future | By next month, they will have submitted their reports. |
| To show an expectation of completed actions in the future | By the end of the year, she will have mastered the piano. |
| To summarize progress made by a future date | By 2025, Fatima will have achieved her academic goals. |
| To highlight a milestone | Ahmed will have completed his course before summer. |
Examples of the Future Perfect Tense in Use
Affirmative:
- Bilal will have reached Lahore by noon.
- Ayesha will have cleaned the house by evening.
- Ahmed will have graduated by next summer.
Negative:
- Bilal will not have reached Lahore by noon.
- Ayesha won’t have cleaned the house by evening.
- Ahmed will not have graduated by next summer.
Interrogative:
- Will Bilal have reached Lahore by noon?
- Will Ayesha have cleaned the house by evening?
- Will Ahmed have graduated by next summer?
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Structure of the Future Perfect Continuous Tense
The future perfect continuous tense describes actions that will have been happening for a duration of time at a specific point in the future. It is formed using “will have been” followed by the present participle (verb+ing).
Affirmative: Subject + will have been + present participle
- Ahmed will have been studying for three hours by 8 PM.
- Fatima will have been cooking dinner for an hour before the guests arrive.
Negative: Subject + will not (won’t) have been + present participle
- Ahmed will not have been studying for three hours by 8 PM.
- Fatima won’t have been cooking dinner for an hour before the guests arrive.
Interrogative: Will + subject + have been + present participle?
- Will Ahmed have been studying for three hours by 8 PM?
- Will Fatima have been cooking dinner for an hour before the guests arrive?
Double Interrogative: Question word + will + subject + have been + present participle?
- How long will Ahmed have been studying by 8 PM?
- What will Fatima have been cooking before the guests arrive?
Uses of the Future Perfect Continuous Tense
The future perfect continuous tense is used in the following cases:
| Use | Example |
| To describe the duration of an ongoing action at a specific point in the future | By next year, Ali will have been working at the company for five years. |
| To emphasize the continuity of an action up to a future time | When the train arrives, they will have been waiting for over an hour. |
| To highlight progress or development over time | By the end of the month, Ahmed will have been practicing his presentation for weeks. |
| To describe the effort leading to a significant achievement | Fatima will have been studying for her exams for months by the time they start. |
Examples of the Future Perfect Continuous Tense in Use
Affirmative:
- Bilal will have been exercising for two hours by 7 PM.
- Fatima will have been writing her book for months by December.
- Ahmed will have been practicing for the competition all day.
Negative:
- Bilal will not have been exercising for two hours by 7 PM.
- Fatima won’t have been writing her book for months by December.
- Ahmed will not have been practicing for the competition all day.
Interrogative:
- Will Bilal have been exercising for two hours by 7 PM?
- Will Fatima have been writing her book for months by December?
- Will Ahmed have been practicing for the competition all day?
FAQs:
The basic structure of the future tense is formed using “will” or “shall” followed by the base form of the verb.
We use the future tense to talk about actions or events that will happen at some point after the present moment.
The future continuous tense is formed using “will be” + the present participle (base form + -ing) of the verb.
The future continuous tense is used to describe actions that will be ongoing or in progress at a specific point in the future.
The future perfect tense is formed using “will have” + the past participle of the main verb.
The future perfect tense is used to express actions that will be completed before a specific point or event in the future.
You May Also Like