Passive voice and modal verbs are two essential aspects of English grammar, each serving a unique purpose. Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs that express certainty, possibility, permission, or obligation in a sentence. On the other hand, the passive voice is a grammatical construction in which the subject receives the action rather than performing it. In this article, we’ll explore how modal verbs and passive voice work together to create different sentence structures. We’ll also share rules and examples to enhance your understanding of this concept. So, let’s get started!
What is Passive Voice?
Passive voice is a way of constructing sentences where the subject of the sentence receives the action of the verb rather than performing it. In passive voice, the focus is on the receiver of the action rather than the doer. For example, “The ball was kicked by Sarah.” In this sentence, the ball (the receiver) is the focus, even though Sarah (the doer) is mentioned.
Structure: Subject + (to be) + past participle + (by + agent, if mentioned)
Passive voice is formed by using a form of the verb “to be” (such as “is,” “am,” “are,” “was,” “were,” etc.) followed by the past participle form of the main verb. It’s often used when the doer of the action is unknown, or unimportant, or when the focus needs to be shifted to the receiver of the action.
What are Modal Verbs?
Modal verbs are a category of auxiliary verbs (also called helping verbs) that express the mood or attitude of the speaker toward the action or state of the main verb in a sentence. These verbs indicate possibility, necessity, permission, ability, obligation, or likelihood. In English, the most common modal verbs include:
- Can: Shows ability or possibility.
- Could: Often used for past ability or polite requests.
- May: Expresses permission or possibility.
- Might: Indicates a possibility, often with uncertainty.
- Must: Shows necessity or strong obligation.
- Shall: Used for making suggestions, promises, or offers.
- Should: Indicates advice, obligation, or expectation.
- Will: Shows future intention or prediction.
- Would: Used for polite requests or hypothetical situations.
- Ought to: Used to express moral obligation or duty.
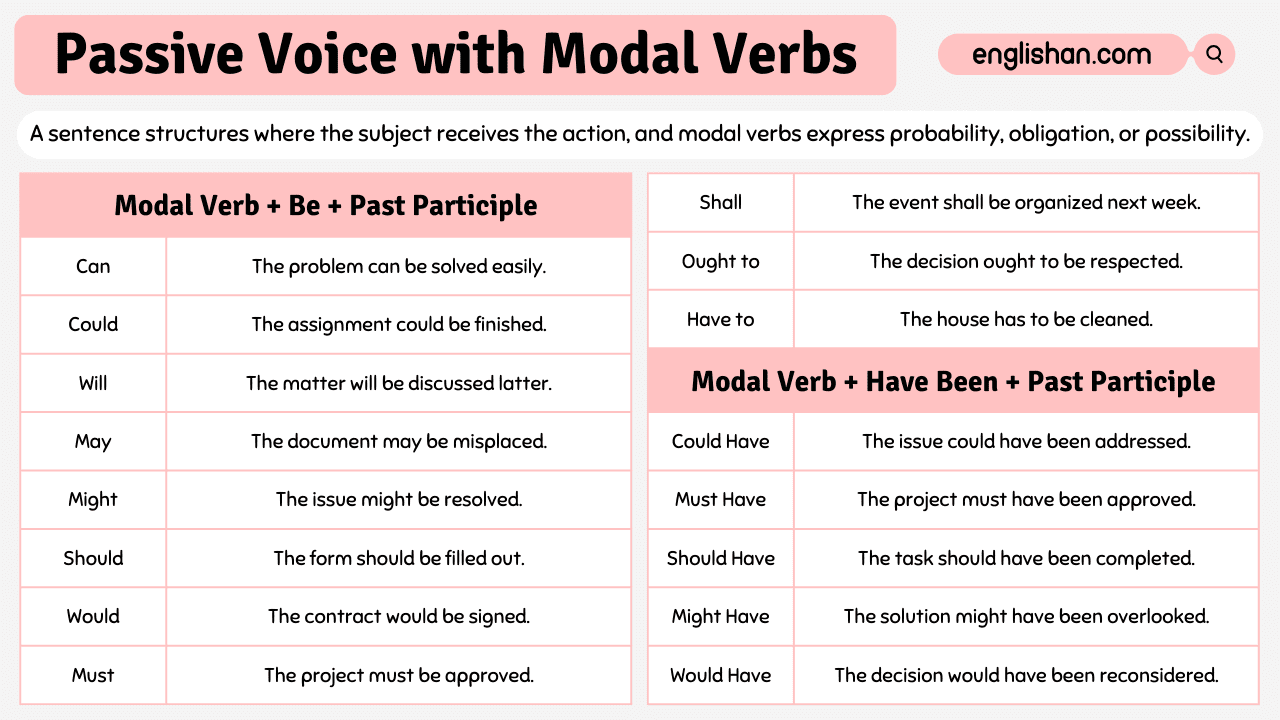
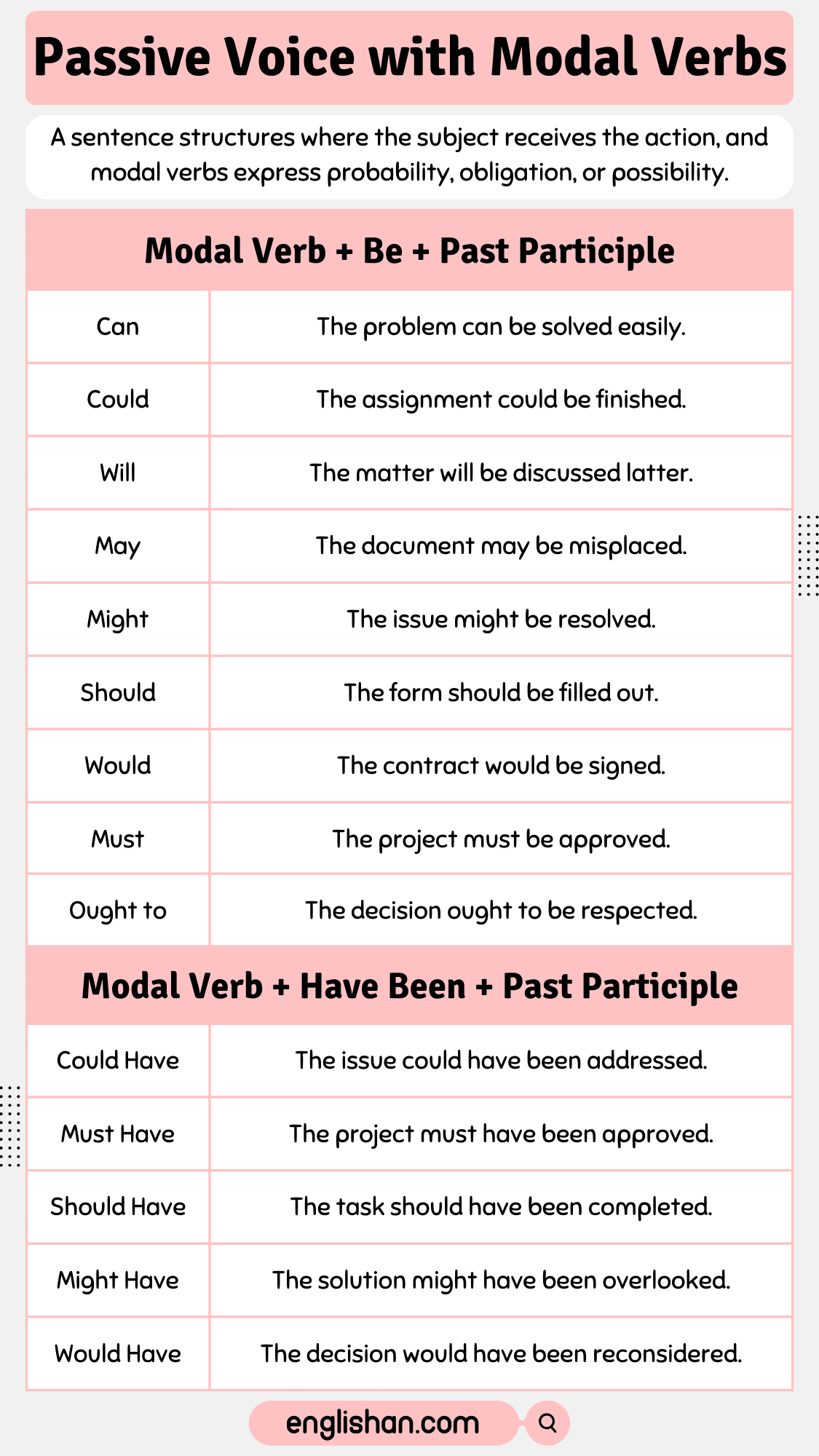
Passive Voice with Modal Verbs Rules
When combining passive voice with modal verbs, the modal verb appears before the main verb in its past participle form.
Modal + Be + Past Participle
Use a modal verb (can, should, must, might, will, could) followed by a form of the verb “to be” (am, is, are, was, were) and the past participle of the main verb.
- Structure:
- Examples:
- The problem can be solved.
- The document may be misplaced.
- The solution should be considered.
| Modal Verb | Passive Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Can | can be + past participle | The car can be repaired. |
| Could | could be + past participle | The problem could be solved. |
| May | may be + past participle | The document may be approved. |
| Might | might be + past participle | The answer might be known. |
| Will | will be + past participle | The project will be completed. |
| Would | would be + past participle | The task would be finished. |
| Shall | shall be + past participle | The rules shall be followed. |
| Should | should be + past participle | The instructions should be read. |
| Must | must be + past participle | The report must be submitted. |
| Ought to | ought to be + past participle | The issue ought to be addressed. |
Modal + Have Been + Past Participle
This structure is used to talk about actions that were completed or ongoing at a specific time in the past.
- Structure: + +
- Examples:
- The problem can have been solved.
- The document may have been misplaced.
- The solution should have been implemented.
| Modal Verb | Passive Voice Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|
| can | can have been + v3 | The problem can have been solved. |
| could | could have been + v3 | The issue could have been addressed. |
| may | may have been + v3 | The document may have been misplaced. |
| might | might have been + v3 | The solution might have been overlooked. |
| shall | shall have been + v3 | The task shall have been completed. |
| should | should have been + v3 | The assignment should have been submitted. |
| will | will have been + v3 | The report will have been reviewed. |
| would | would have been + v3 | The decision would have been reconsidered. |
| must | must have been + v3 | The project must have been approved. |
| ought to | ought to have been + v3 | The error ought to have been detected. |
These structures allow us to express various ideas such as possibility, necessity, permission, etc., in passive voice. The first structure emphasizes actions that can happen, are expected, or are allowed to happen, while the second structure highlights actions that likely happened or were ongoing in the past.
Passive Voice with Modal Verbs
It is a grammatical construction where the subject of a sentence receives the action, and a modal verb is used to express the possibility, necessity, permission, or other qualities of the action. Below is a list of Passive Voice with all Modal Verbs along with their structure and example sentences.
Can
- It indicates ability, possibility, or permission.
- Structure: Subject + can + be/have been + past participle
- Example: The problem can be solved easily.
Could
- Represents past ability, possibility, or permission.
- Structure: Subject + could + be/have been + past participle
- Example: The task could have been completed earlier.
May
- Expresses permission, possibility, or likelihood.
- Structure: Subject + may + be/have been + past participle
- Example: The decision may be reconsidered later.
Might
- It suggests a possibility or uncertain future.
- Structure: Subject + might + be/have been + past participle
- Example: The missing keys might be found soon.
Must
- Conveys necessity, obligation, or a strong recommendation.
- Structure: Subject + must + be/have been + past participle
- Example: The rules must be followed by all participants.
Shall
- It indicates a future event or offers a suggestion.
- Structure: Subject + shall + be/have been + past participle
- Example: The decision shall have been made by now.
Should
- Advises or recommends something.
- Structure: Subject + should + be/have been + past participle
- Example: The instructions should be followed carefully.
Will
- Indicates future events, intentions, or promises.
- Structure: Subject + will + be/have been + past participle
- Example: The message will be delivered by noon.
Would
- Expresses hypothetical situations or polite requests.
- Structure: Subject + would + be/have been + past participle
- Example: The problem would be solved with the right approach.
Ought to
- Used to suggest moral obligations or duties.
- Structure: Subject + ought to + be/have been + past participle
- Example: Safety precautions ought to be taken seriously.
Passive Voice with Modals Examples
- The matter will be discussed.
- The contract would be signed.
- The problem can be solved.
- The document may be misplaced.
- The cake may be baked by the chef.
- The solution might be overlooked.
- The keys might be found later.
- The issue might be resolved.
- The task should be completed.
- The form should be filled out.
- The project must be approved.
- The rules must be followed.
- The report must be reviewed.
- The problem ought to be addressed.
- The news will be announced soon.
- The job will be done by the deadline.
- The decision ought to be respected.
- The agreement shall be signed shortly.
- The task should have been completed.
Passive Voice with Modal Verbs Exercises
Put the following sentences into passive voice. (Modals)
- Active: She can solve the problem.
- Passive:
- Active: He must finish the assignment.
- Passive:
- Active: They should clean the room.
- Passive:
- Active: We might visit the museum.
- Passive:
- Active: They will paint the house.
- Passive:
- Active: She would bake a cake.
- Passive:
- Active: He could solve the puzzle.
- Passive:
- Active: They need to repair the car.
- Passive:
- Active: She has to write the report.
- Passive:
- Active: We have to finish the project.
- Passive:
- Active: They had to cancel the event.
- Passive:
- Active: Someone might have forgotten her.
- Passive:
Answers:
- The problem can be solved by her.
- The assignment must be finished by him.
- The room should be cleaned by them.
- The museum might be visited by us.
- The house will be painted by them.
- A cake would be baked by her.
- The puzzle could be solved by him.
- The car needs to be repaired by them.
- The report has to be written by her.
- The project has to be finished by us.
- The event had to be canceled by them.
- She might have been forgotten.
FAQs
Passive voice is a grammatical construction where the subject of a sentence undergoes an action rather than performing it. In passive-voice sentences, the focus is on the action or the recipient of the action rather than the doer.
Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs that express various attitudes including possibility, necessity, permission, ability, obligation, and prediction. The ten main modal verbs are can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would, and ought to.
To form passive voice with modal verbs, you use the modal verb followed by “be” and the past participle of the main verb. For example: “The door can be opened.” Here, “can” is the modal verb, “be” is the auxiliary verb, and “opened” is the past participle of the main verb “open”.
Modal verbs in passive voice constructions indicate the possibility, necessity, permission, ability, obligation, or prediction associated with the action being described in the passive voice sentence. They modify the verb to convey the desired meaning.
1. The problem can be solved.
2. The assignment could be finished.
3. The proposal may be approved.
4. The task must be completed.
5. The report shall be submitted.
6. The decision ought to be respected.
You May Also Like