Contents
Stative and dynamic verbs are two main types of verbs. Stative verbs describe a state, condition, or feeling that doesn’t involve action, like know, believe, or love. Dynamic verbs show actions or processes, like run, write, or speak. These types help us express if something is or happens. We’ll learn them in detail below with clear meanings, usage, and examples to help you use them correctly in everyday English.
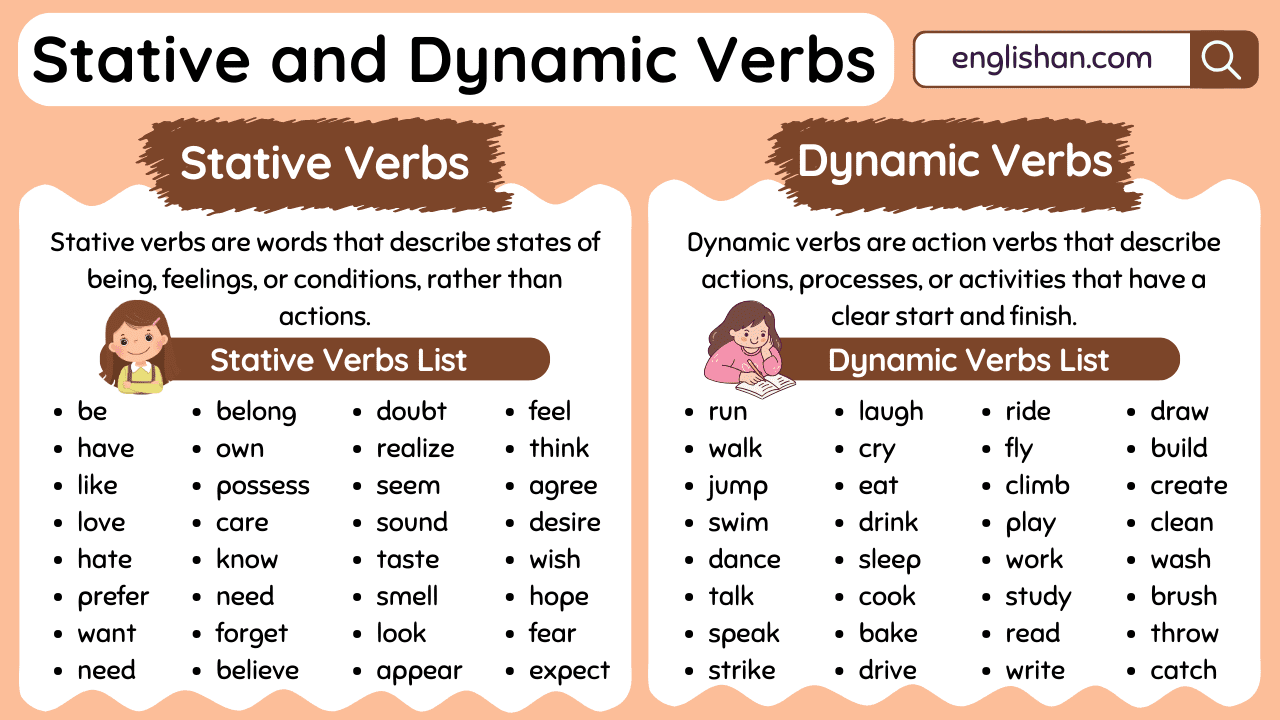
What are Stative Verbs?
Stative verbs describe a state or condition, not an action. They relate to feelings, thoughts, possession, or being. These verbs do not show movement and are usually not used in continuous forms.
Common stative verbs: be, have, know, like, love, want, need, see, feel
Examples:
- She hates rainy days.
- They believe in ghosts.
- He seems tired.
- They dislike spicy food.
- I love chocolate ice cream.
Stative Verbs List
Here is a list of commonly used stative verbs:
- be
- have
- like
- love
- hate
- prefer
- want
- need
- belong
- own
- possess
- understand
- know
- remember
- forget
- believe
- doubt
- recognize
- realize
- seem
- appear
- resemble
- sound
- taste
- smell
- look
- feel
- think
- agree
- disagree
- desire
- wish
- hope
- fear
- suppose
- expect
- appreciate
- enjoy
- dislike
- mind
- care
- concern
- consist
- contain
- depend
- matter
- weigh
- cost
- owe
- mean
- imply
- include
- exclude
- need
- deserve
- value
- satisfy
- surprise
- deny
- doubt
What are Dynamic Verbs?
Dynamic verbs (action verbs) show physical, mental, or emotional actions. They describe things that happen or change. These verbs have a clear start and end. Unlike stative verbs, they don’t describe states — they show what someone does.
Examples:
- They played soccer in the park.
- The baby cried for attention.
- We cooked dinner together.
- He ran to catch the bus.
- They laughed at the joke.
Dynamic Verbs List
Here is a list of commonly used dynamic verbs:
- Run
- Walk
- Jump
- Swim
- Dance
- Talk
- Speak
- Strike
- Laugh
- Cry
- Eat
- Drink
- Sleep
- Cook
- Bake
- Drive
- Ride
- Fly
- Climb
- Play
- Work
- Study
- Read
- Write
- Draw
- Paint
- Build
- Create
- Destroy
- Clean
- Wash
- Brush
- Throw
- Catch
- Kick
- Punch
- Push
- Pull
- Lift
- Drop
- Open
- Close
- Cut
- Sew
- Tie
- Untie
- Break
- Fix
- Ride
- Drive
- Shake
- Bake
- Balance
- Bounce
- Dig
- Slide
- Squeeze
- Push
- Pull
- Bite
Stative vs Dynamic Verbs Distinctions
| Feature | Stative Verbs | Dynamic Verbs |
|---|---|---|
| What they describe | A state, condition, or feeling | An action, process, or movement |
| Example verbs | be, know, like, believe, love | run, eat, write, jump, talk |
| Use in continuous tense | Rarely used (e.g., I am knowing ❌) | Commonly used (e.g., I am running ✅) |
| Start and end | No clear beginning or end | Has a clear start and finish |
| Ongoing action? | No, they describe something stable | Yes, they show something happening |
| Needs an object? | Often doesn’t (e.g., I believe) | Often does (e.g., I eat lunch) |
| Used for | Thoughts, feelings, senses, possession | Physical actions, changes, movement |
| Focus | On what something is | On what something does |
Stative Verbs vs Dynamic Verbs Chart
Key Differences:
| Stative Verbs | Dynamic Verbs |
|---|---|
| Describe states or conditions | Describe actions or processes |
| Focus on how things are | Emphasize what things do |
| Lack a clear start or finish | Have a definite beginning and end |
| Don’t show ongoing action | Often show ongoing or continuous action |
| Aren’t used in continuous tenses | Often used in continuous tenses |
| Convey a fixed state | Suggest movement or change |
| Involve senses, emotions, thoughts | Involve physical actions or processes |
| Don’t usually need objects | Often need objects to complete meaning |
| Include verbs like “be,” “like,” “belong” | Include verbs like “run,” “eat,” “write” |
Stative and Dynamic Verbs Examples
Dynamic Verbs:
- She runs every morning.
- He eats breakfast quickly.
- She writes stories in her free time.
- They paint the walls of the house.
- She cooks dinner for her family.
- He ate his lunch quickly.
- She is studying for her exam.
- She runs five miles every morning.
- She drives to work every day.
- He plants flowers in the garden.
- He throws the ball to his friend.
- The dog barks loudly at strangers.
Stative Verbs:
- She is a teacher. (State of being)
- She feels tired. (State of being)
- They own a beautiful house. (Possession)
- He knows Spanish. (Knowledge)
- She loves chocolate. (Emotion)
- The coffee tastes bitter. (Sensation)
- He believes in ghosts. (Belief)
- They seem happy. (Appearance)
- She has a pet cat. (Possession)
- He hates Mondays. (Emotion)
- The cake smells delicious. (Stative)
- The flowers smell lovely. (Sensation)
Stative and Dynamic Verbs Exercises
Choose whether the underlined verb is stative or dynamic.
- She knows the answer to the question.
- Stative
- Dynamic
- He is writing a novel about his travels.
- Stative
- Dynamic
- They own a beautiful house by the lake.
- Stative
- Dynamic
- The children are playing in the garden.
- Stative
- Dynamic
- She likes vanilla ice cream.
- Stative
- Dynamic
- He is driving to the airport to catch his flight.
- Stative
- Dynamic
- They understand the concept of teamwork.
- Stative
- Dynamic
- The flowers smell fragrant in the garden.
- Stative
- Dynamic
- She believes in living life to the fullest.
- Stative
- Dynamic
- He is cooking dinner for his family.
- Stative
- Dynamic
Answers:
- a) Stative
- b) Dynamic
- a) Stative
- b) Dynamic
- a) Stative
- b) Dynamic
- a) Stative
- a) Stative
- a) Stative
- b) Dynamic
FAQs
Stative verbs describe states, conditions, or situations that are not actions or processes. They express feelings, thoughts, possession, senses, or relationships. Examples include: “be,” “seem,” “like,” “own,” “belong,” “know,” and “love.”
Dynamic verbs describe actions, processes, or changes that happen and can be observed or experienced. They show activities, movements, or transitions from one state to another. Examples include: “run,” “eat,” “dance,” “write,” “play,” and “build.”
Stative verbs describe states or conditions that are usually unchanging, while dynamic verbs describe actions or processes that involve movement or change. Stative verbs often express feelings, thoughts, senses, or possession, while dynamic verbs involve physical actions or observable events.
Some verbs can function as both stative and dynamic, depending on the context and the meaning they convey. For example, the verb “have” can be stative when used to express possession (“She has a car”) and dynamic when used to indicate actions like experiencing or consuming (“She’s having dinner”).
Here are some example sentences of stative and dynamic verbs:
1. She feels tired. (Stative)
2. He is watching a movie. (Dynamic)
3. He believes in ghosts. (Stative)
4. We are playing soccer. (Dynamic)
5. The cake smells delicious. (Stative)
6. They are laughing at the joke. (Dynamic)
You May Also Like