Prepositions are essential parts of speech that connect nouns and pronouns to other words in a sentence. These little words help us understand the relationships between words and phrases, such as time, place, direction, and other relationships. Even though prepositions are common words, it isn’t easy to know all of them and use them correctly. However, using the wrong preposition can completely change the meaning of a sentence. In this article, we’ll explore the different types of prepositions and provide examples to help you understand their usage. So, let’s get started!
The term “preposition” comes from Latin, where “pre” means “before,” and “position” refers to the placement of something. Prepositions are called so because they are positioned before nouns or pronouns in a sentence to indicate the relationship between these elements and other parts of the sentence. They often show location, direction, time, or how something is done. They’re often placed before a noun or pronoun to indicate its position or relationship to other words in a sentence. Some prepositions are made up of multiple words, forming compound prepositions. For example, “in front of,” “next to,” or “due to.”
Examples:
- The book is on the table.
- We will meet at the park.
- I am going to the store.
- We will have dinner after the movie.
- He painted the wall with a brush.
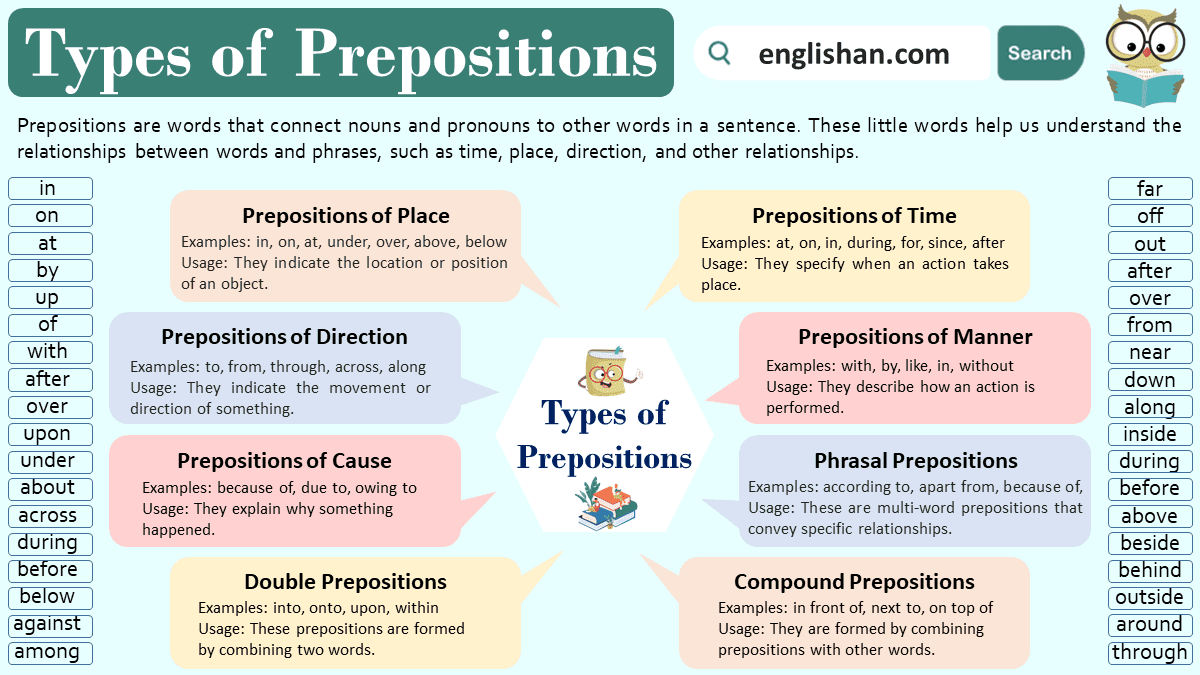
Types of Prepositions
Prepositions can be categorized into various types based on their functions and usage in a sentence. Here are some common types of prepositions:
- Prepositions of Place
- Prepositions of Time
- Phrasal Prepositions
- Prepositions of Direction
- Prepositions of Manner
- Prepositions of Agent
- Double Prepositions
- Compound Prepositions
- Participle Prepositions
- Prepositions of Condition
- Prepositions of Possession
- Prepositions of Cause or Reason
Prepositions of Place:
These prepositions describe the location or position of an object or person. Common prepositions of place include:
- In: The cat is in the box.
- On: The book is on the table.
- Under: The shoes are under the bed.
- Between: The ball is between the two chairs.
- Next to: The park is next to the school.
Prepositions of Time:
Prepositions of time help us understand when an action takes place. Some examples include:
- At: We have a meeting at 3 PM.
- On: I will see you on Monday.
- In: She was born in May.
- Before: Finish your homework before dinner.
- After: The concert starts after the sunset.
Prepositions of Direction:
These prepositions indicate the direction of movement. Common prepositions of direction include:
- To: I am going to the store.
- From: He is coming from the library.
- Toward(s): The cat is moving towards the door.
- Through: We walked through the forest.
- Across: The store is across the street.
Prepositions of Manner:
Prepositions of manner explain how an action is performed. Examples include:
- With: She writes with a pen.
- By: The book was written by Mark Twain.
- Like: He runs like a cheetah.
- In: She spoke in a soft voice.
- Without: I eat my pizza without cheese.
Prepositions of Possession:
These prepositions show ownership or possession. Common ones include:
- Of: The tail of the dog.
- ’s (apostrophe s): The car’s engine is powerful.
- Belonging to: The key belongs to the door.
- Owned by: The house is owned by my uncle.
- Possessed by: The charm possessed by the necklace.
Prepositions of Agent:
These prepositions indicate the agent or doer of an action. Examples include:
- By: The book was written by the author.
- With: The painting was created with a brush.
- Through: Success was achieved through hard work.
Prepositions of Cause or Reason:
These prepositions explain the cause or reason behind an action. Examples include:
- Because of: The flight was delayed because of bad weather.
- Due to: The cancellation was due to technical issues.
- Owing to: The match was postponed owing to rain.
Prepositions of Condition:
Prepositions of condition express the circumstances necessary for an action to take place. Examples include:
- If: I will go to the party if you come with me.
- Unless: Unless you finish your homework, you can’t go out.
- Provided: You can borrow my car provided you return it by 7 PM.
Double Prepositions:
Some prepositions come in pairs, and they are known as double prepositions. Examples include:
- Into: She walked into the room.
- Onto: The cat jumped onto the table.
- Upon: The letter is upon the desk.
Compound Prepositions:
Compound prepositions are formed by combining prepositions with nouns, adjectives, or adverbs. Examples include:
- According to: According to the weather forecast, it will rain tomorrow.
- Because of: The flight was delayed because of technical issues.
- In spite of: In spite of the challenges, she succeeded.
Phrasal Prepositions:
These are groups of words that act as a single preposition. Examples include:
- Because of: The game was canceled because of the heavy rain.
- Due to: The flight was delayed due to technical issues.
- In front of: There’s a beautiful garden in front of the house.
- On behalf of: I am writing this letter on behalf of the entire committee.
Participle Prepositions:
These are formed by combining a preposition with a present participle (-ing form) or past participle (-ed or irregular form). Examples include:
- Regarding: I have a question regarding the new policy.
- Concerned: He is concerned about the team’s performance.
- Excluding: Excluding weekends, the office operates every day.
Common Prepositions
In, On, At (Time):
- Use “in” for longer periods (months, years, centuries).
- Example: I was born in 1990.
- Use “on” for specific days and dates.
- Example: I have a meeting on Monday.
- Use “at” for specific times.
- Example: We will meet at the park at 3 PM.
- Use “in” for longer periods (months, years, centuries).
In, On, At (Place):
- Use “in” for enclosed spaces or general locations.
- Example: I am in the office.
- Use “on” for surfaces.
- Example: The book is on the table.
- Use “at” for specific points or addresses.
- Example: I’ll meet you at the corner.
- Use “in” for enclosed spaces or general locations.
By, Next to, Beside:
- Use “by” for proximity or close contact.
- Example: She sat by the window.
- Use “next to” or “beside” to indicate a position alongside something.
- Example: The cat is next to the dog.
- Use “by” for proximity or close contact.
Under, Below, Above:
- Use “under” for things that are covered or beneath something.
- Example: The keys are under the mat.
- Use “below” for lower position.
- Example: The temperature is below freezing.
- Use “above” for higher position.
- Example: The bird is flying above the trees.
- Use “under” for things that are covered or beneath something.
Between, Among, Over:
- Use “between” when referring to two items or people.
- Example: Choose between the red and blue shirts.
- Use “among” when referring to more than two items or people.
- Example: The secret is among us.
- Use “over” for things that are covered or positioned above something.
- Example: The plane flew over the mountains.
- Use “between” when referring to two items or people.
During, While, Of:
- Use “during” to indicate a period of time.
- Example: I slept during the storm.
- Use “while” to indicate a simultaneous action.
- Example: I listened to music while studying.
- “Of” Indicates possession, origin, or relationship.
- Example: The color of the sky is blue.
- Use “during” to indicate a period of time.
Under, Below:
- “Under” indicates a position beneath or covered by something.
- Example: The cat is under the table.
- “Below” indicates a lower position in comparison but is not necessarily covered.
- Example: The fish swim below the surface.
- “Under” indicates a position beneath or covered by something.
For, Since, To:
- “For” used for a period of time.
- Example: I will be on vacation for a week.
- “Since” is used for a specific point in time.
- Example: I have known her since high school.
- “To” denotes direction or recipient.
- Example: I am going to the store.
- “For” used for a period of time.
Through, Into, Onto:
- “Through” indicates movement from one side to the other.
- Example: We walked through the park.
- “Into” indicates movement toward the inside.
- Example: The water turned into ice.
- “Onto” indicates movement to a position on or on top of.
- Example: The cat jumped onto the table.
- “Through” indicates movement from one side to the other.
By, With, From:
- “By” indicates the method or means.
- Example: The letter was sent by mail.
- “With” denotes being together or using something.
- Example: She cut the cake with a knife.
- “From” indicates the source or starting point.
- Example: I received a gift from my friend.
- “By” indicates the method or means.
Example Sentences
- I’ll meet you at the park.
- The sun rises in the morning.
- The ball is under the table.
- The plane is flying above the clouds.
- We’ll finish the project by tomorrow.
- She is sitting beside her friend.
- The flowers are in the garden.
- She is sleeping on the chair.
- The store is across the street.
- The movie starts at 8 o’clock.
- He lives in a small town.
- The cat jumped over the fence.
- They’ll arrive at the airport.
- I’ll be back in a few minutes.
- The cat is hiding behind the curtain.
- He is standing in front of the building
- The sun sets behind the mountains.
- The birds are flying above us.
- The ball is between the two chairs.
- We went for a walk along the beach.
FAQs
Prepositions can indicate specific times, durations, or points in time. For example, “at” for specific times (“at 3 PM”), “in” for general times (“in the morning”), and “for” for durations (“for two hours”).
Prepositions can be categorized into several types, including prepositions of time, place, direction, agent, manner, and more. There is no fixed number of types, as they can be classified based on different criteria.
“In” is used for larger, enclosed spaces or periods of time. “On” is used for surfaces, and “at” is used for specific points in time or locations.
The eight basic types of prepositions are:
Time Prepositions
Place Prepositions
Direction Prepositions
Phrasal Prepositions
Participle Prepositions
Manner Prepositions
Causative Prepositions
Double Prepositions
Read More